Map Snapshot


3 Records
Seasonality Snapshot
Source: Wikipedia
| Pagurus pollicaris | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Malacostraca |
| Order: | Decapoda |
| Suborder: | Pleocyemata |
| Infraorder: | Anomura |
| Family: | Paguridae |
| Genus: | Pagurus |
| Species: | P. pollicaris
|
| Binomial name | |
| Pagurus pollicaris | |
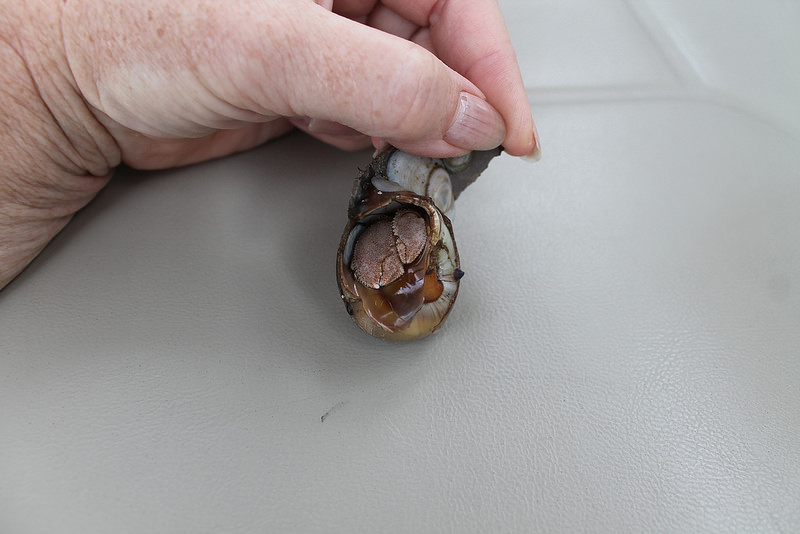
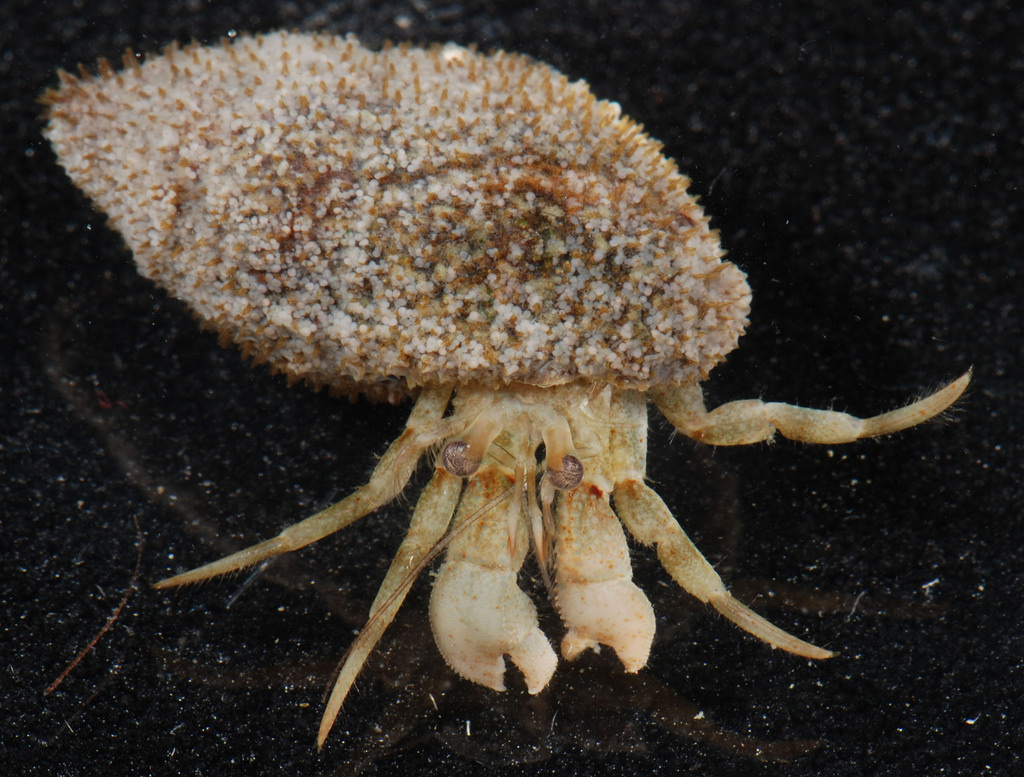
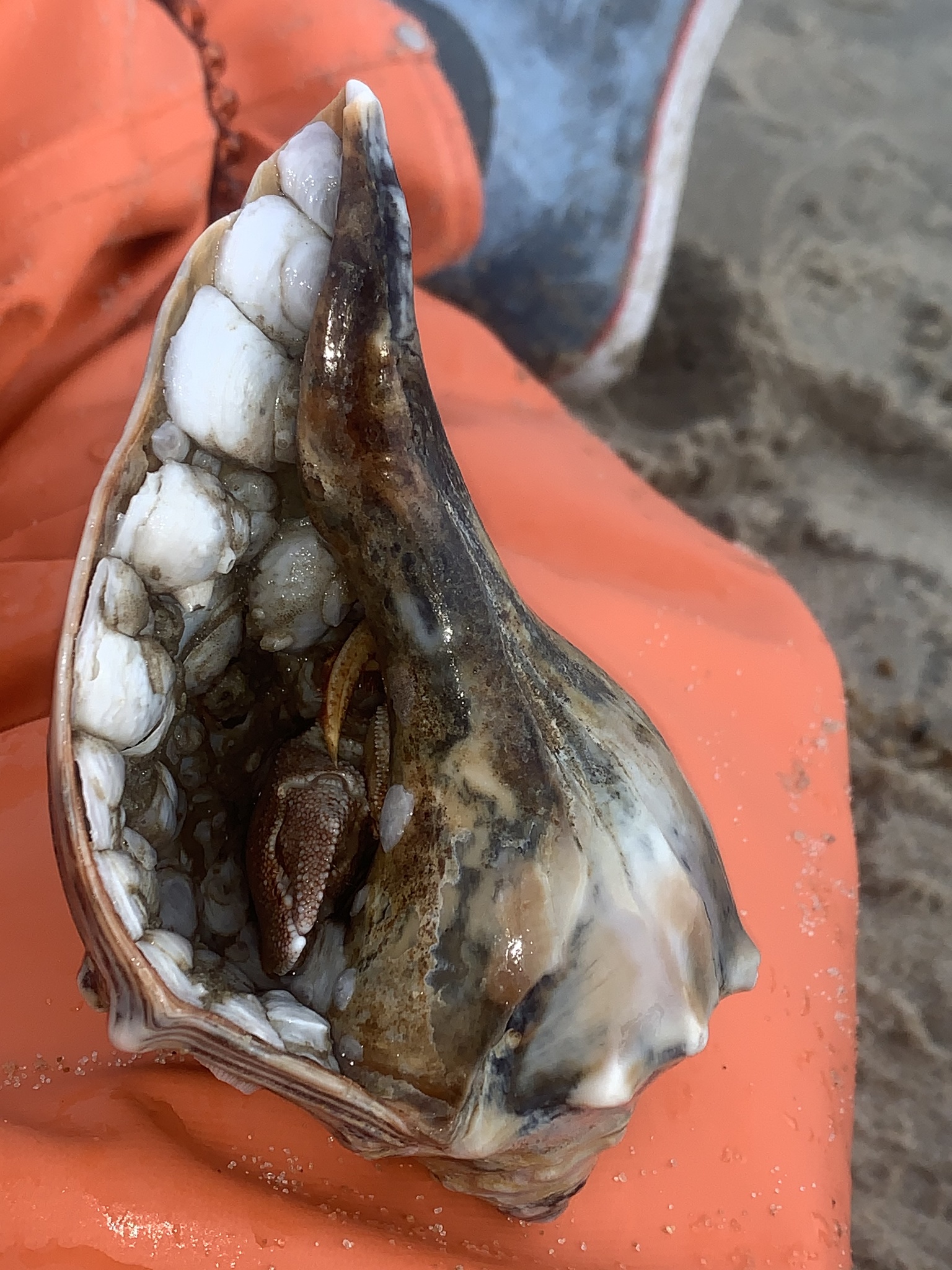
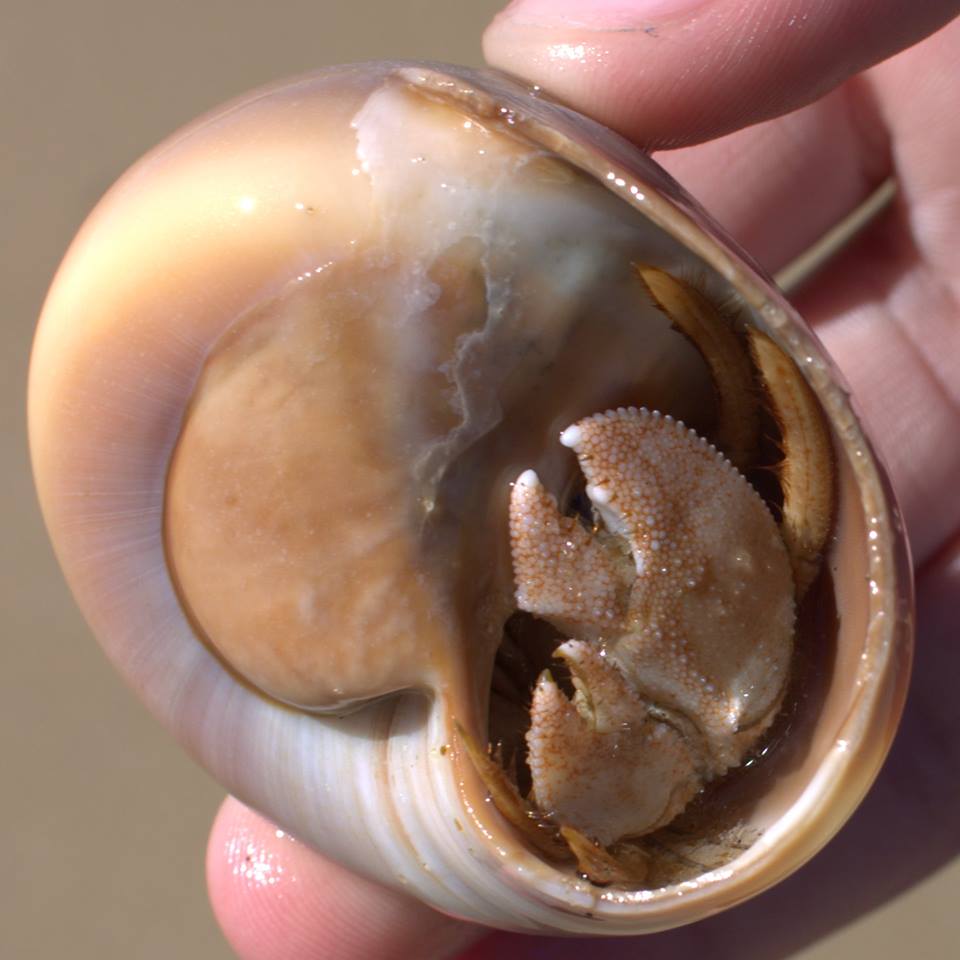
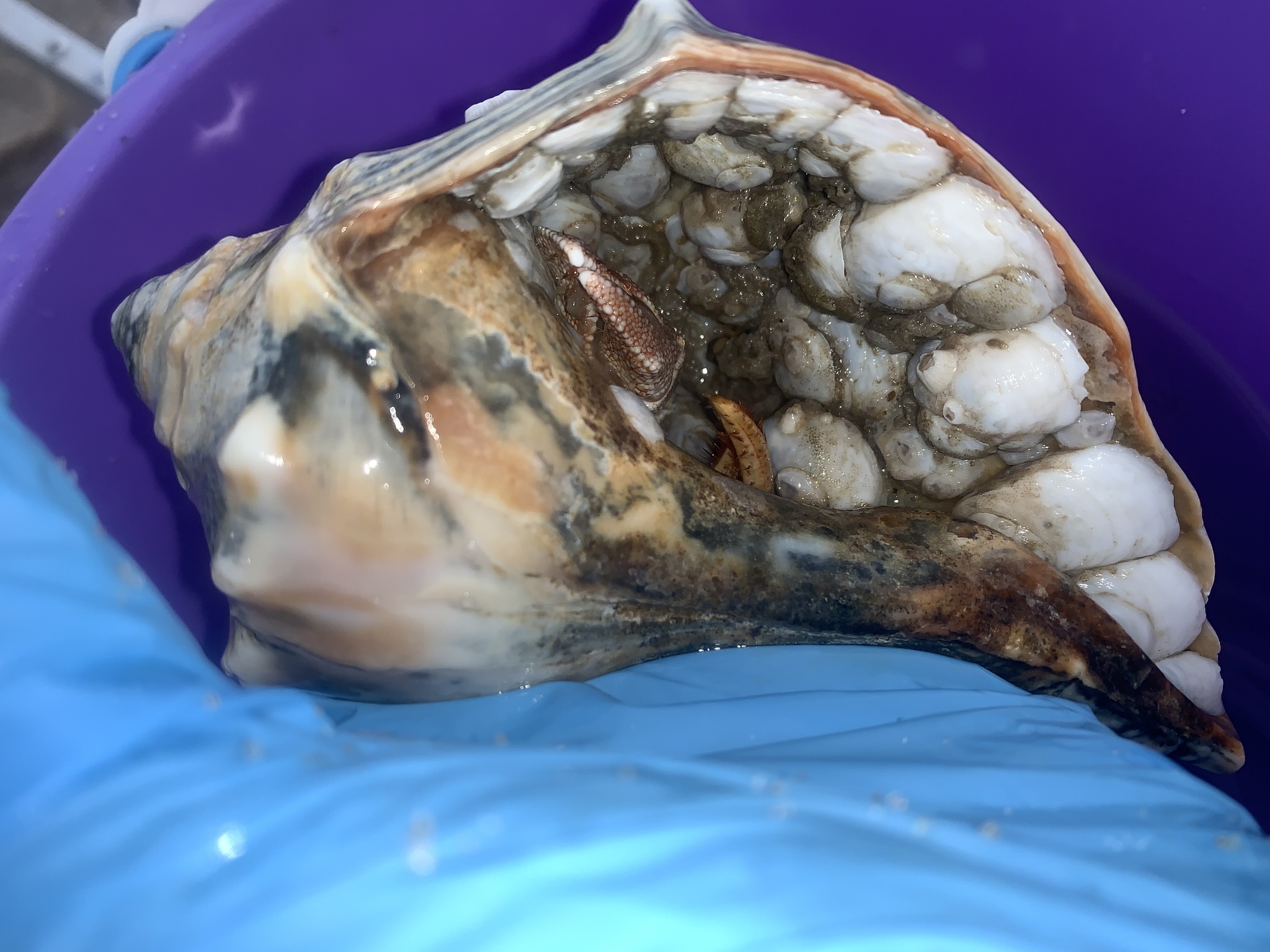
Pagurus pollicaris is a hermit crab commonly found along the Atlantic coast of North America from New Brunswick to the Gulf of Mexico. It is known by a number of common names, including gray hermit crab,[1] flat-clawed hermit crab,[2] flatclaw hermit crab,[1] shield hermit crab,[2] thumb-clawed hermit crab,[3] broad-clawed hermit crab,[4] and warty hermit crab.[5]
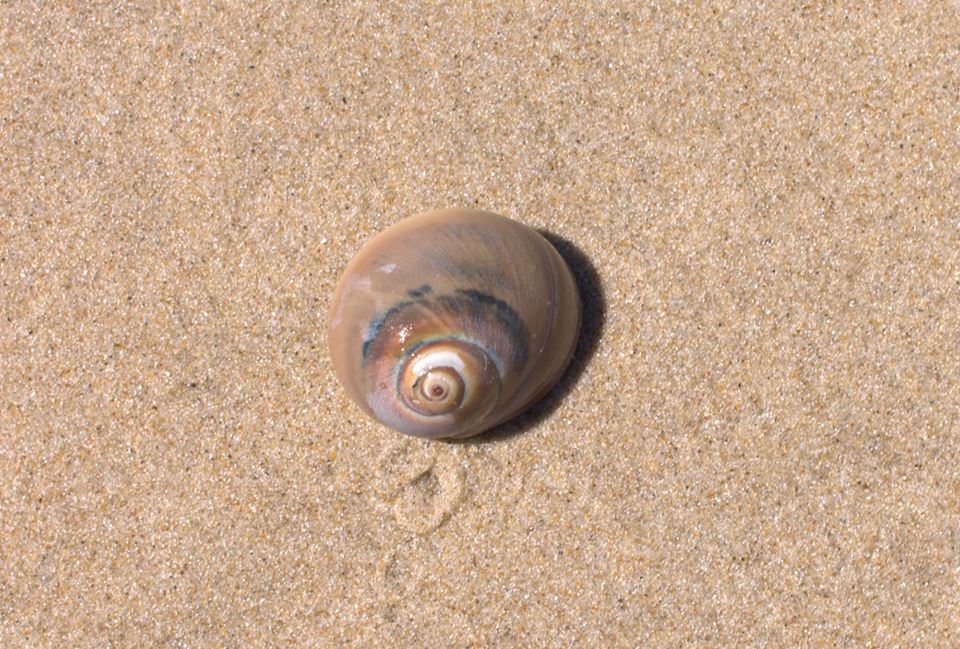
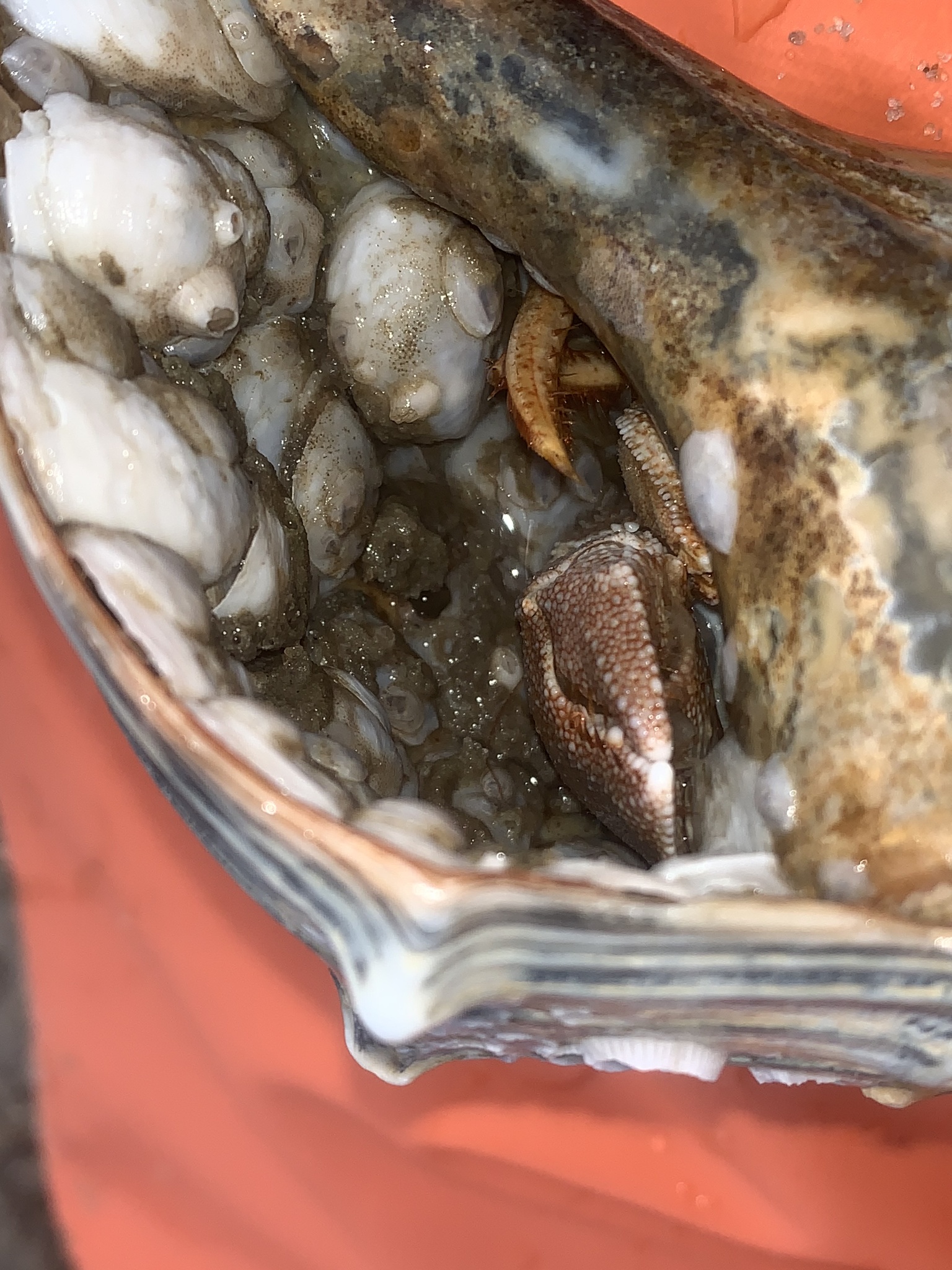
P. pollicaris inhabits the shells of shark eye snails and whelks.[4] It grows to a length of 31 millimetres (1.2 in) and a width of 25 mm (1.0 in).[2] The shell is often shared by the commensal zebra flatworm (Stylochus ellipticus).[2]
The diet of the flat-clawed hermit crab comprises organic matter, algae, and sometimes other hermit crabs. Fish are the most important predators of this species.
References
[edit]- ^ a b c "Pagurus pollicaris Say, 1817". Integrated Taxonomic Information System.
- ^ a b c d Andrew J. Martinez & Candace Storm Martinez (2003). "Flat-clawed hermit crab Pagurus pollicaris". Marine Life of the North Atlantic: Canada to New England (3rd ed.). Aqua Quest Publications. p. 162. ISBN 978-1-881652-32-8.
- ^ Susan B. Rothschild (2004). Beachcomber's Guide to Gulf Coast Marine Life: Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida (3rd ed.). Taylor Trade Publications. ISBN 978-1-58979-061-2.
- ^ a b Alice Jane Lippson & Robert L. Lippson (2006). "Intertidal flats". Life in the Chesapeake Bay (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 57–93. ISBN 978-0-8018-8338-5.
- ^ R. P. Cowles (1930). "A biological study of the offshore waters of Chesapeake Bay" (PDF). Bulletin of the Bureau of Fisheries. 46: 276–381.