Map Snapshot


6 Records
Description
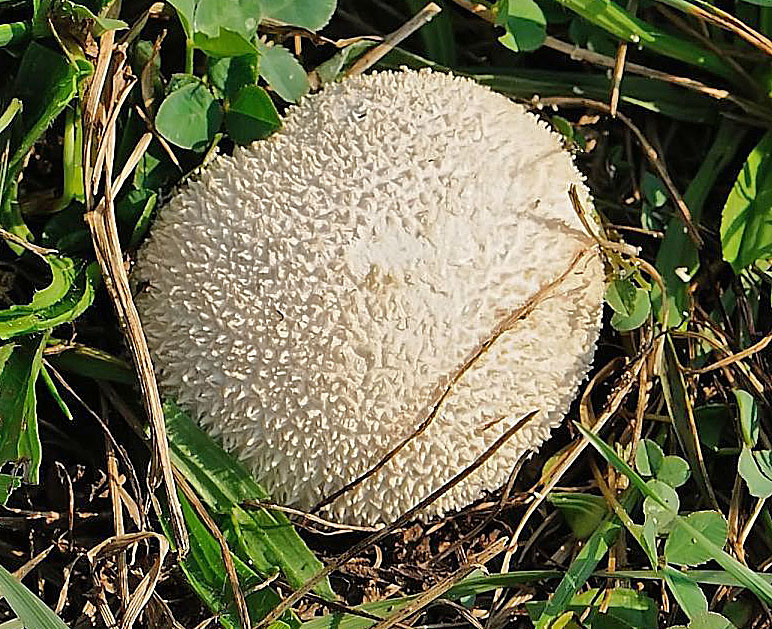
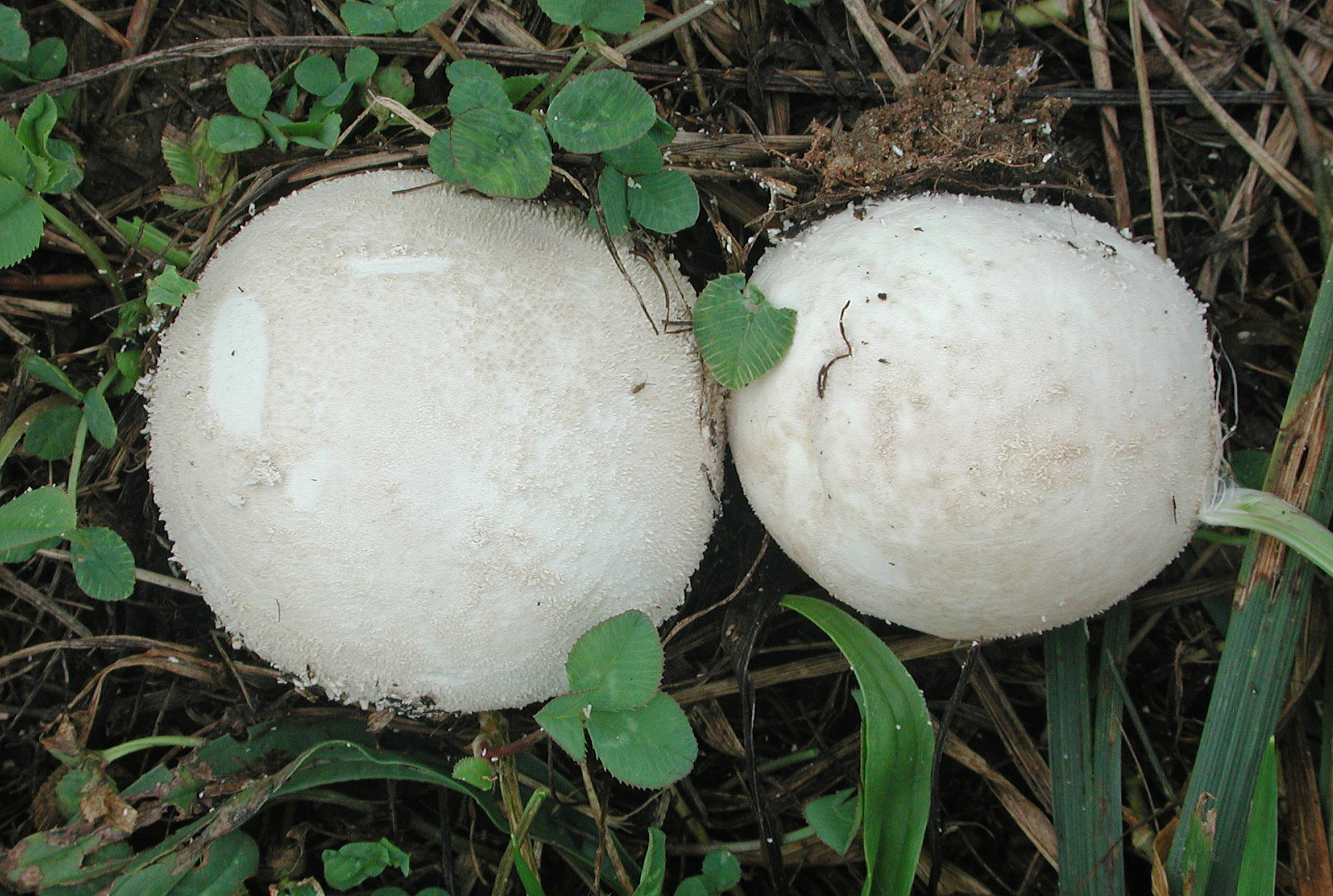
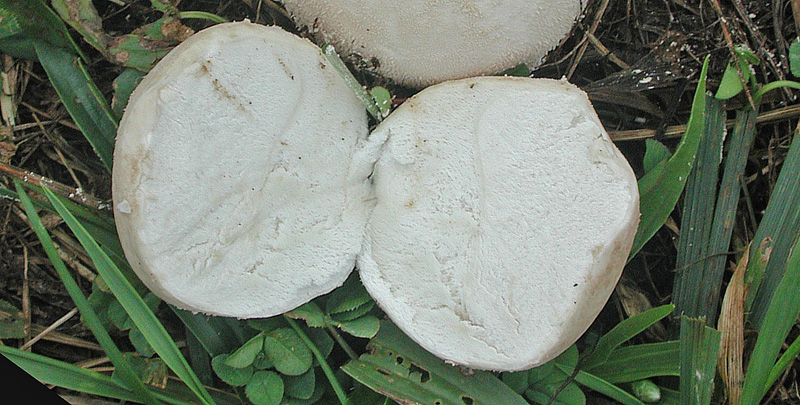
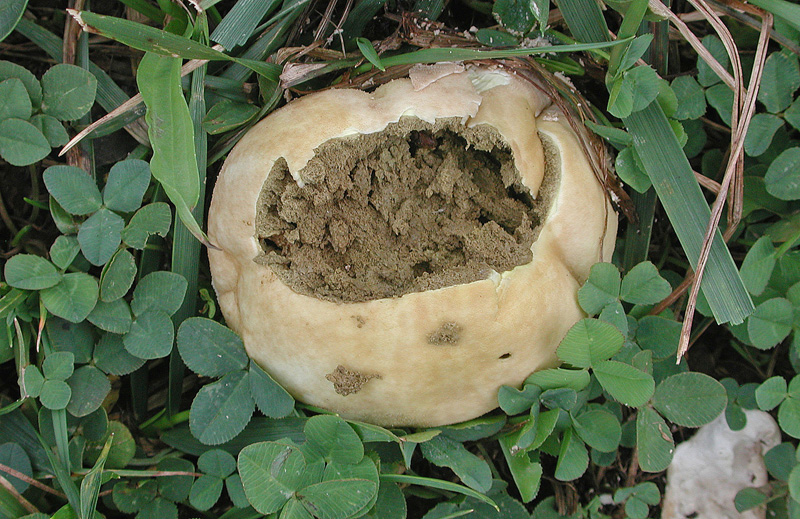
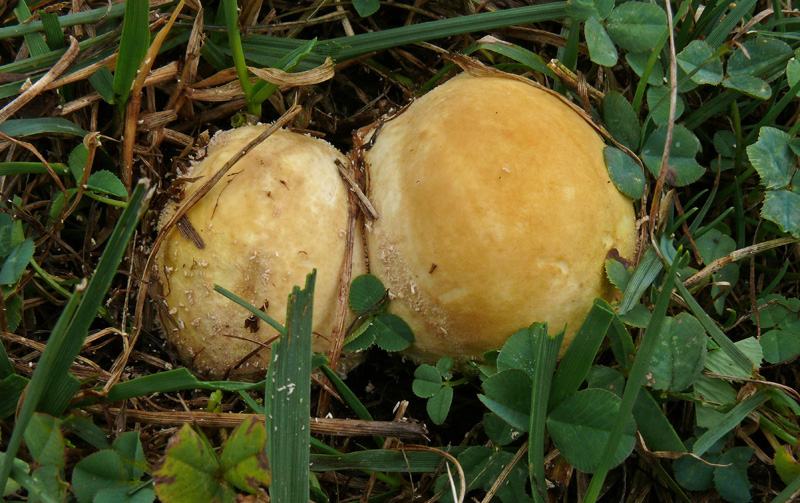
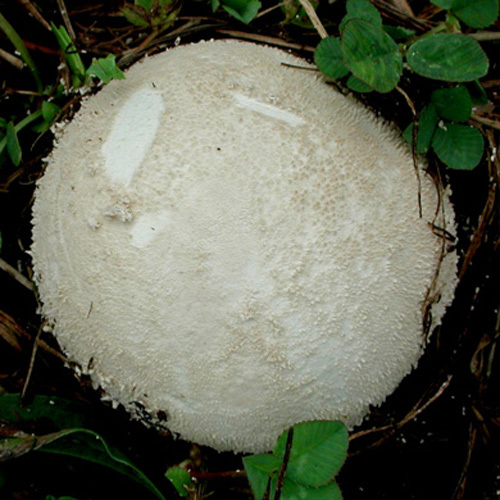
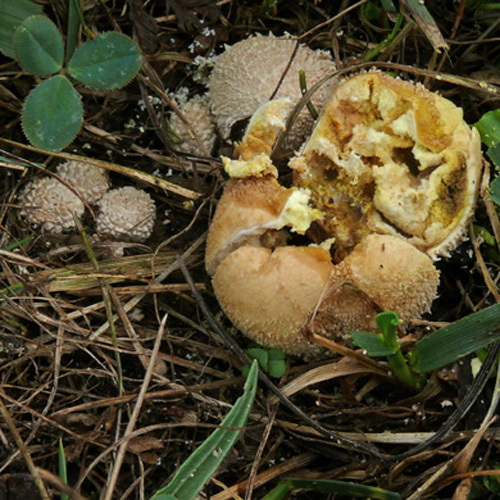
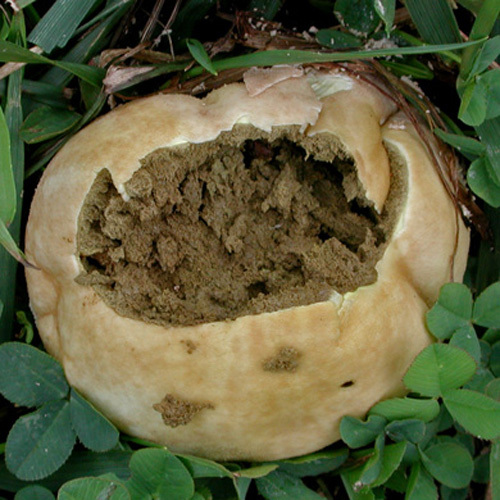
Fruiting body up to 4" (10 cm); white when young with scurfy surface/pyramidal warts, becoming yellow-tan, and gray-brown in age. Large tear or pore at apex at maturity. Initially spore mass white, becoming yellowish, finally brown. Tapered root-like rhizomorph anchors fruiting body (J. Solem, pers. comm.).
Where To Find
On ground in grassy areas, pastures, open woods.
Seasonality Snapshot
Source: Wikipedia
| Lycoperdon radicatum | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Division: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | L. radicatum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Lycoperdon radicatum | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
|
Bovistella radicata (Durieu & Mont.) Pat. (1889) | |
| Lycoperdon radicatum | |
|---|---|
| Glebal hymenium | |
| Lacks a stipe | |
| Spore print is brown | |
| Ecology is saprotrophic | |
| Edibility is edible or inedible | |
Lycoperdon radicatum is a species of puffball mushroom, also called rooting puffball, in the family Agaricaceae. It was described in 1848 by French botanists Michel Charles Durieu de Maisonneuve and Camille Montagne in Algeria.[2] Due to its Bovista-like capillitium it was previously placed in the genus Bovistella.[3] It is nonpoisonous.[4] It is easily recognised by its 4-8 cm rigid, white-gray pseudoroot.[5]
Its cylindrical fruiting body is up to 10 cm in size, and is white when young with a pyramidal warts, becoming yellow-tan, and gray-brown in age. At maturity, it develops a large tear at its apex. The spore mass also changes colour when it ages; initially it is white, and then becomes yellowish and finally, brown.[6] The spores are round to ellipsoid, warted, and 4-5 x 3-4.5 μm in size. [5]
Lycoperdon radicatum is found in grassy areas, pastures and in acidic soils in open woods. It is considered endangered in Sweden. [7]
References
[edit]- ^ "Species synonymy: Lycoperdon radicatum Durieu & Mont". Species Fungorum. CAB International. Retrieved 2013-01-13.
- ^ Bory de St.-Vincent, Durieu de Maisonneuve MC. (eds.) (1848). Exploration scientifique de l'Algérie (in French). Vol. 1–10. Paris. pp. 361–400.
{{cite book}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ^ Reid, D. A. (1953). "Bovistella radicata (Mont.) Pat. A Gasteromycete New to Britain". Kew Bulletin. 8 (1): 47–48. doi:10.2307/4117155. ISSN 0075-5974.
- ^ Miller Jr., Orson K.; Miller, Hope H. (2006). North American Mushrooms: A Field Guide to Edible and Inedible Fungi. Guilford, CN: FalconGuides. p. 449. ISBN 978-0-7627-3109-1.
- ^ a b Labbé, Roland (March 2023). "Lycoperdon radicatum". MycoQuebec. Retrieved 2024-01-27.
- ^ "Maryland Biodiversity Project - Lycoperdon radicatum". www.marylandbiodiversity.com. Retrieved 2024-01-27.
- ^ "Lycoperdon radicatum Durieu & Mont". www.gbif.org. Retrieved 2024-01-27.
External links
[edit]