Map Snapshot














54 Records
Status
This is a microscopic, pathogenic fungus. Observations without microscopic confirmation are speculative. There are many fungal species that cause powdery mildew in Maryland.
Description
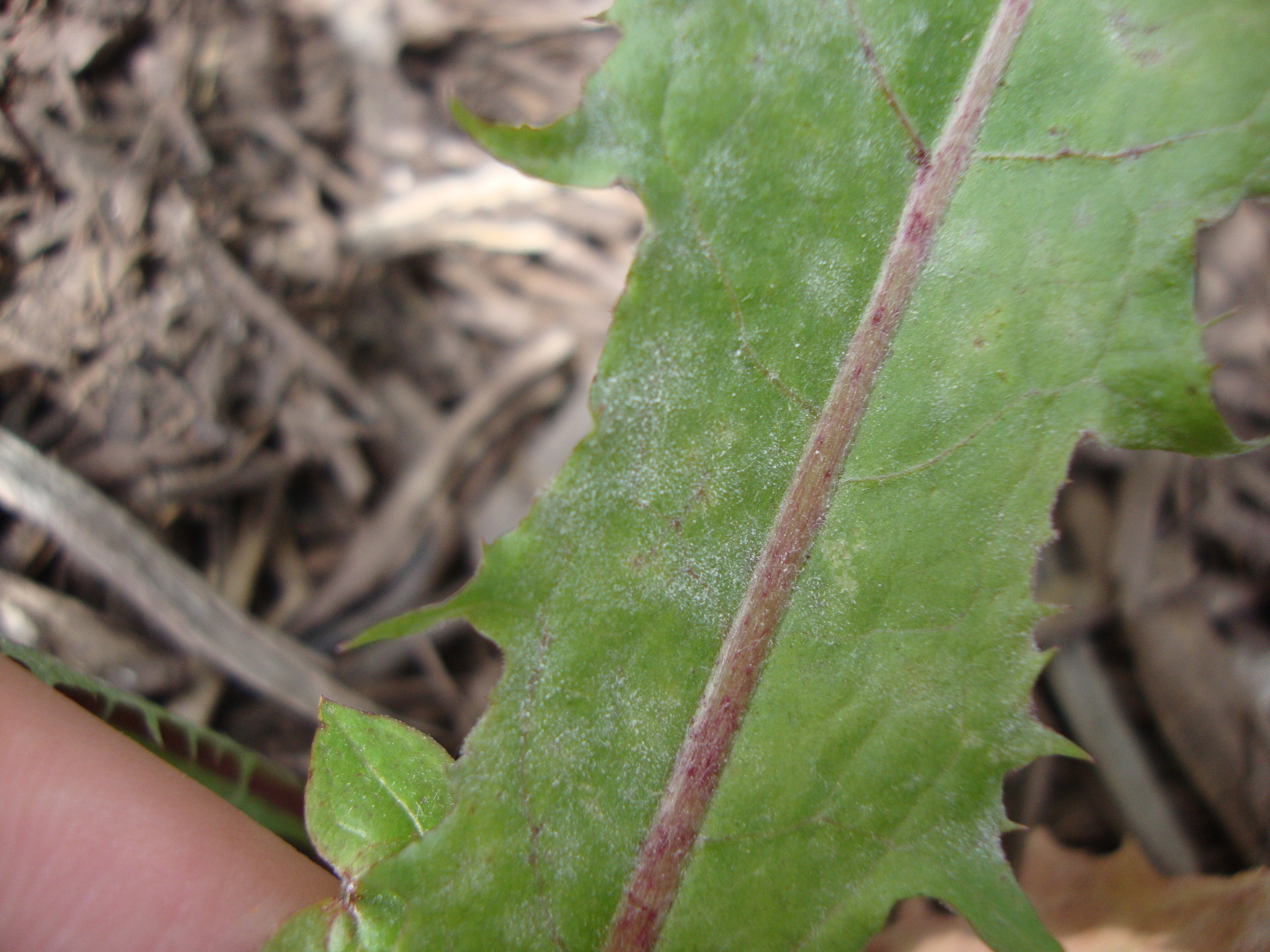
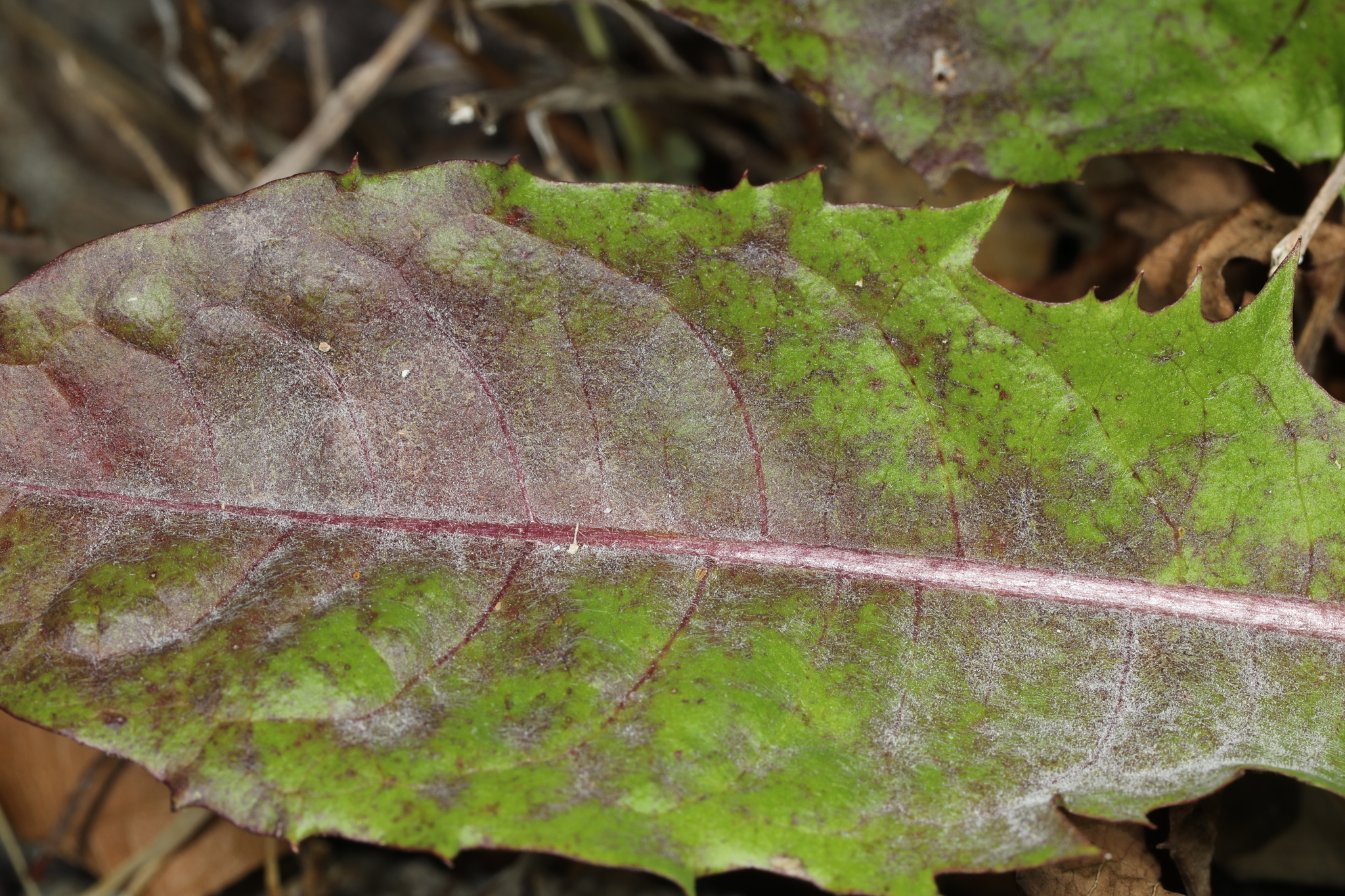
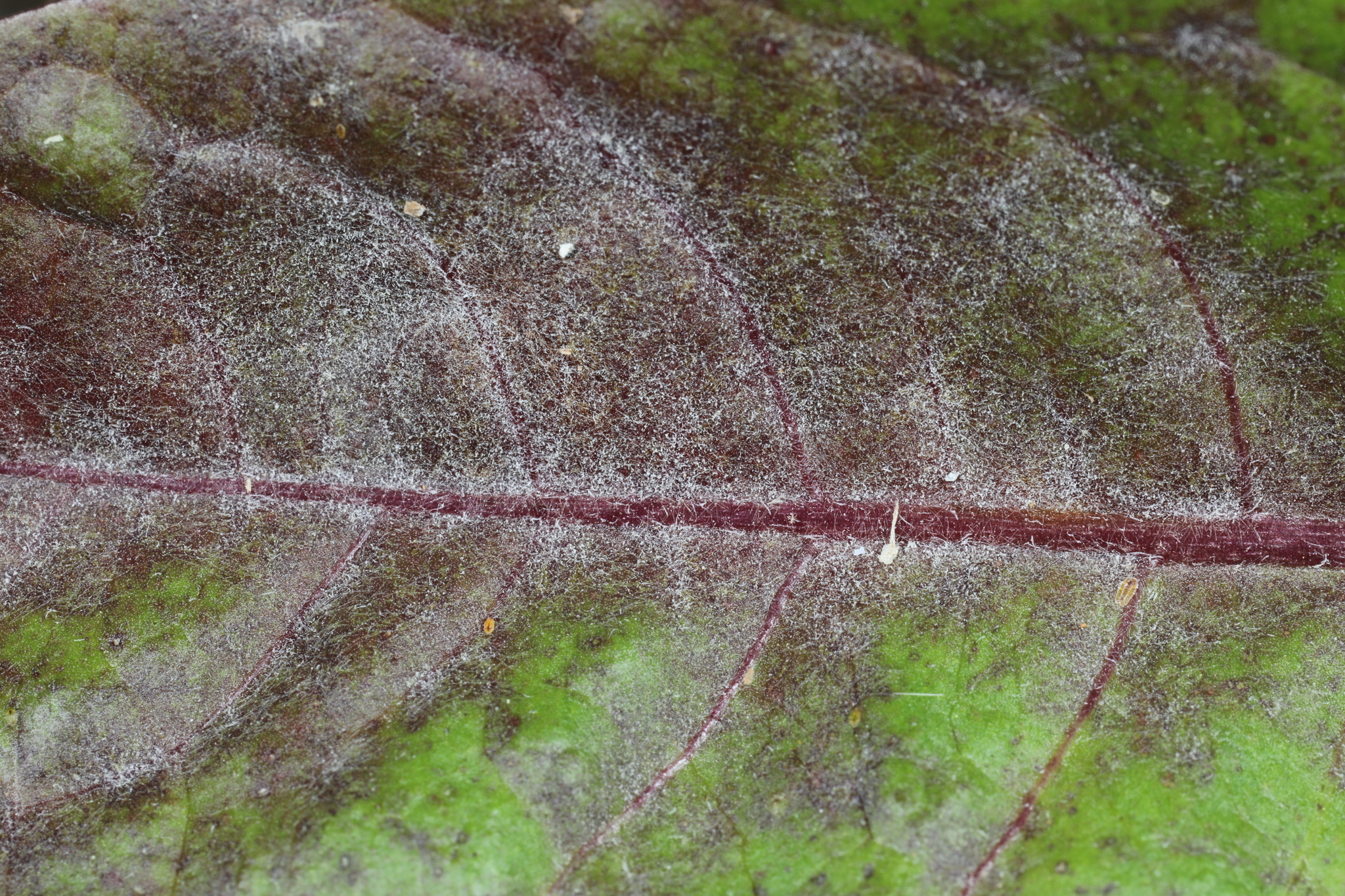
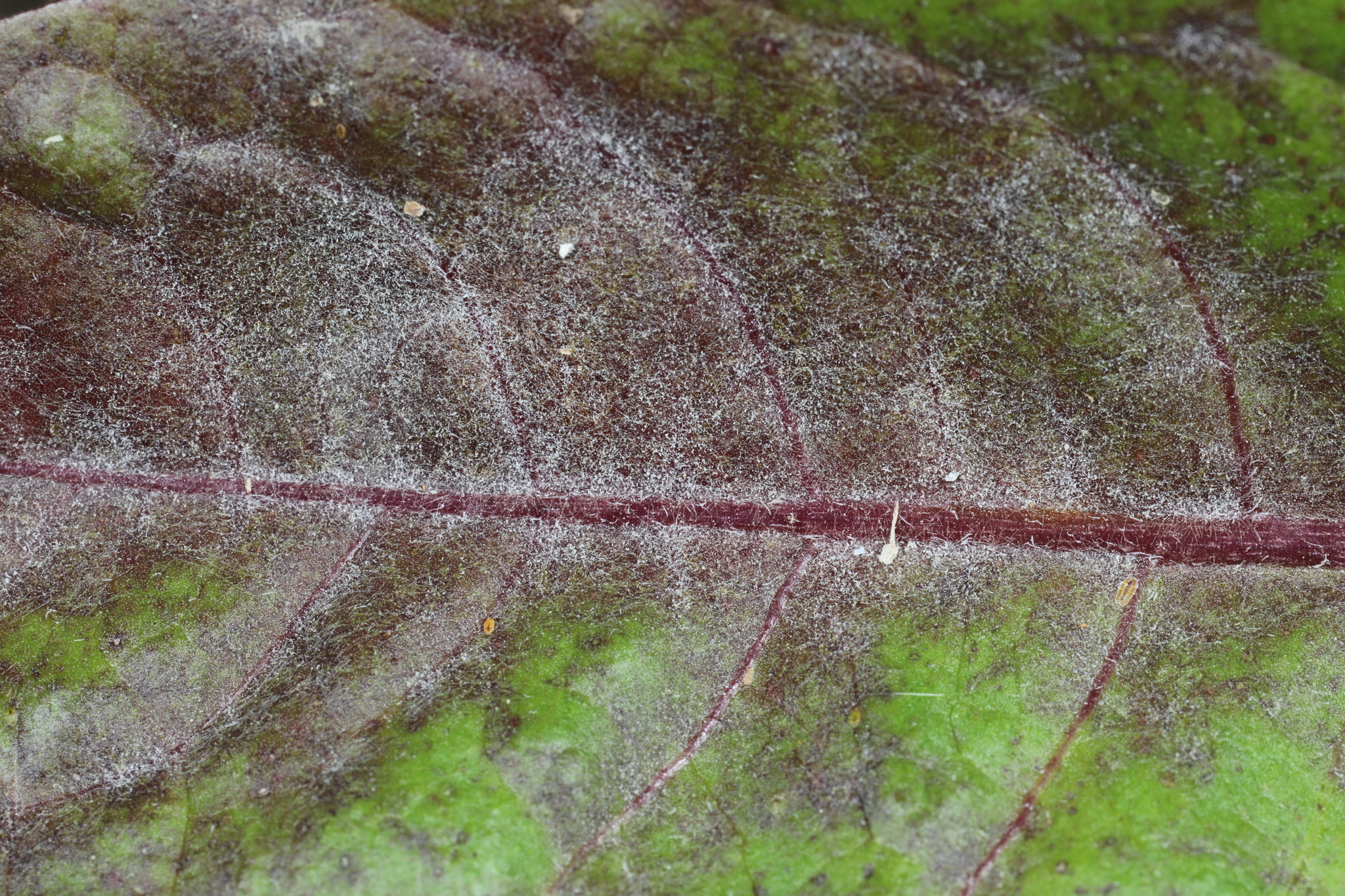
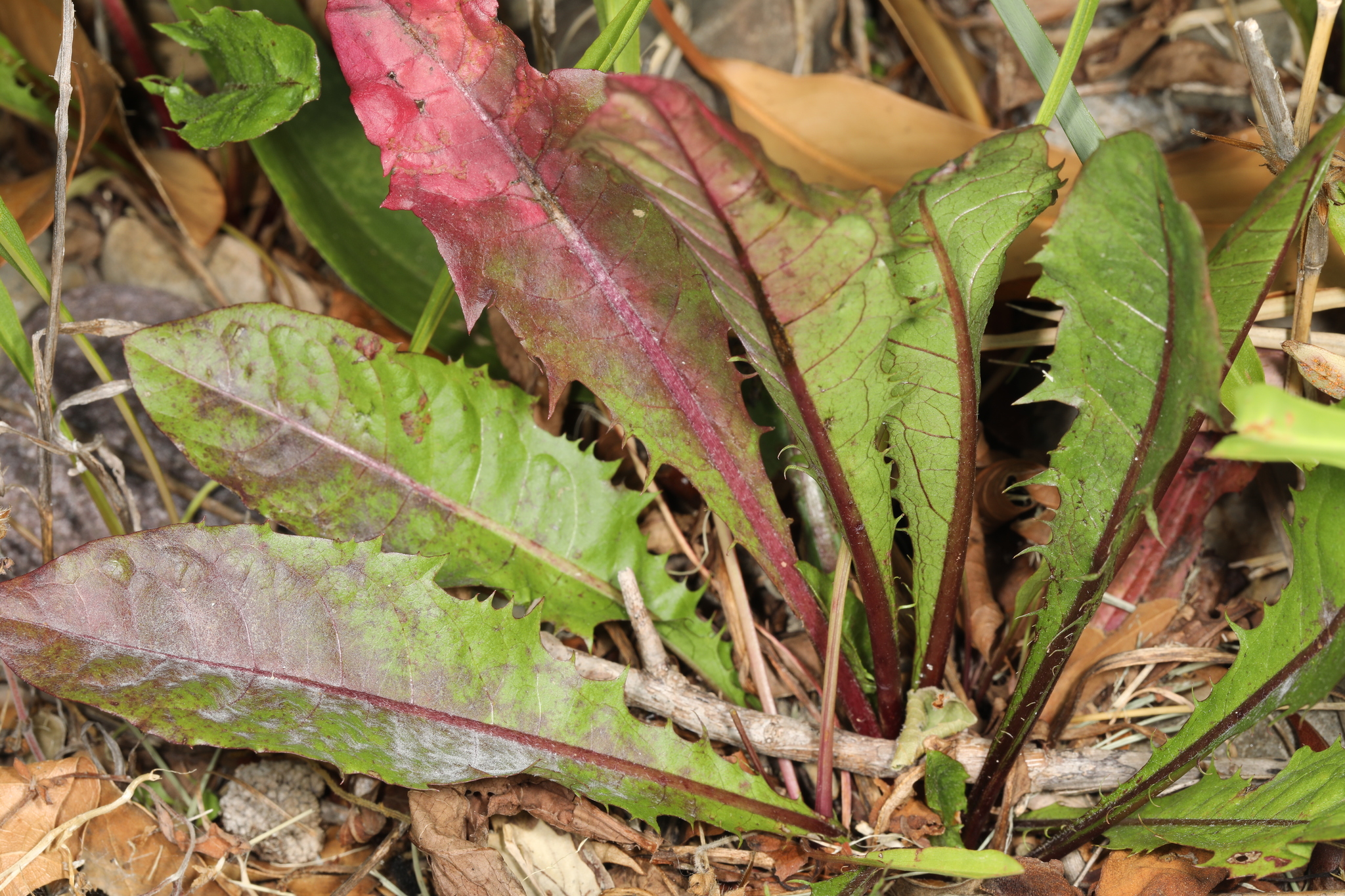
Causes a white, powdery mildew on many plant species including Asteraceae and Cucurbitaceae.
Seasonality Snapshot
Eating mushrooms can be dangerous. One should do so only with expert advice and great care. MBP accepts no liability for injury sustained in consuming fungi or other biodiversity. Use of media featured on Maryland Biodiversity Project is only permitted with express permission of the photographer.
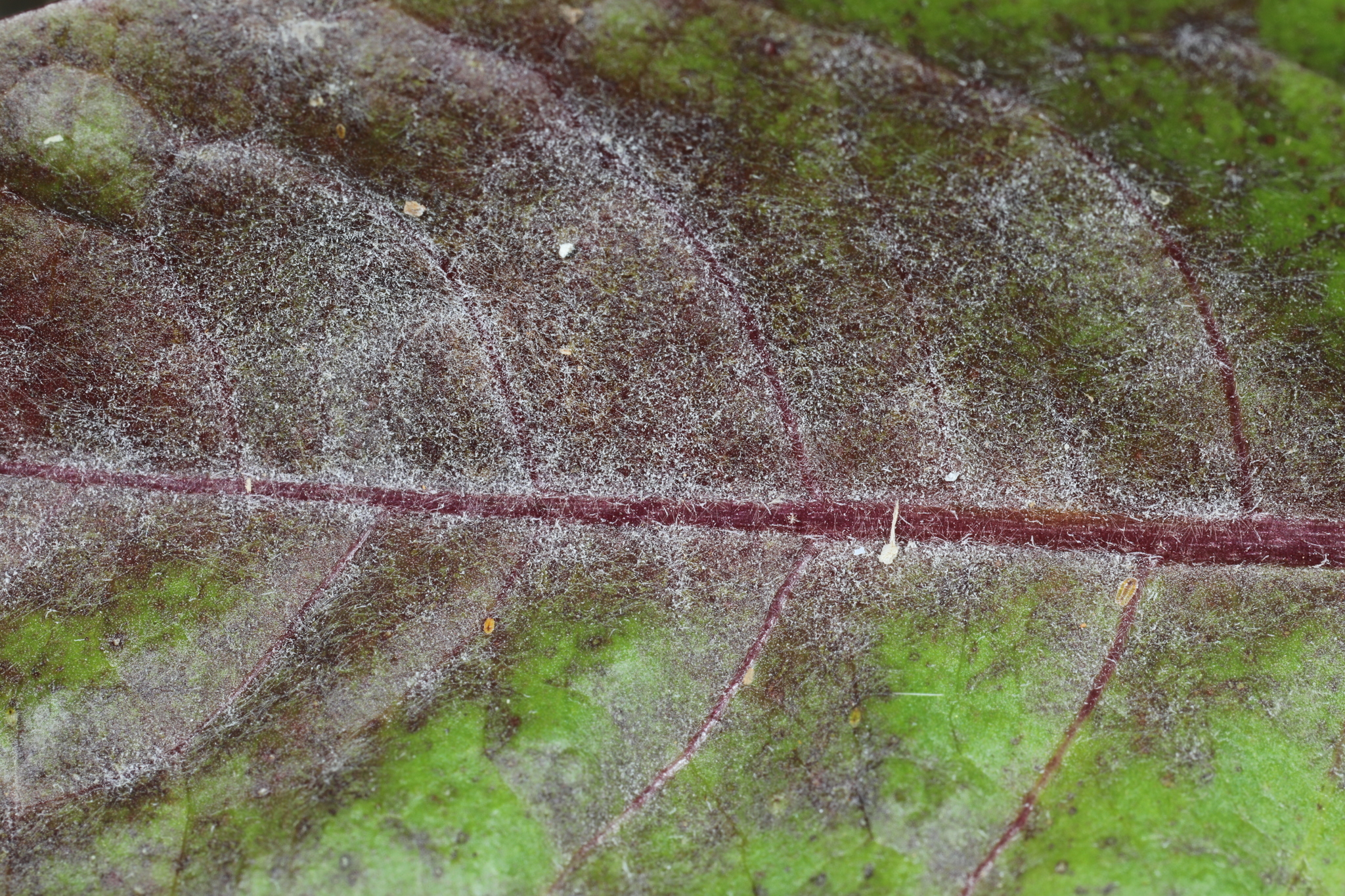
Powdery Mildew of Chicory in Prince George's Co., Maryland (5/22/2019). (c) William J. Davis, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC-ND).
View Record Details
Media by
William J. Davis via iNaturalist.
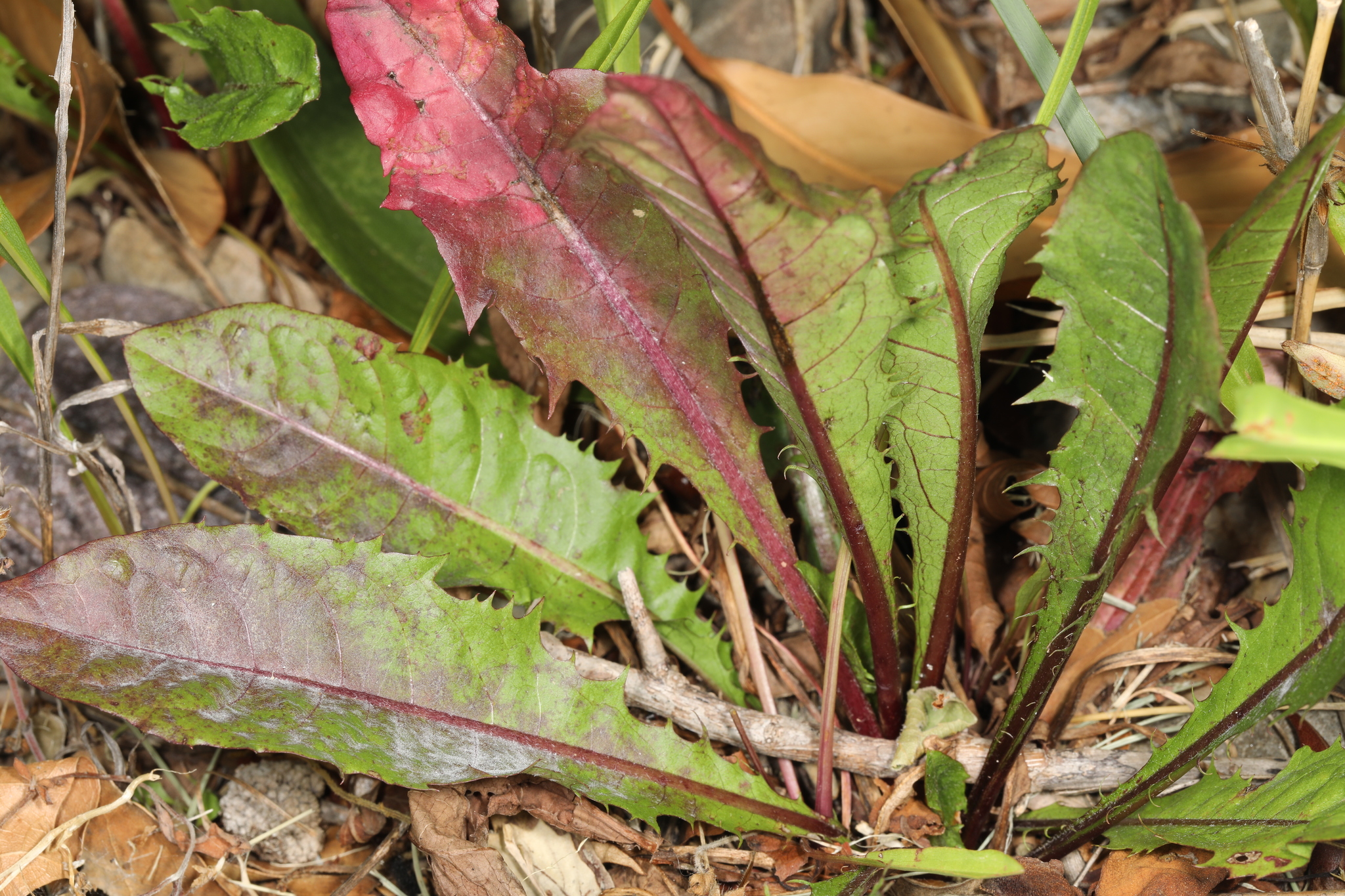
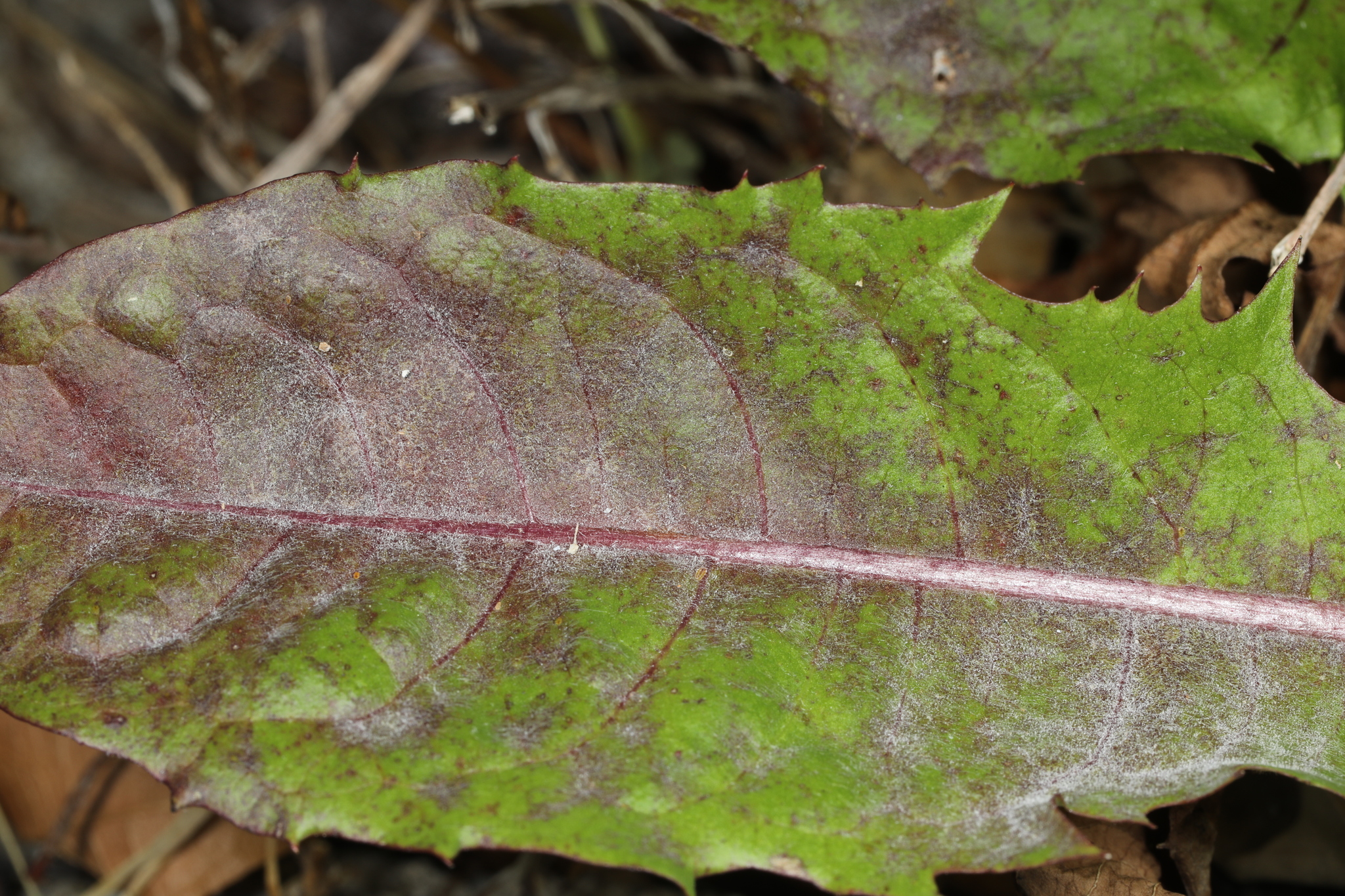
Powdery Mildew of Chicory in Worcester Co., Maryland (6/29/2020). (c) John Plischke, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC).
View Record Details
Media by
John Plischke.
Powdery Mildew of Chicory in Prince George's Co., Maryland (5/22/2019). (c) William J. Davis, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC-ND).
View Record Details
Media by
William J. Davis via iNaturalist.
Powdery Mildew of Chicory in Worcester Co., Maryland (6/29/2020). (c) John Plischke, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC).
View Record Details
Media by
John Plischke.
Powdery Mildew of Chicory in Worcester Co., Maryland (6/29/2020). (c) John Plischke, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC).
View Record Details
Media by
John Plischke.
Powdery Mildew of Chicory in Worcester Co., Maryland (6/29/2020). (c) John Plischke, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC).
View Record Details
Media by
John Plischke.
Powdery Mildew of Chicory in Worcester Co., Maryland (6/29/2020). (c) John Plischke, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC).
View Record Details
Media by
John Plischke.
Powdery Mildew of Chicory in Worcester Co., Maryland (6/29/2020). (c) John Plischke, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC).
View Record Details
Media by
John Plischke.
Powdery Mildew of Chicory in Prince George's Co., Maryland (5/22/2019). (c) William J. Davis, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC-ND).
View Record Details
Media by
William J. Davis via iNaturalist.
Powdery Mildew of Chicory in Worcester Co., Maryland (6/29/2020). (c) John Plischke, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC).
View Record Details
Media by
John Plischke.
Source: Wikipedia
| Erysiphe cichoracearum | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Ascomycota |
| Class: | Leotiomycetes |
| Order: | Erysiphales |
| Family: | Erysiphaceae |
| Genus: | Erysiphe |
| Species: | E. cichoracearum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Erysiphe cichoracearum (DC.) (1805)
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Golovinomyces cichoracearum (DC.) V.P. Heluta [as 'cichoraceorum'], (1988) | |
Erysiphe cichoracearum is a fungal plant pathogen that causes powdery mildew disease of cucurbits, including melon, cucumber, pumpkin, and squash.[1] The primary symptoms are white, powder-like spots on the leaves and stems. Sphaerotheca fuliginea causes a similar looking powdery mildew of cucurbits.
References
[edit]- ^ Koh, Serry; André, Aurélie; Edwards, Herb; Ehrhardt, David; Somerville, Shauna (2005-10-07). "Arabidopsis thaliana subcellular responses to compatible Erysiphe cichoracearum infections: Cellular responses to powdery mildew infections". The Plant Journal. 44 (3): 516–529. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02545.x.
External links
[edit]Wikimedia Commons has media related to Golovinomyces cichoracearum.