Map Snapshot


4 Records
Description
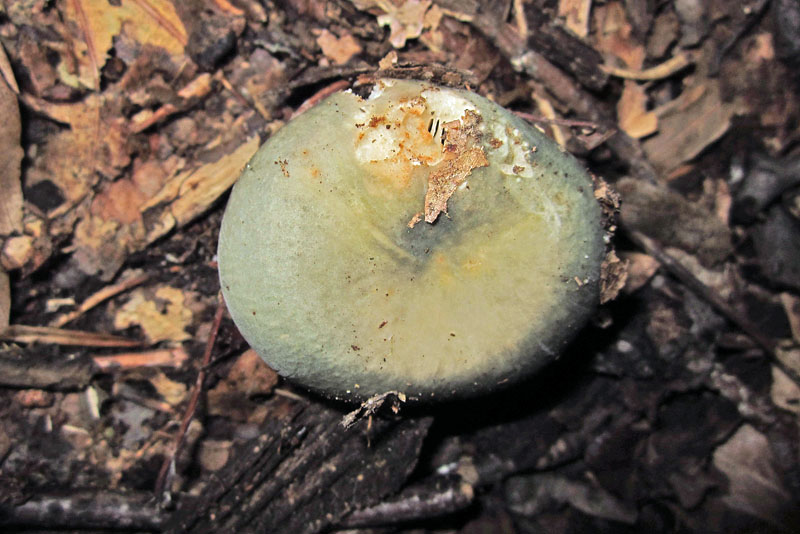
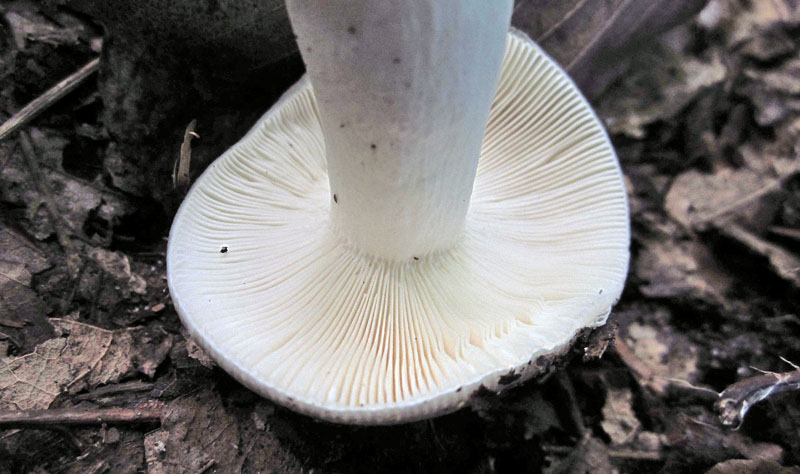
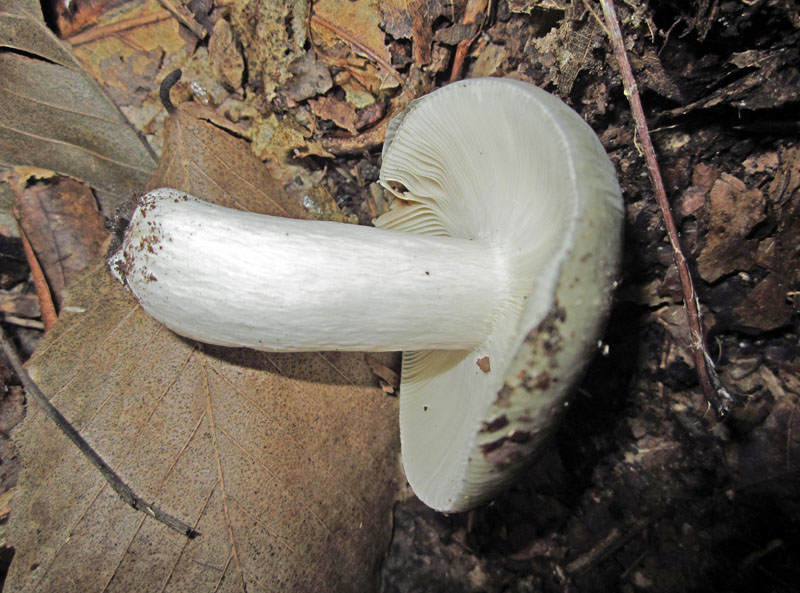
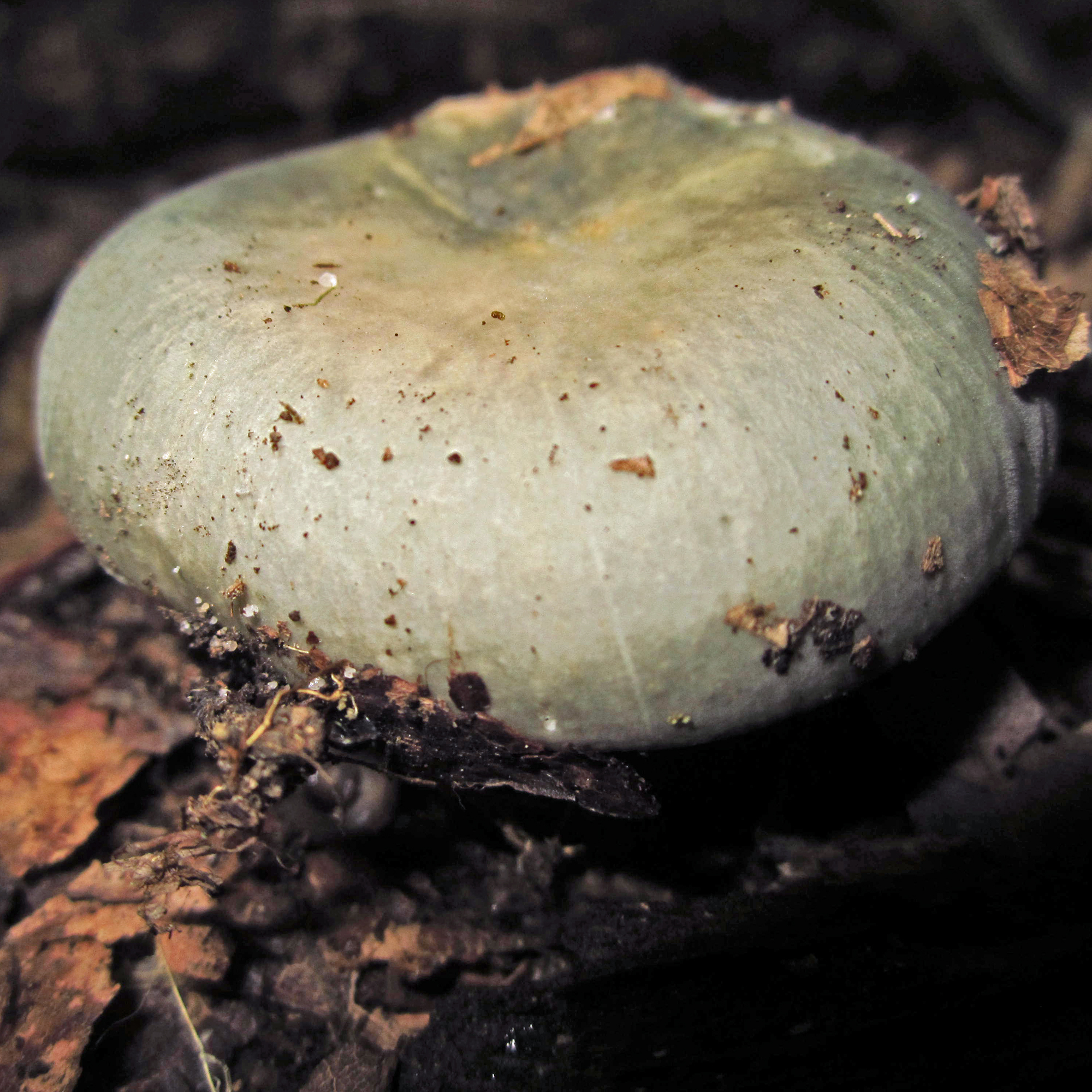
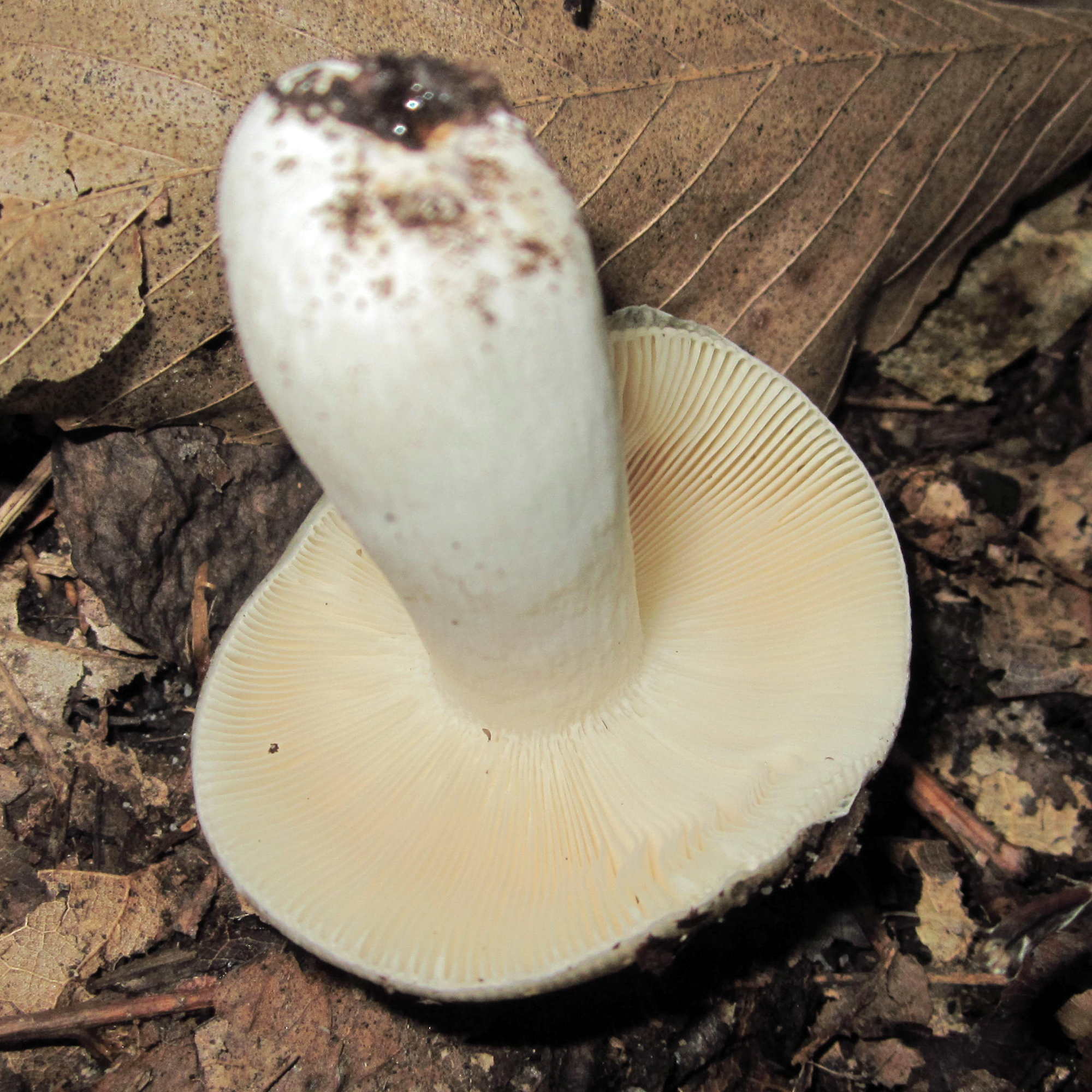
Cap: Olive-green (with some orange); convex (depressed in age); Gills: White, crowded, forked near stalk; Stalk: White, abrupt narrowing at base (J. Solem, pers. comm.).
Where To Find
Habitat: On ground in deciduous woods.
Seasonality Snapshot
Source: Wikipedia
| Russula heterophylla | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Basidiomycota |
| Class: | Agaricomycetes |
| Order: | Russulales |
| Family: | Russulaceae |
| Genus: | Russula |
| Species: | R. heterophylla
|
| Binomial name | |
| Russula heterophylla | |
| Russula heterophylla | |
|---|---|
| Gills on hymenium | |
| Cap is convex or flat | |
| Hymenium is adnexed | |
| Stipe is bare | |
| Spore print is white | |
| Edibility is edible | |
The edible wild mushroom Russula heterophylla, that has lately been given the common name of the greasy green brittlegill[1] is placed in the genus Russula, the members of which are mostly known as brittlegills. It is a variably colored mushroom, found in deciduous forests, and woods in Britain, Europe, and Scandinavia.[2] Appearing with broad-leaved trees in summer to early autumn, it usually has a greenish coloration.
Taxonomy
[edit]Noted and described by the South African-born mycologist Christian Hendrik Persoon as Agaricus lividus in 1801. It was placed in the Russula Genus by the Swedish mycologist, and botanist Elias Magnus Fries in 1838, with the epithet heterophylla. Despite many changes, by several mycologists over the years since then, it is this binomial that is currently recognised,[3] and is in use at present.
The variants Russula heterophylla var. chlora Gillet 1876, and Russula heterophylla var. virginea (Cooke and Massee) A.Pearson & Dennis, have been given species status as Russula violeipes, and Russula virginea respectively.
Description
[edit]The cap is 5 to 10 centimetres (2.0 to 3.9 in) in diameter. It is known to vary in colour, and can be various shades of green, brown, or ochre. It is initially round, flattening with age, and laters develops a depression. The white stem is firm, browning, and gives a salmon reaction when rubbed with ferrous sulfate. The gills are adnexed, and white giving a spore print of the same colour.[1]
Microscopic characteristics
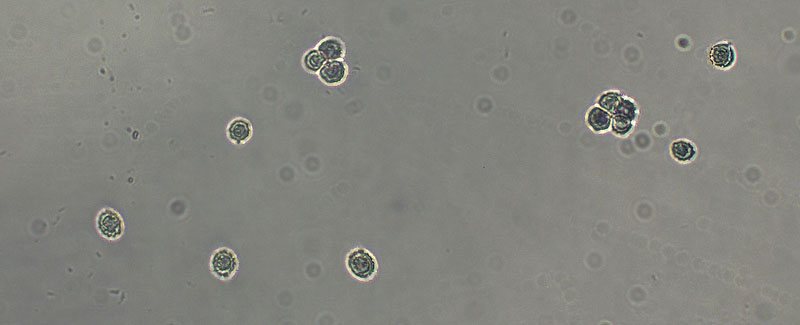
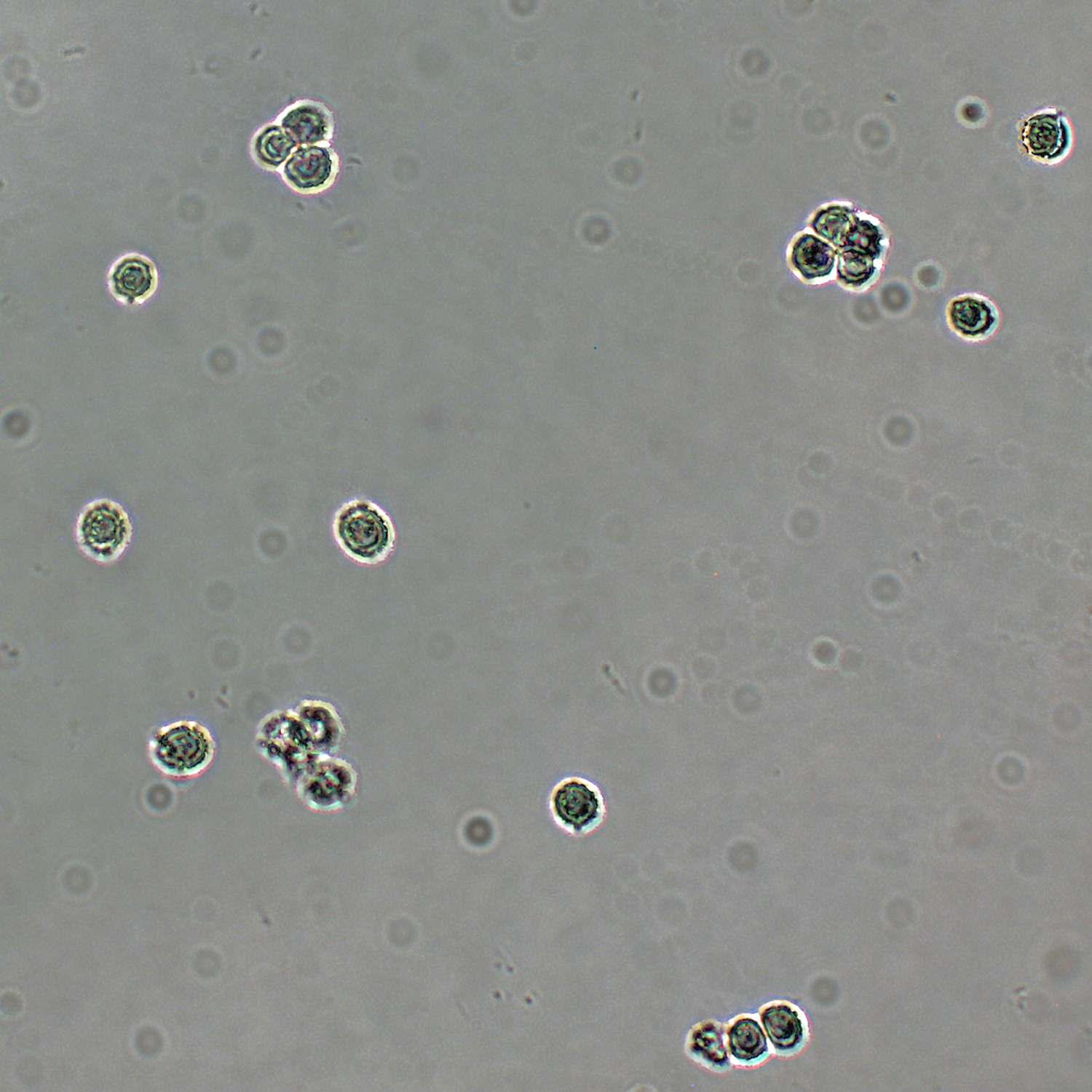
[edit]The spores are the smallest in the genus, and are 5–7 by 4–6 μm, spherical to elliptical, or pear shaped; warts 0.2–0.6 μm high, mostly isolated, but occasionally two or three joined together, or connected by a line.[1]
Similar species
[edit]Green forms of Russula cyanoxantha can be distinguished, because they give a greenish reaction, or no reaction when rubbed with iron salts such as ferrous sulfate, and have the flexible, 'greasy' feeling gills characteristic of that species.
Russula virescens (Schaeff.) Fr., has a cracked or fragmented cap surface.
Russula aeruginea Fr., grows with Birch.
Russula langei Bon, also has a green reaction to ferrous sulphate, and smells like shellfish, with flesh that stains orange-brown.
Distribution and habitat
[edit]Russula heterophylla appears in summer to early autumn, usually growing in small groups. It is occasional in Britain, Europe, and Scandinavia.[2] It grows with several species of broad-leaved trees, on the roots of which it is ectomycorrhizal.
Edibility
[edit]This mushroom is edible[4] and good, although care must be taken as it is very like the deadly Amanita phalloides (death cap) when young. It is also prone to slug attacks.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c Roger Phillips (2006). Mushrooms. Pan MacMillan. ISBN 978-0-330-44237-4.
- ^ a b Regis Courtecuisse and Bernard Duhem (1995). Mushrooms and Toadstools of Britain and Europe. Harper Collins. ISBN 978-0-00-220025-7.
- ^ "Species Fungorum Current Name: Russula heterophylla (Fr.)". Archived from the original on 2007-11-08. Retrieved 2009-04-20.
- ^ Phillips, Roger (2010) [2005]. Mushrooms and Other Fungi of North America. Buffalo, NY: Firefly Books. p. 141. ISBN 978-1-55407-651-2.
External links
[edit]