Map Snapshot


1 Record
Seasonality Snapshot
Source: Wikipedia
| Britzelmayria multipedata | |
|---|---|

| |

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Basidiomycota |
| Class: | Agaricomycetes |
| Order: | Agaricales |
| Family: | Psathyrellaceae |
| Genus: | Britzelmayria |
| Species: | B. multipedata
|
| Binomial name | |
| Britzelmayria multipedata | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Psathyra multipedata Peck (1905) | |
| Britzelmayria multipedata | |
|---|---|
| Gills on hymenium | |
| Cap is conical or convex | |
| Hymenium is adnate or adnexed | |
| Stipe is bare | |
| Spore print is purple-brown | |
| Ecology is saprotrophic | |
| Edibility is unknown | |
Britzelmayria multipedata is a species of mushroom producing fungus in the family Psathyrellaceae.[1] It is commonly known as the clustered brittlestem.
Taxonomy
[edit]It was first described in 1905 by the American mycologist Charles Horton Peck who classified it as Psathyra multipedata.[2] It was reclassified as Psathyrella multipedata in 1941 by the American mycologistAlexander H. Smith[3] and remained known as such until recently. In 2020 the German mycologists Dieter Wächter & Andreas Melzer reclassified many species in the Psathyrellaceae family based on phylogenetic analysis and placed this species in the newly created genus Britzelmayria.[4]
Many mushroom field guides and websites still refer to this species as Psathyrella multipedata.
Description
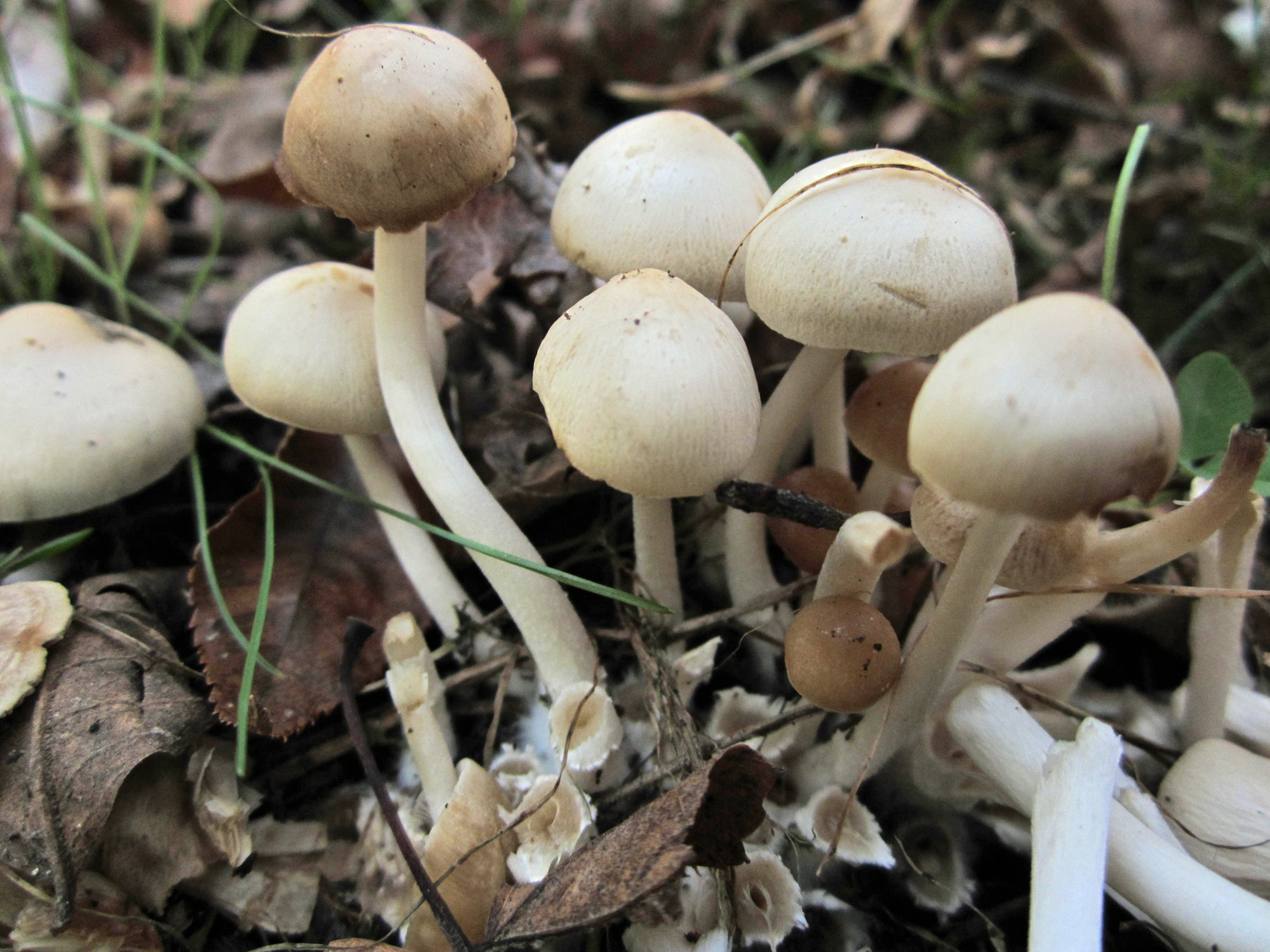
[edit]Britzelmayria multipedata is a small brittlestem mushroom with white flesh and a brown cap which is known for growing in dense clusters.
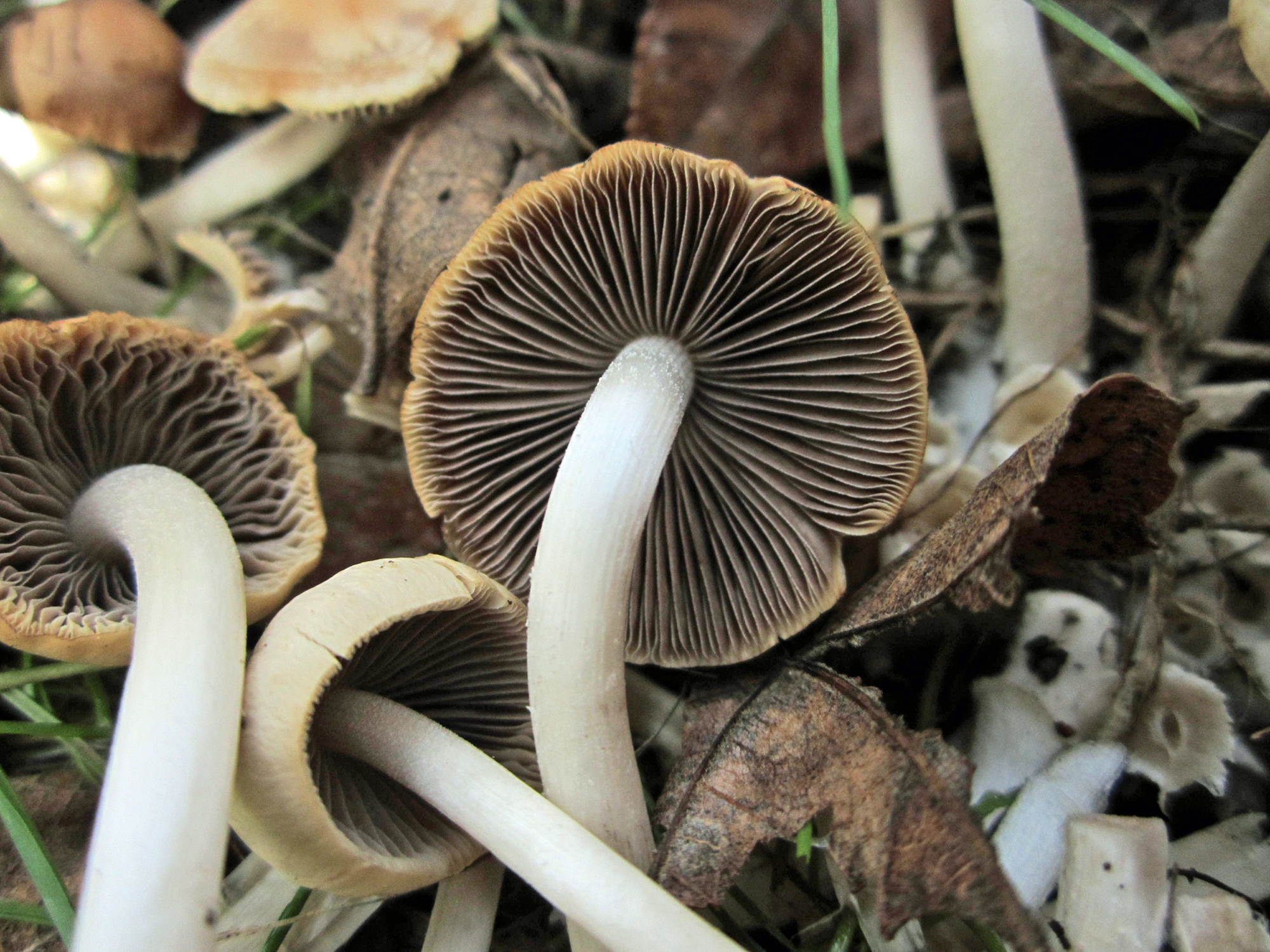
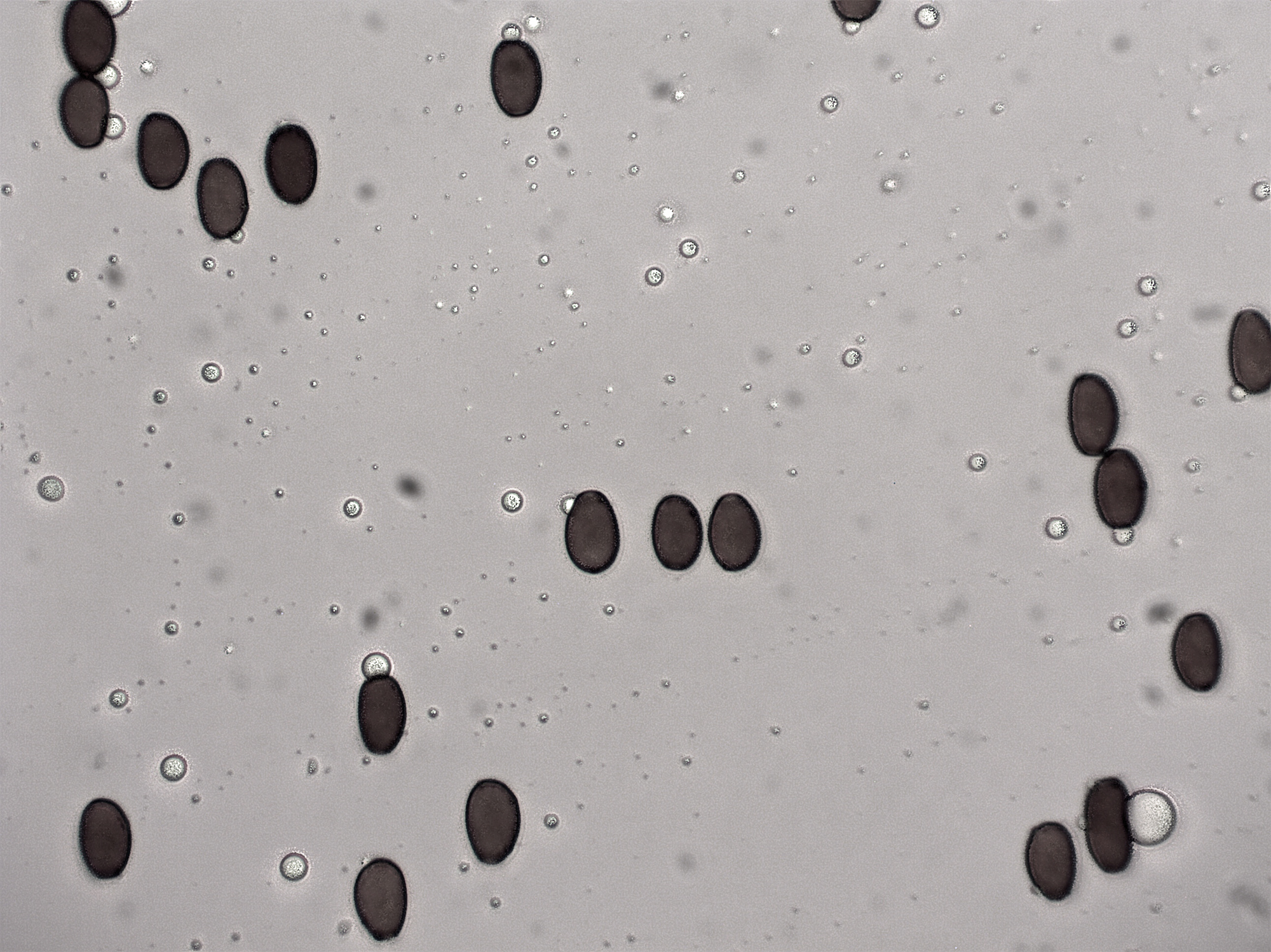
Cap: 1-3cm. Starts conical before flattening into a convex cap which may become campanulate or bell shaped with age. The smooth, brown cap becomes paler when dry. Gills: Adnate or adnexed. Crowded. Light grey or brown with white fringes maturing to dark brown. Stem: 7-12cm in height with a thickness of 3-6mm tapering slightly towards the cap. It often grows in a wavy fashion with the base fused together with other members of the cluster. Spore print: Dark purplish brown. Spores: Ellipsoid and smooth with a germ pore. 6.5-10 x 3.5-4 μm. Taste: Indistinct and mild. Smell: Faint and mushroomy.[5][6]

Habitat and distribution
[edit]Britzelmayria multipedata is found on soil amongst grass and in open grassy spaces amongst woodland. It is saprotrophic and grows on buried fallen trees through the late Summer to Autumn. This species is widespread and found occasionally.[5][6]
Observations of this species appear most common in the UK, West Europe and the East Coast of the United States.[7][8]
References
[edit]- ^ "Species Fungorum - Britzelmayria multipedata (Peck) D. Wächt. & A. Melzer, Mycol. Progr. 19(11): 1213 (2020)". www.speciesfungorum.org. Retrieved 2022-07-16.
- ^ "Species Fungorum - Psathyra multipedata Peck, Bull. Torrey bot. Club 32(2): 80 (1905)". www.speciesfungorum.org. Retrieved 2022-07-16.
- ^ "Species Fungorum - Psathyrella multipedata (Peck) A.H. Sm., Contr. Univ. Mich. Herb. 5: 33 (1941)". www.speciesfungorum.org. Retrieved 2022-07-16.
- ^ Wächter, Dieter; Melzer, Andreas (2020-11-01). "Proposal for a subdivision of the family Psathyrellaceae based on a taxon-rich phylogenetic analysis with iterative multigene guide tree". Mycological Progress. 19 (11): 1151–1265. doi:10.1007/s11557-020-01606-3. ISSN 1861-8952.
- ^ a b Buczacki, Stefan (2012). Collins fungi guide. London: Collins. ISBN 978-0-00-724290-0. OCLC 793683235.
- ^ a b "Psathyrella multipedata, Clustered Brittlestem mushroom". www.first-nature.com. Retrieved 2022-07-16.
- ^ "Clustered Brittlestem (Britzelmayria multipedata)". iNaturalist. Retrieved 2022-07-16.
- ^ "Mushroom Observer". mushroomobserver.org. Retrieved 2022-07-16.