Map Snapshot



6 Records
Description
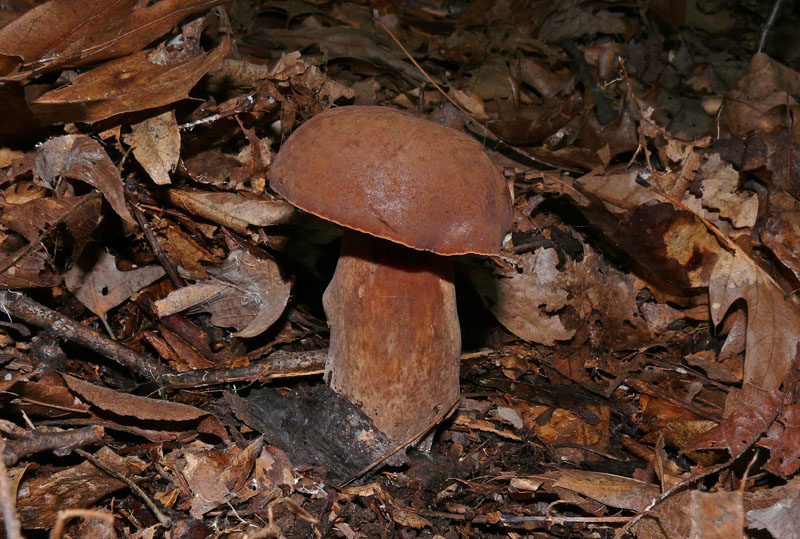
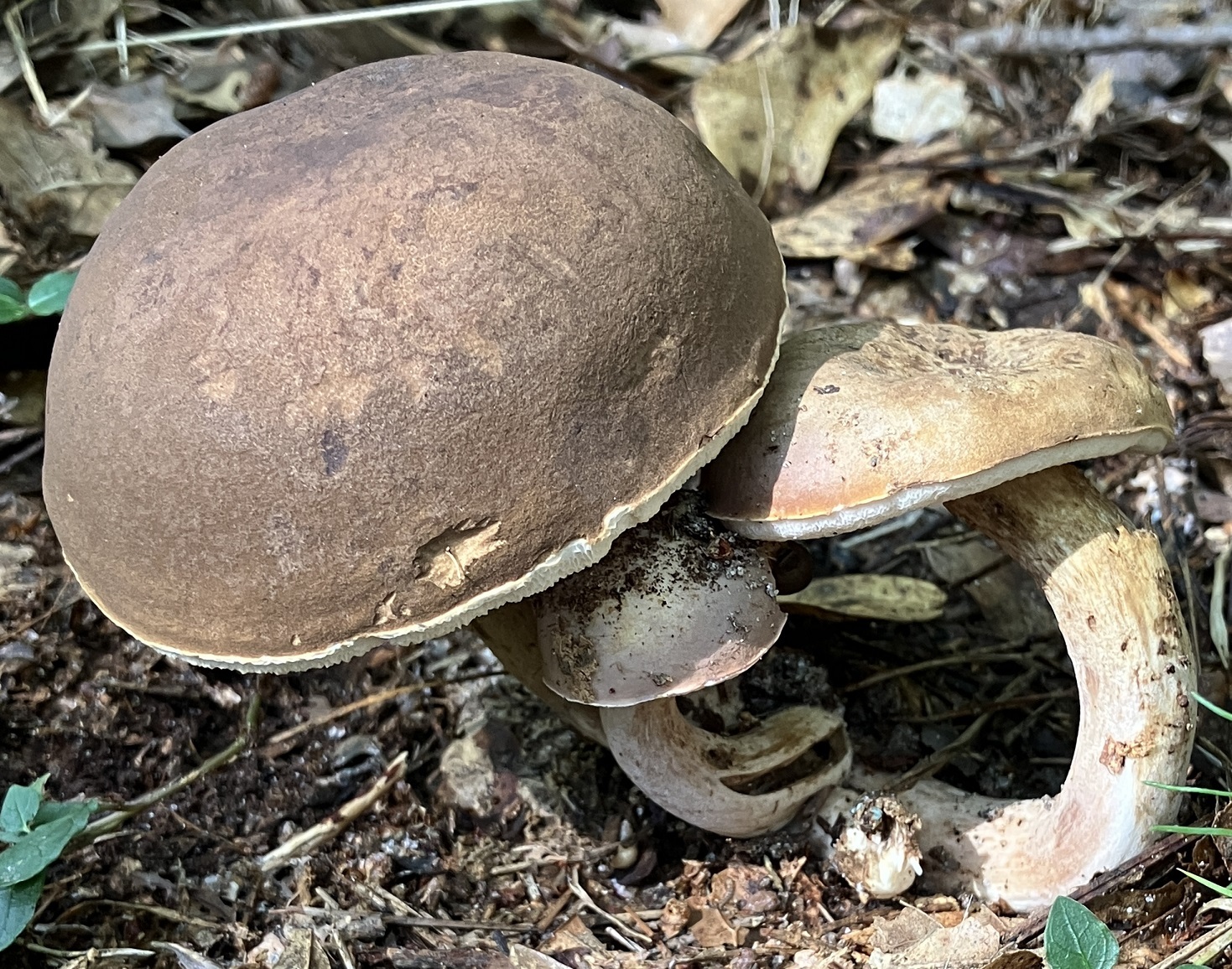
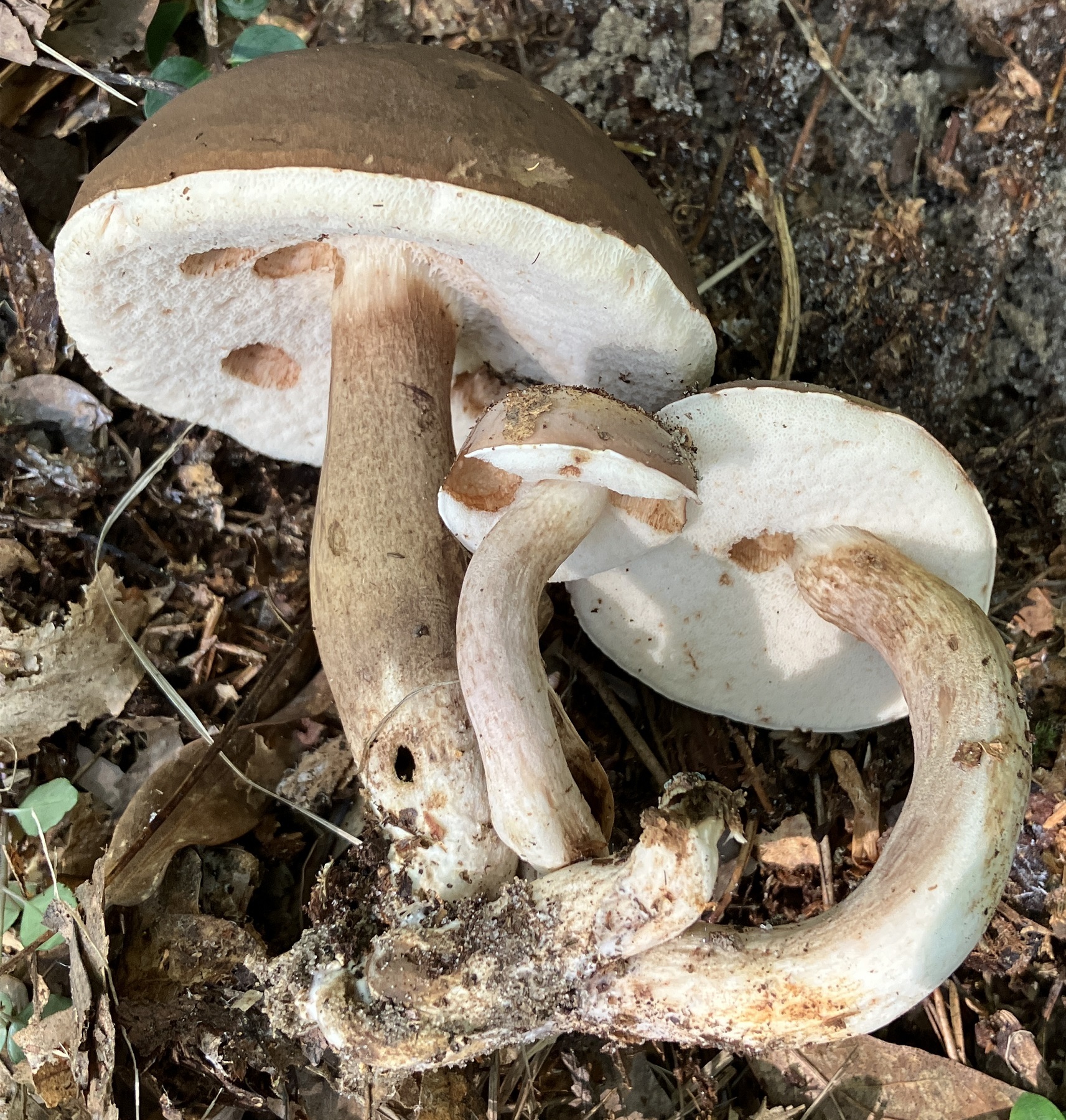
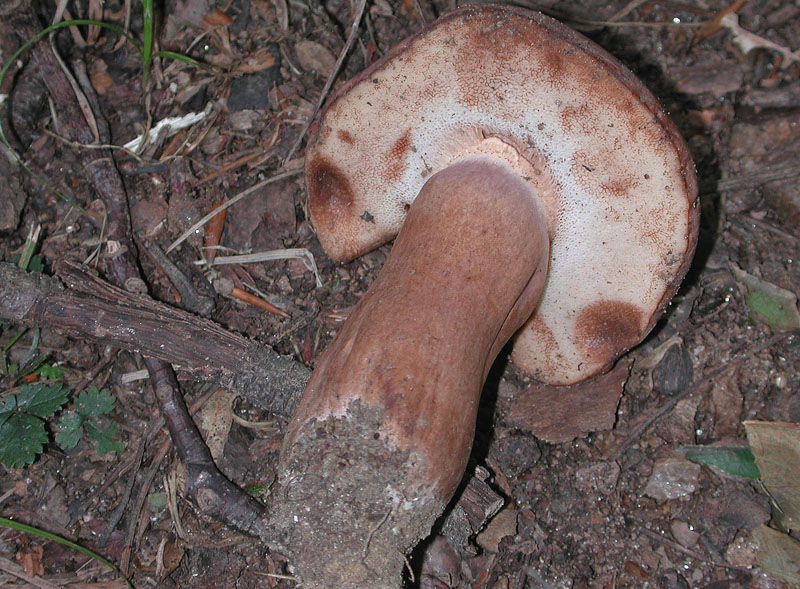
Cap: Maroon to dark reddish-brown, velvety to smooth, convex to broadly convex; margin may have band of sterile tissue; white flesh slowly stains pinkish-brown when cut. Pores: White, then dingy; bruise pinkish-brown. Stalk: Brown, usually white at apex; white mycelium at base (J. Solem, pers. comm.).
Where To Find
Habitat: Solitary or small groups on ground under hardwoods, especially oaks.
Seasonality Snapshot
Eating mushrooms can be dangerous. One should do so only with expert advice and great care. MBP accepts no liability for injury sustained in consuming fungi or other biodiversity. Use of media featured on Maryland Biodiversity Project is only permitted with express permission of the photographer.
A Tylopilus ferrugineus (fruiting body) in Howard Co., Maryland (8/17/2011).
View Record Details
Media by
Robert Solem.
Tylopilus ferrugineus in Caroline Co., Maryland (Date obscured). (c) Cindi Fitzgerald, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC).
View Record Details
Media by
cin579 via iNaturalist.
Tylopilus ferrugineus in Caroline Co., Maryland (Date obscured). (c) Cindi Fitzgerald, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC).
View Record Details
Media by
cin579 via iNaturalist.
A Tylopilus ferrugineus in Howard Co., Maryland (9/2/2011). Stalk and pores, including color change from bruising.
View Record Details
Media by
Joanne Solem.
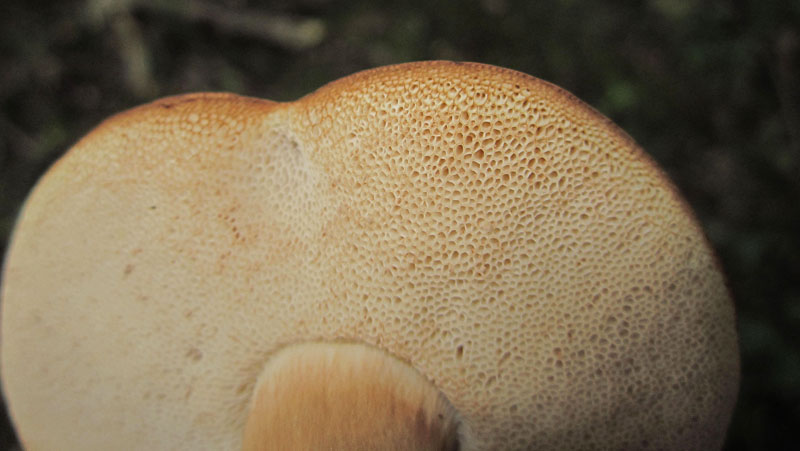
A Tylopilus ferrugineus (closeup of pores) in Howard Co., Maryland (7/10/2016).
View Record Details
Media by
Joanne Solem.
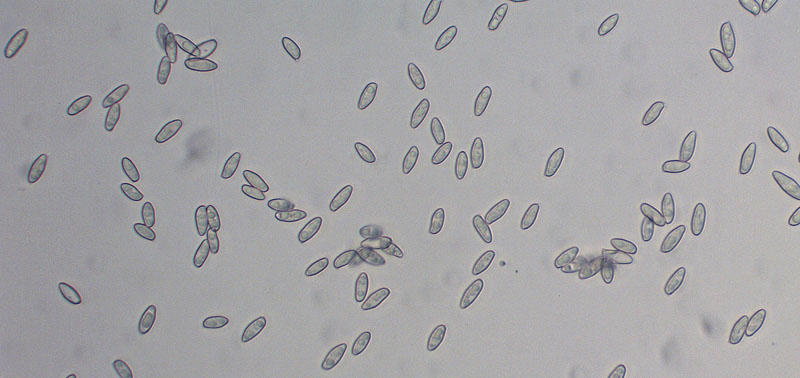
Tylopilus ferrugineus spores collected in Howard Co., Maryland (7/10/2016). Subfusiform, smooth; measured 10.3-12.3 X 4.2-4.8 microns.
View Record Details
Media by
Robert Solem.
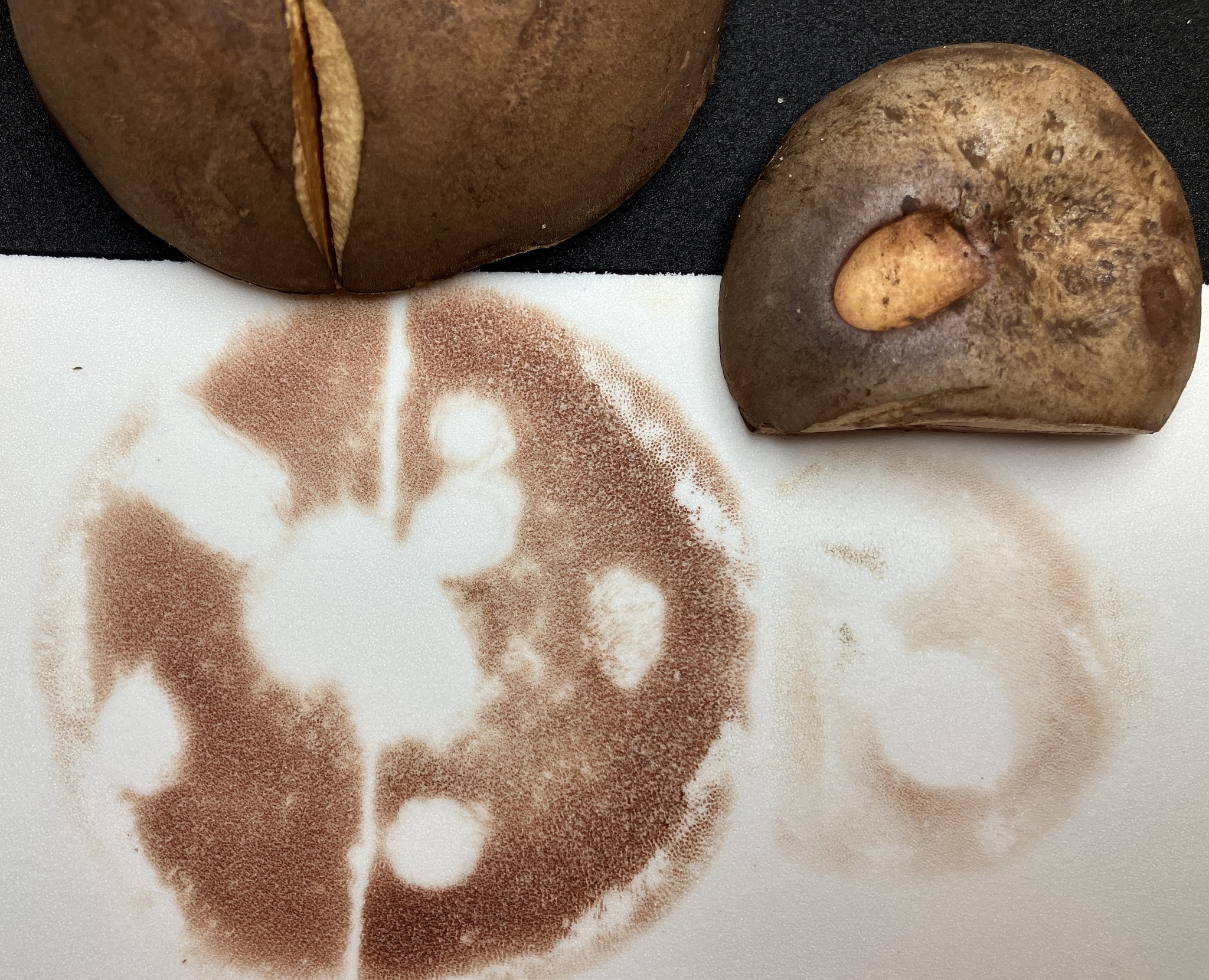
Spore print of Tylopilus ferrugineus in Caroline Co., Maryland (Date obscured). (c) Cindi Fitzgerald, some rights reserved (CC BY-NC).
View Record Details
Media by
cin579 via iNaturalist.
Source: Wikipedia
| Tylopilus ferrugineus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Basidiomycota |
| Class: | Agaricomycetes |
| Order: | Boletales |
| Family: | Boletaceae |
| Genus: | Tylopilus |
| Species: | T. ferrugineus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Tylopilus ferrugineus | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
|
Boletus ferrugineus Frost (1874) | |
Tylopilus ferrugineus is a bolete fungus in the family Boletaceae native to North America. Originally described by Charles Christopher Frost in 1874 as Boletus ferrugineus, it was placed in the genus Tylopilus by Rolf Singer in 1947.[2]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Tylopilus ferrugineus (Frost) Singer, The American Midland Naturalist, 37: 106, 1947". MycoBank. International Mycological Association. Retrieved 2013-05-24.
- ^ Singer R. (1947). "The Boletoideae of Florida. The Boletineae of Florida with notes on extralimital species III". The American Midland Naturalist. 37: 106. doi:10.2307/2421647. JSTOR 2421647.
External links
[edit] Media related to Tylopilus ferrugineus at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Tylopilus ferrugineus at Wikimedia Commons- Tylopilus ferrugineus in Index Fungorum