Map Snapshot




8 Records
Status
Found solitary or in small groups in deciduous or mixed forests.
Description
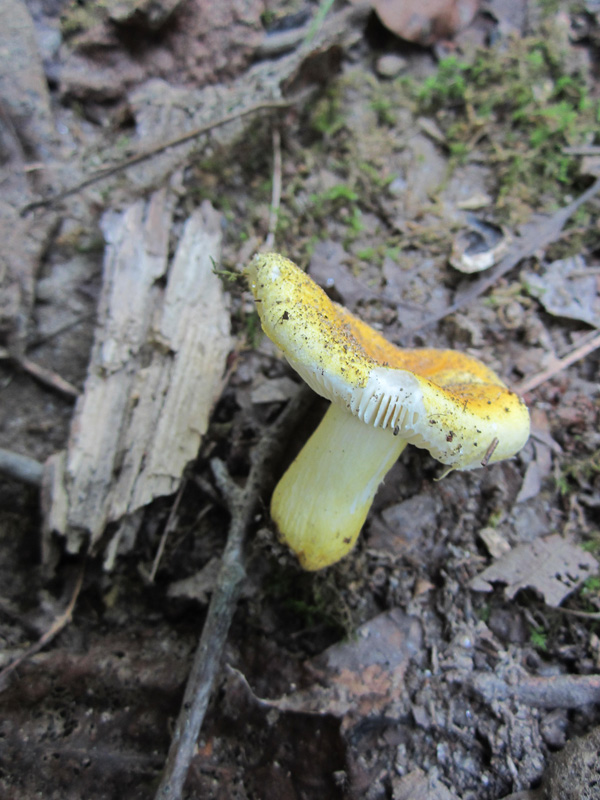
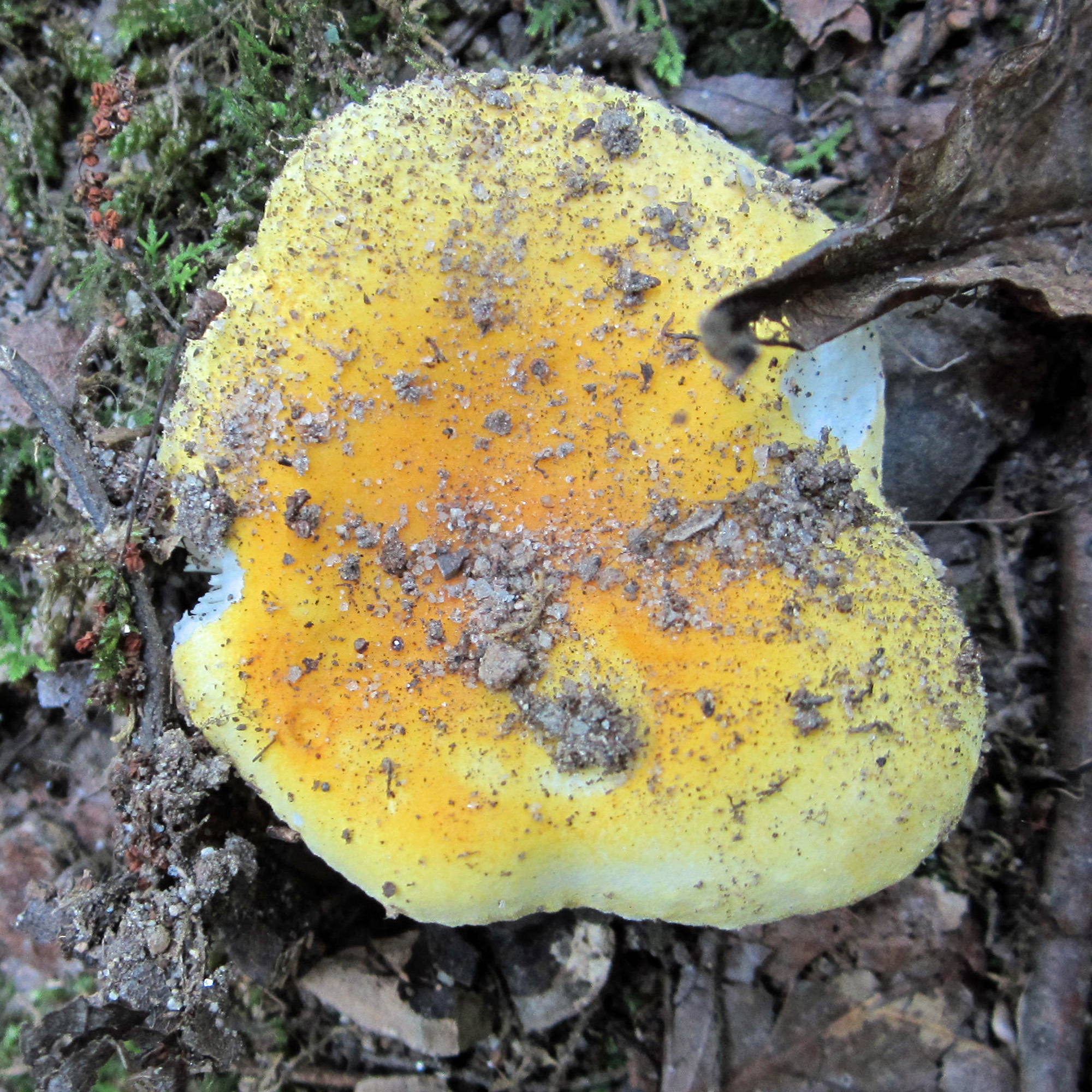
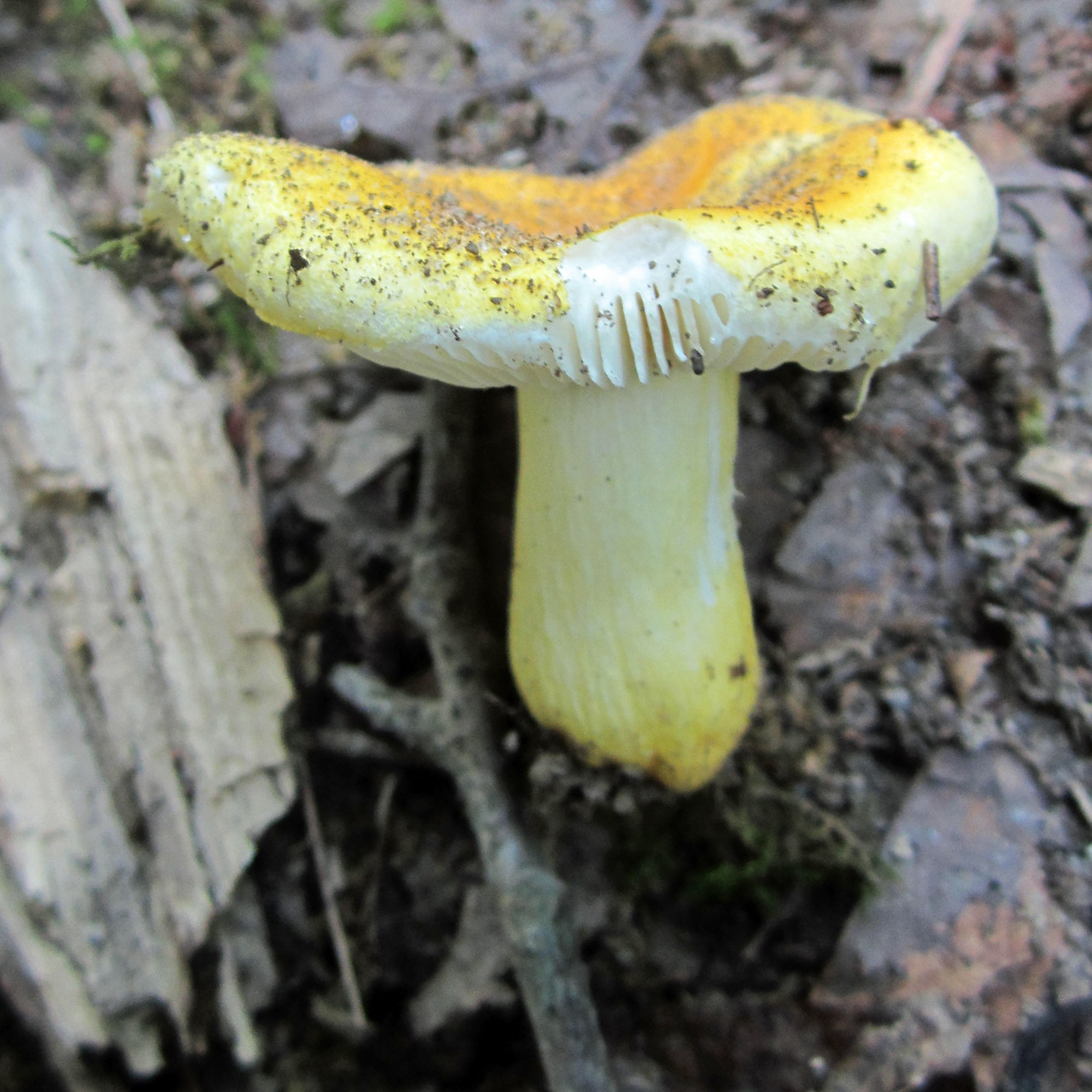
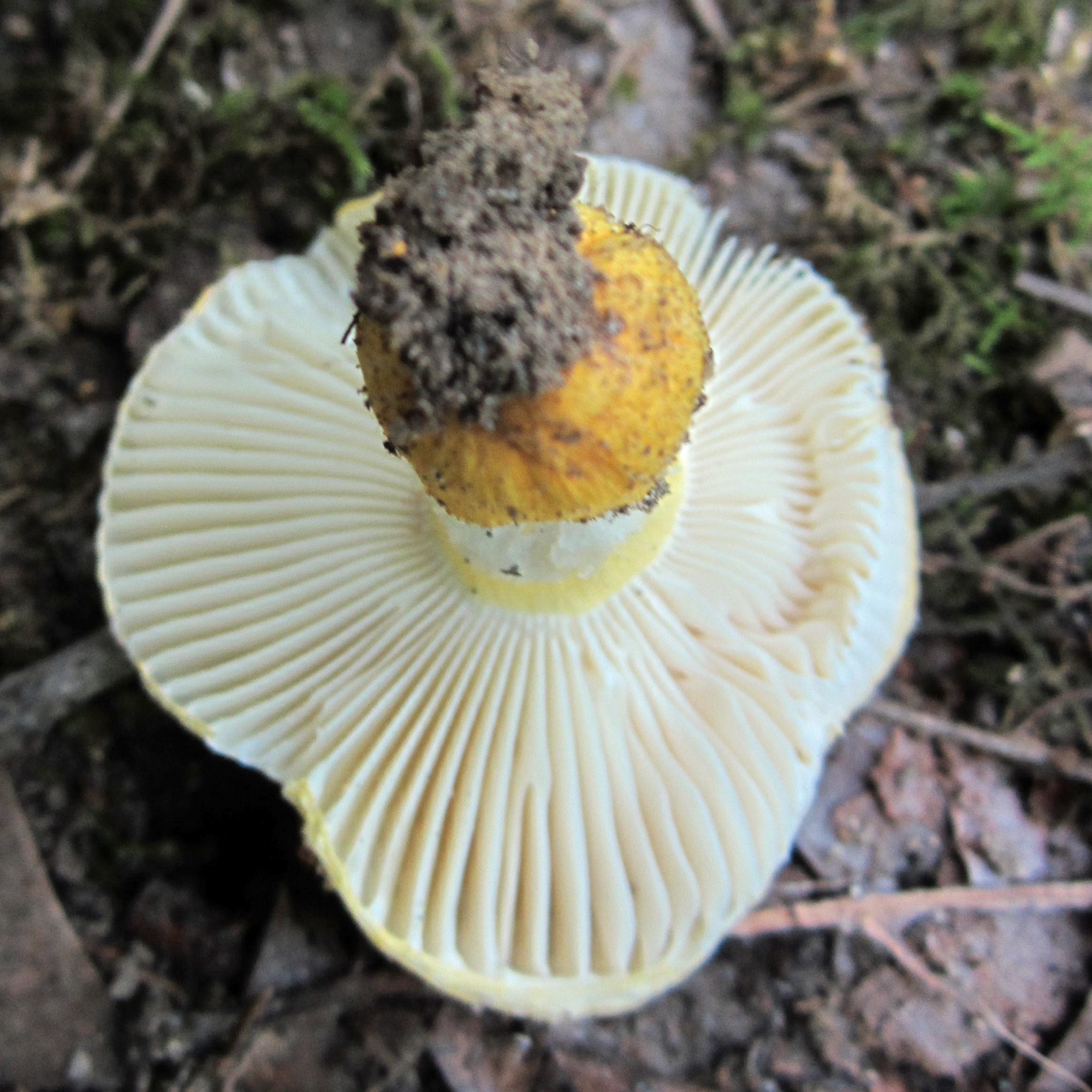
Cap: Yellow, disc brighter; velvety; convex (depressed center in age); flesh white. Gills: White to pale yellow; attached, crowded, may be forked near stem; bruise brown. Stalk: Like cap or paler. (J. Solem, pers. comm.)
Seasonality Snapshot
Source: Wikipedia
| Russula flavida | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Basidiomycota |
| Class: | Agaricomycetes |
| Order: | Russulales |
| Family: | Russulaceae |
| Genus: | Russula |
| Species: | R. flavida
|
| Binomial name | |
| Russula flavida Frost 1880
| |
| Synonyms[1] | |
|
Russula mariae var. flavida (Frost) Singer 1940 | |
Russula flavida is a member of the large mushroom genus Russula.
Taxonomy
[edit]It was described in 1880 by American botanist and mycologist Charles Christopher Frost.[2]
A variant, R. flavida var. dhakurianus, was described in 2005 from Kumaon in the Indian Himalaya.[3]
Description
[edit]Russula flavida has a bright yellow to orange yellow cap and stipe and white gills.[4] The cap is convex with a central depression and 2.5–8 centimetres (1–3+1⁄4 in) wide.[5] The stem is 3–7 cm (1+1⁄4–2+3⁄4 in) long and 1–2 cm (1⁄2–3⁄4 in) thick.[5] The spore print is yellowish-cream.[5]
Distribution and habitat
[edit]From June to September, it appears in North America, from eastern Texas to New Hampshire.[5] It is also found in parts of Asia.[6]
It usually surfaces on the ground under hardwood trees.[5]
Uses
[edit]The species is edible[7] and contains the pigment russulaflavidin and a related compound.[8]
References
[edit]- ^ "MycoBank: Russula flavida". Retrieved 2014-12-24.
- ^ Peck (1879). "Report of the Botanist (1878)". Annual Report on the New York State Museum of Natural History. 32: 17–72.
- ^ Das K, Sharma JR (2005). Russulaceae of Kumaon Himalaya. p. 203.
- ^ Bills GF, Miller OK Jr (1984). "Southern Appalachian Russulas. I". Mycologia. 76 (6): 975–1002. doi:10.2307/3793015. JSTOR 3793015.
- ^ a b c d e Audubon (2023). Mushrooms of North America. Knopf. p. 199. ISBN 978-0-593-31998-7.
- ^ "Russulales News: Russula flavida". Retrieved 2014-12-24.
- ^ Phillips, Roger (2010) [2005]. Mushrooms and Other Fungi of North America. Buffalo, NY: Firefly Books. p. 144. ISBN 978-1-55407-651-2.
- ^ Fröde R, Bröckelmann M, Steffan B, Steglich W, Marumoto R (1995). "A novel type of triterpenoid quinone methide pigment from the toadstool Russula flavida (Agaricales)". Tetrahedron. 51 (9): 2553–2560. doi:10.1016/0040-4020(95)00012-W.
External links
[edit]Russula flavida in Index Fungorum Russula flavida in MycoBank.