Map Snapshot





14 Records
Seasonality Snapshot
Eating mushrooms can be dangerous. One should do so only with expert advice and great care. MBP accepts no liability for injury sustained in consuming fungi or other biodiversity. Use of media featured on Maryland Biodiversity Project is only permitted with express permission of the photographer.
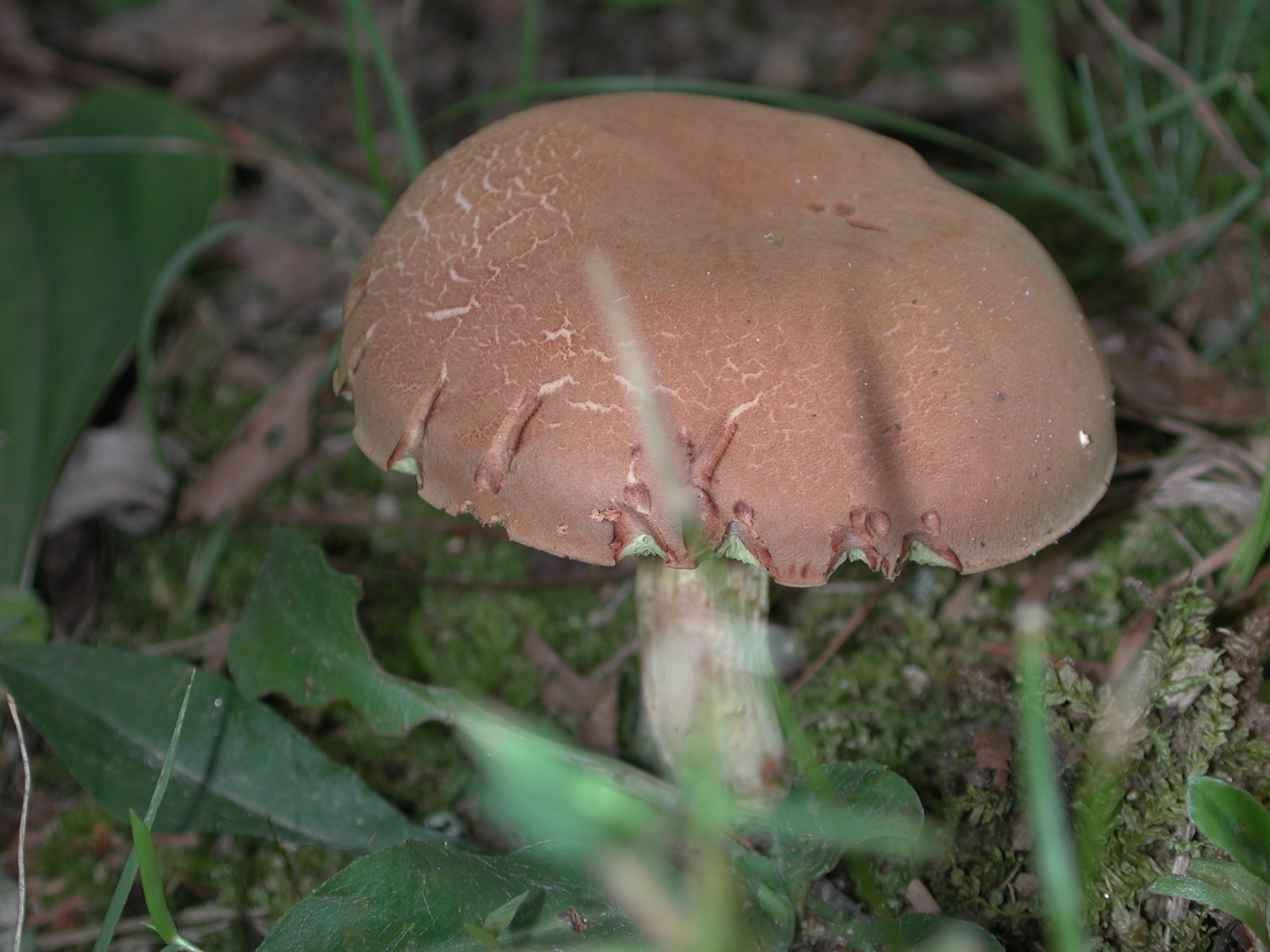
Gold-pored Bolete in Howard Co., Maryland (7/27/2010). (c) Joanne and Robert Solem, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC).
View Record Details
Media by
Joanne Solem.
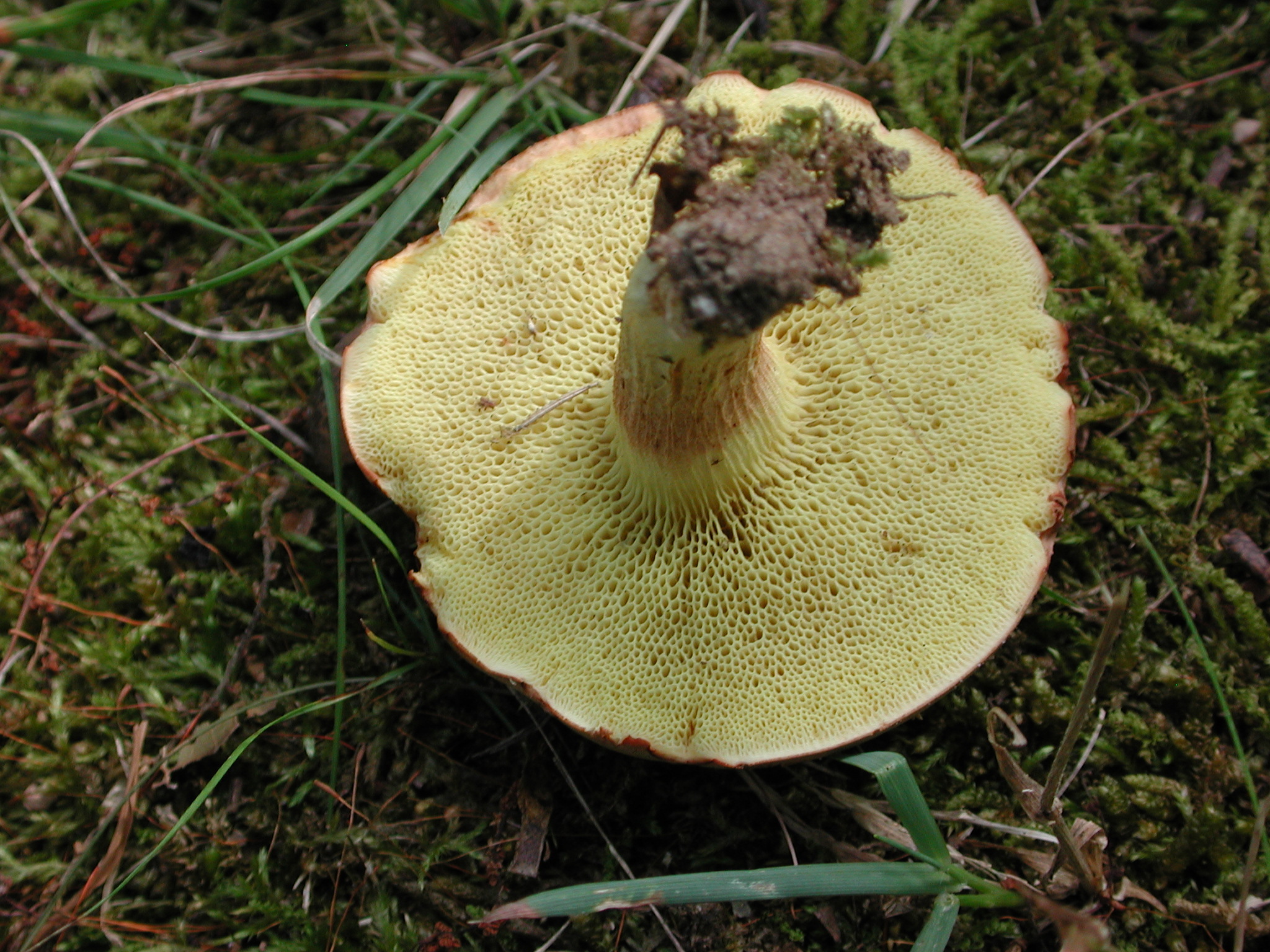
Gold-pored Bolete in Howard Co., Maryland (7/27/2010). (c) Joanne and Robert Solem, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC).
View Record Details
Media by
Joanne Solem.
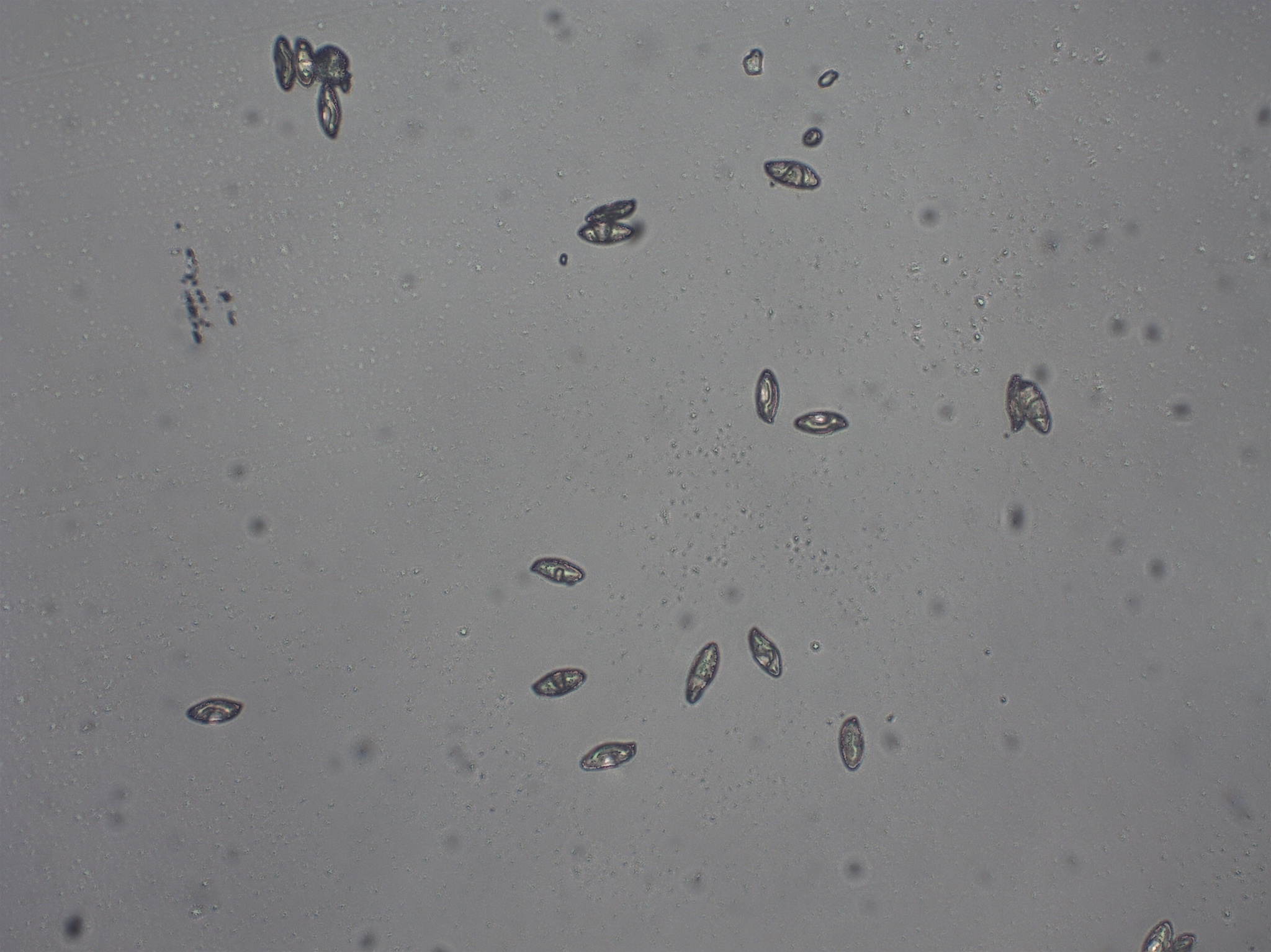
Spores of Gold-pored Bolete in Howard Co., Maryland (7/27/2010). (c) Joanne and Robert Solem, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC).
View Record Details
Media by
Joanne Solem.
Source: Wikipedia
| Aureoboletus auriporus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Basidiomycota |
| Class: | Agaricomycetes |
| Order: | Boletales |
| Family: | Boletaceae |
| Genus: | Aureoboletus |
| Species: | A. auriporus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Aureoboletus auriporus | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
Aureoboletus auriporus is a species of bolete fungus in the family Boletaceae that is found in Europe and North America. It was originally described in 1872 by American mycologist Charles Horton Peck, who called it Boletus auriporus.[2] Zdenek Pouzar transferred it to the genus Aureoboletus in 1957.[3]
The species is edible, and could be confused with (the also edible) Xerocomus illudens.[4]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "GSD Species Synonymy: Aureoboletus auriporus (Peck) Pouzar". Species Fungorum. CAB International. Retrieved 2015-09-10.
- ^ Peck CH. (1873). "Report of the Botanist (1869)". Annual Report on the New York State Museum of Natural History. 23: 27–135 (see p. 133).
- ^ Peck CH. (1957). "Nova genera macromycetum I". Ceská Mykologie. 11 (1): 48–50.
- ^ Phillips, Roger (2010). Mushrooms and Other Fungi of North America. Buffalo, NY: Firefly Books. pp. 256, 258. ISBN 978-1-55407-651-2.
External links
[edit]