Map Snapshot










67 Records
Status
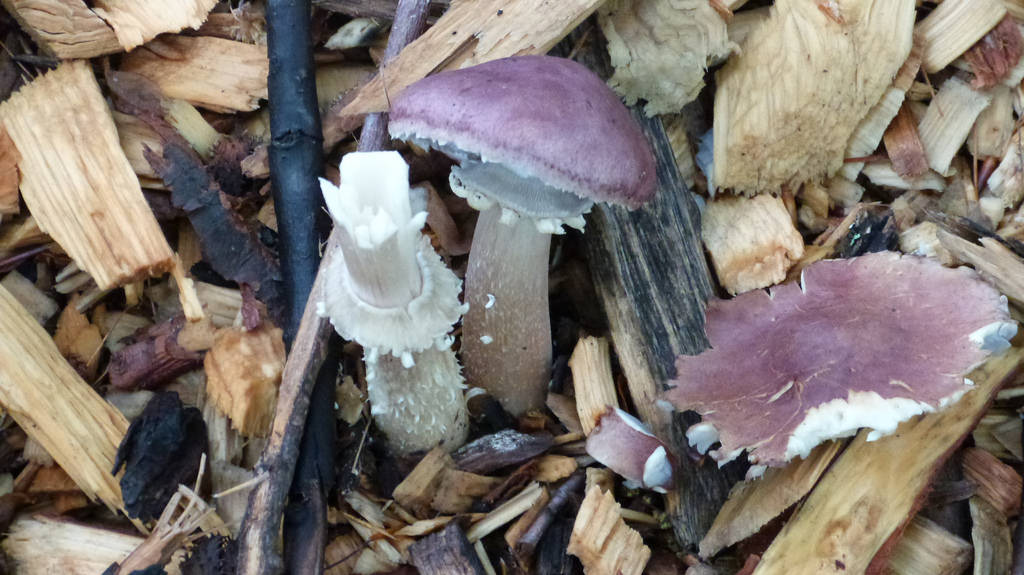
Found scattered or in groups on wood chips, mulch, straw, and lawns.
Description
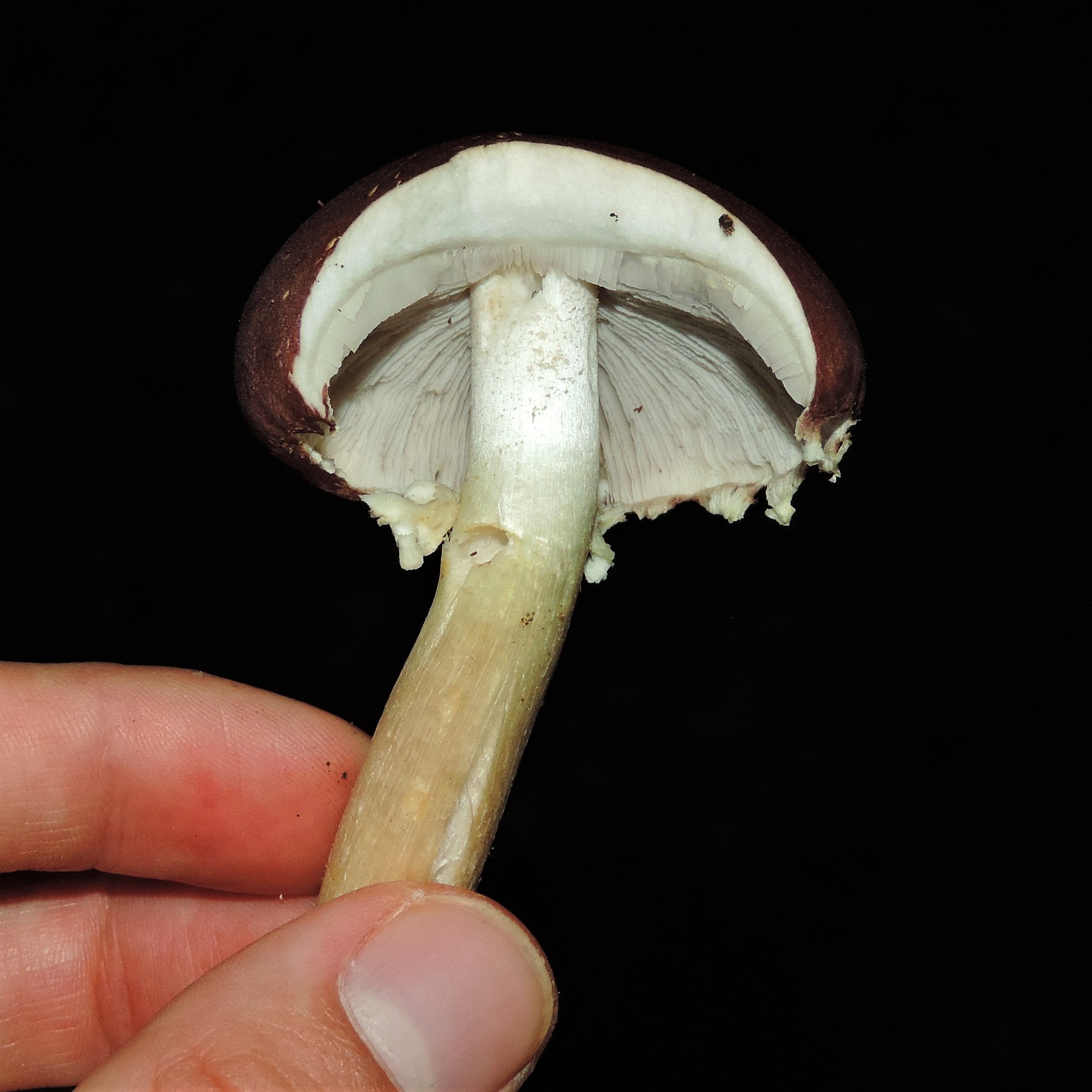
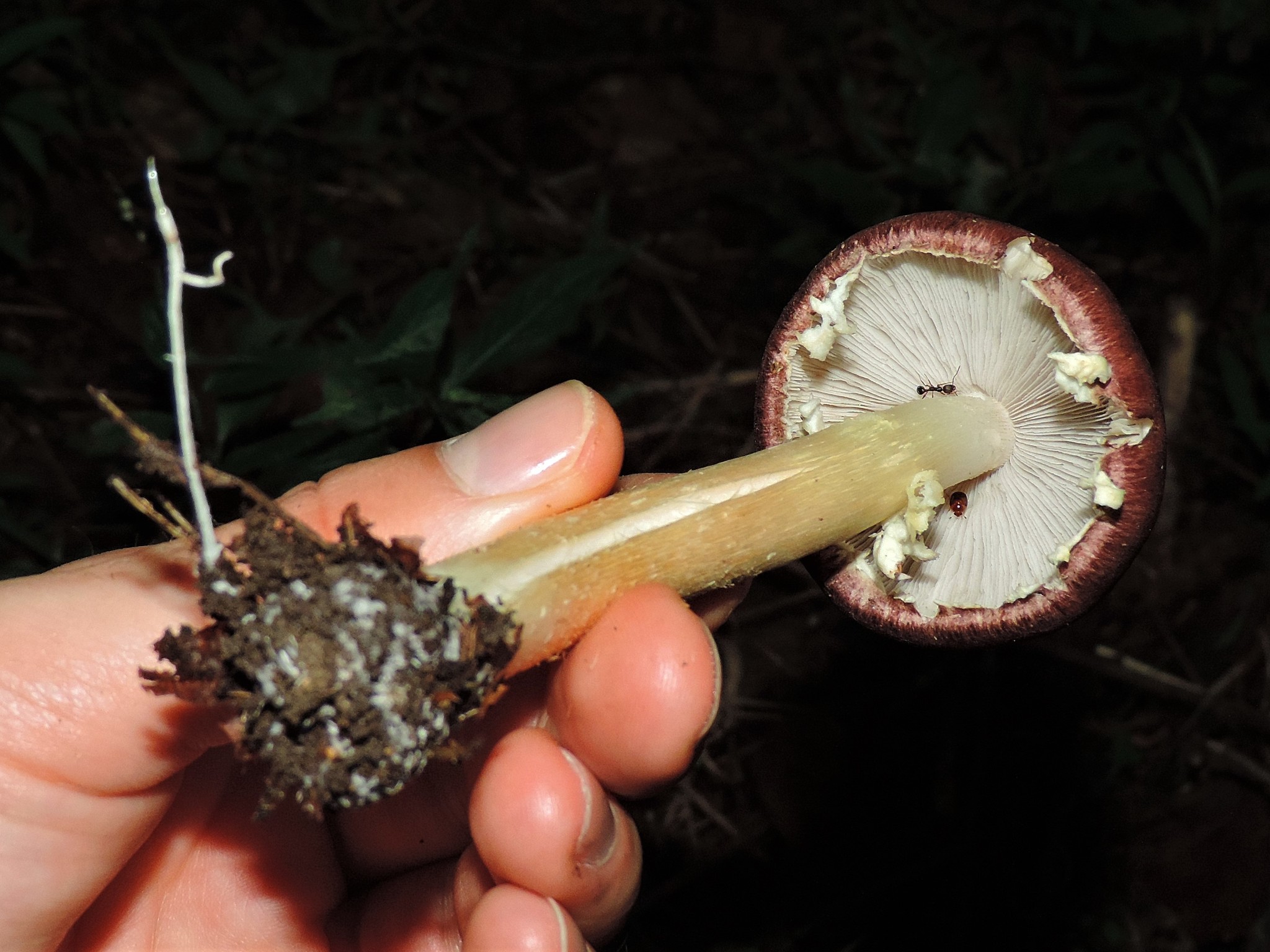
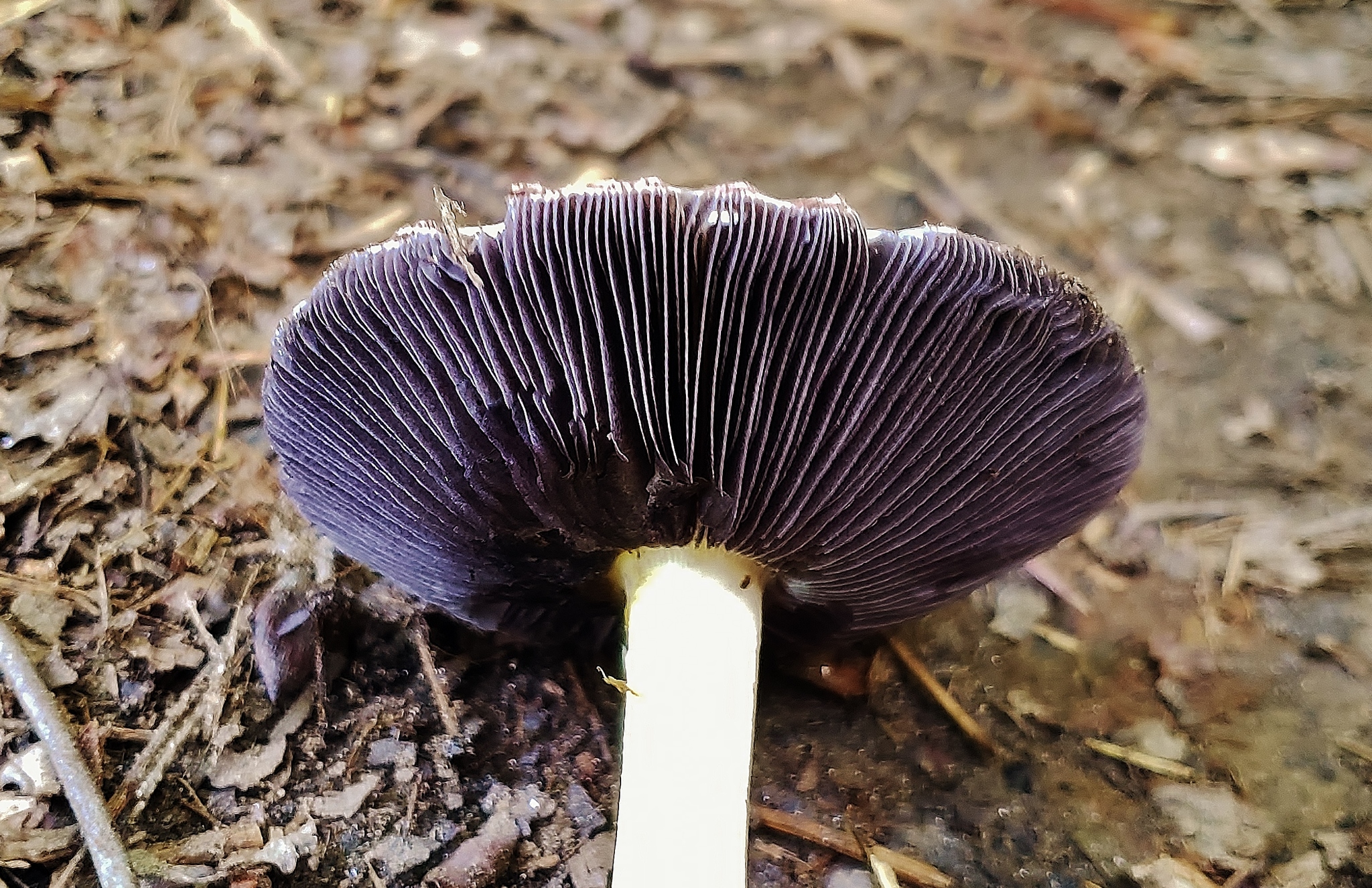
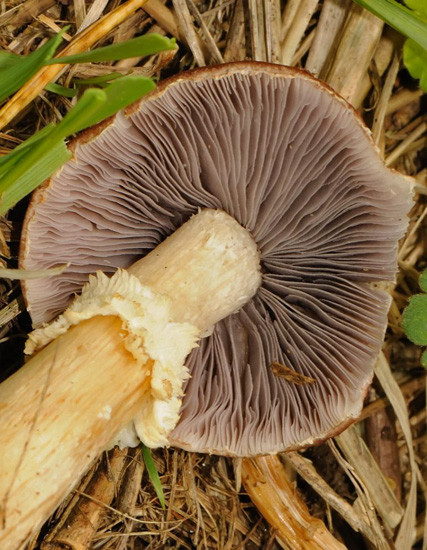
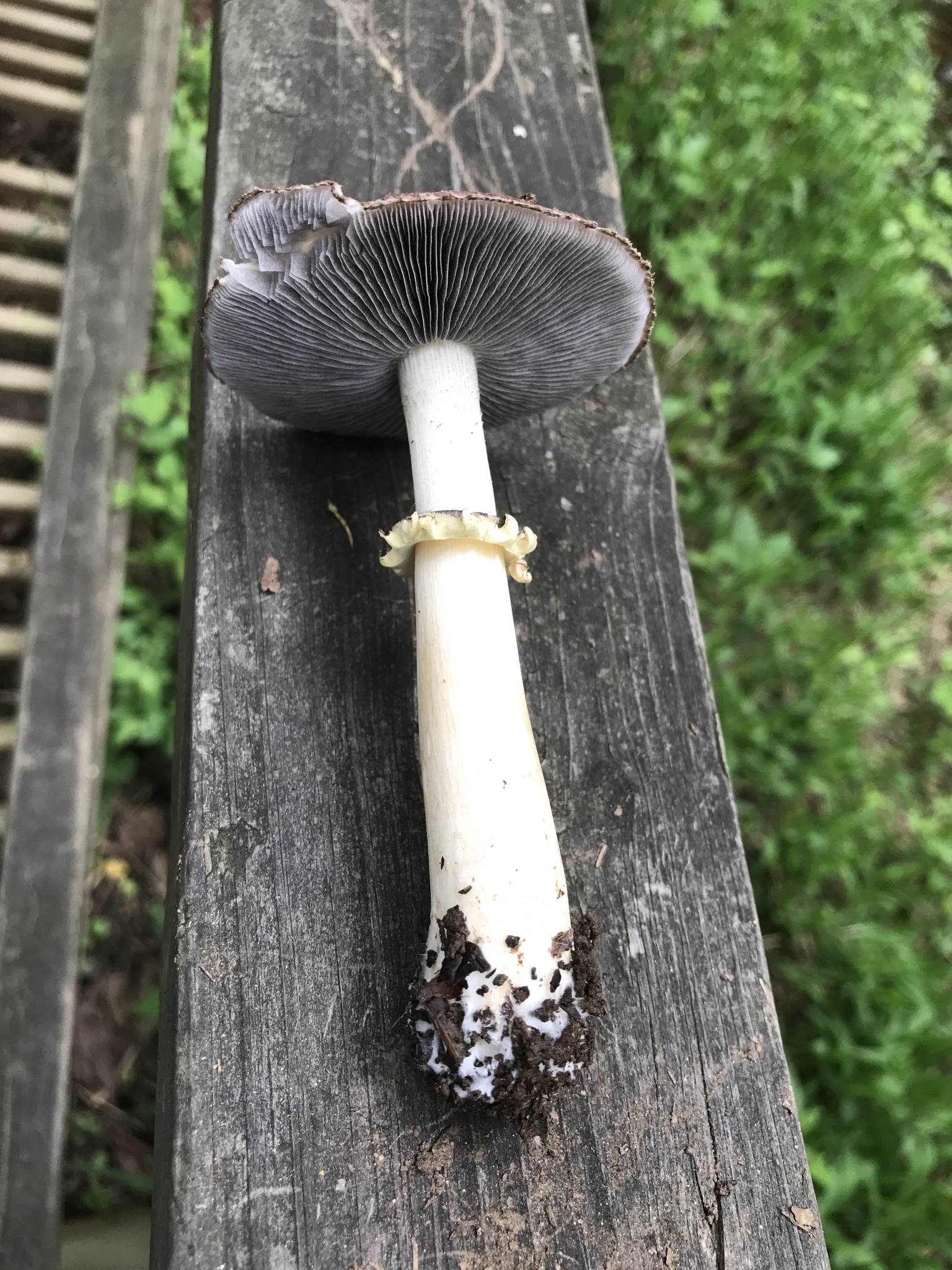
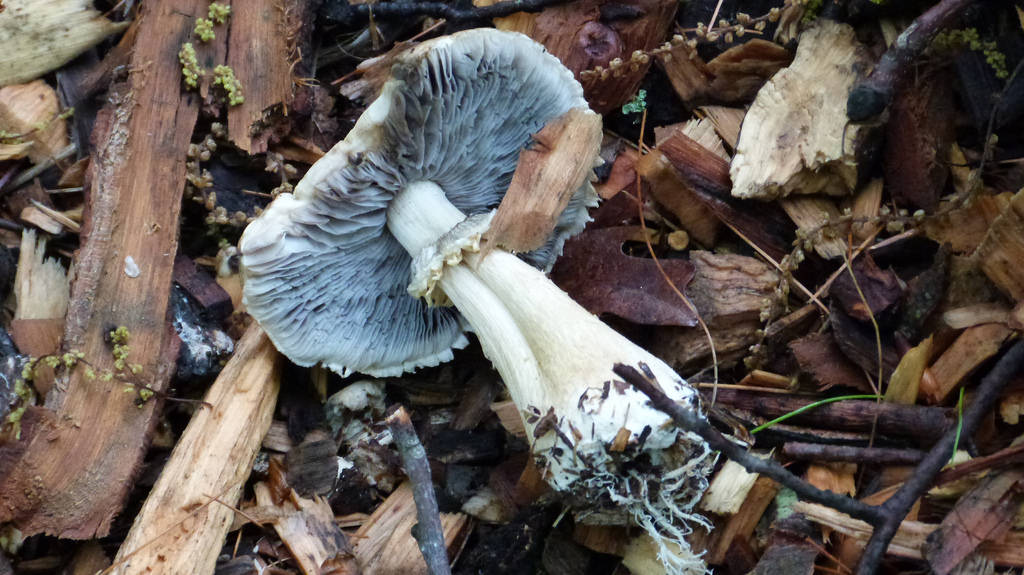
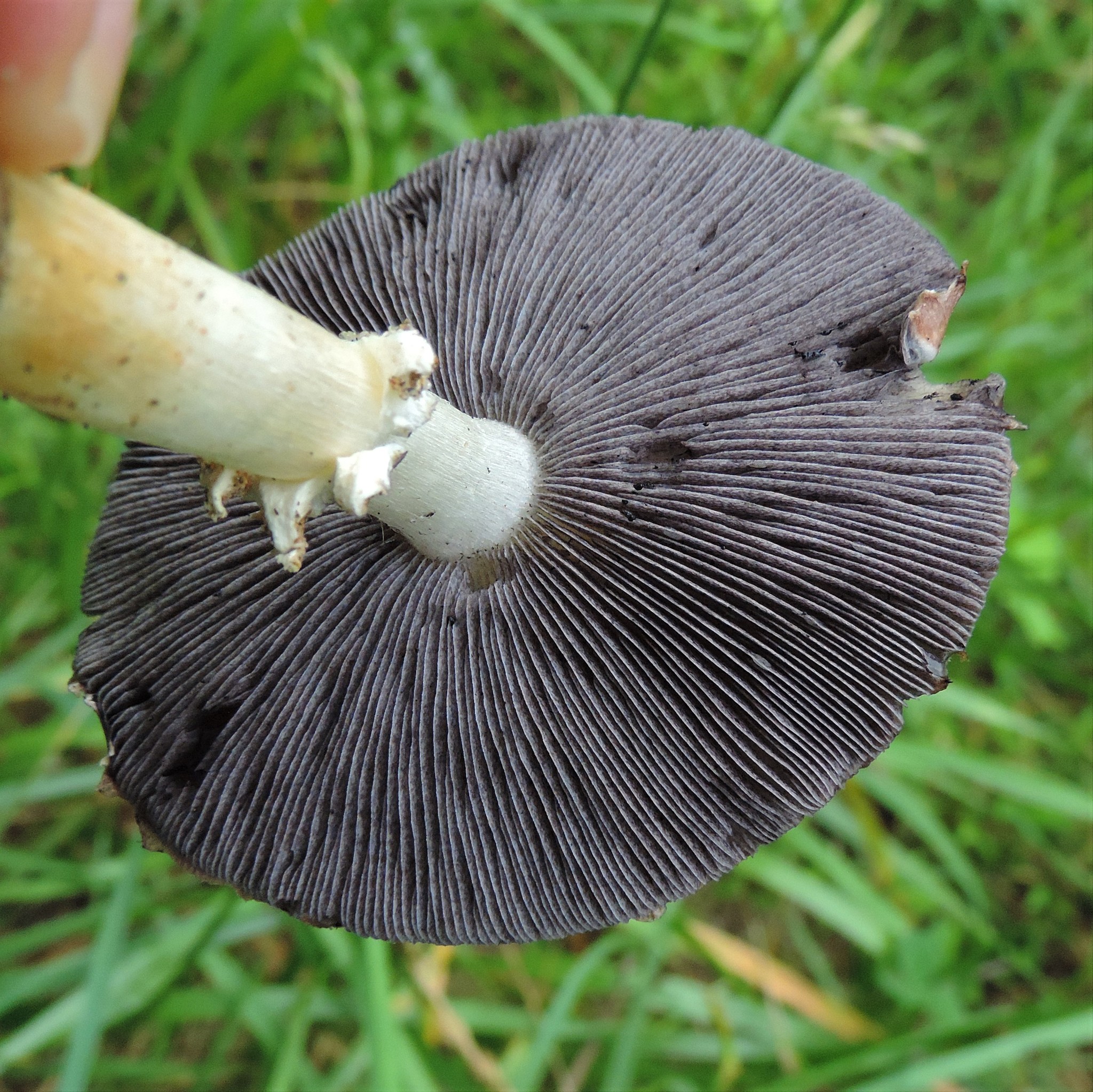
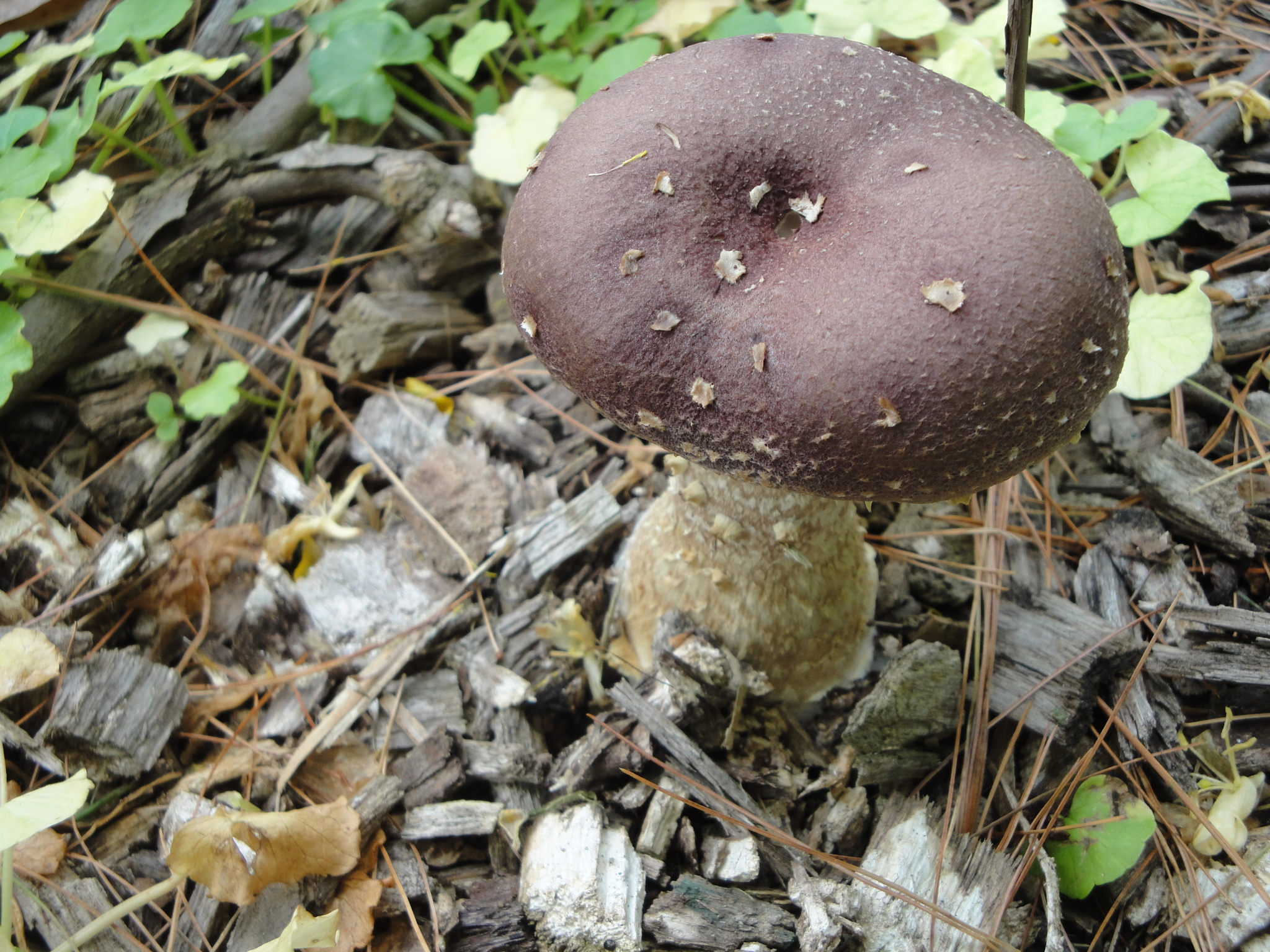
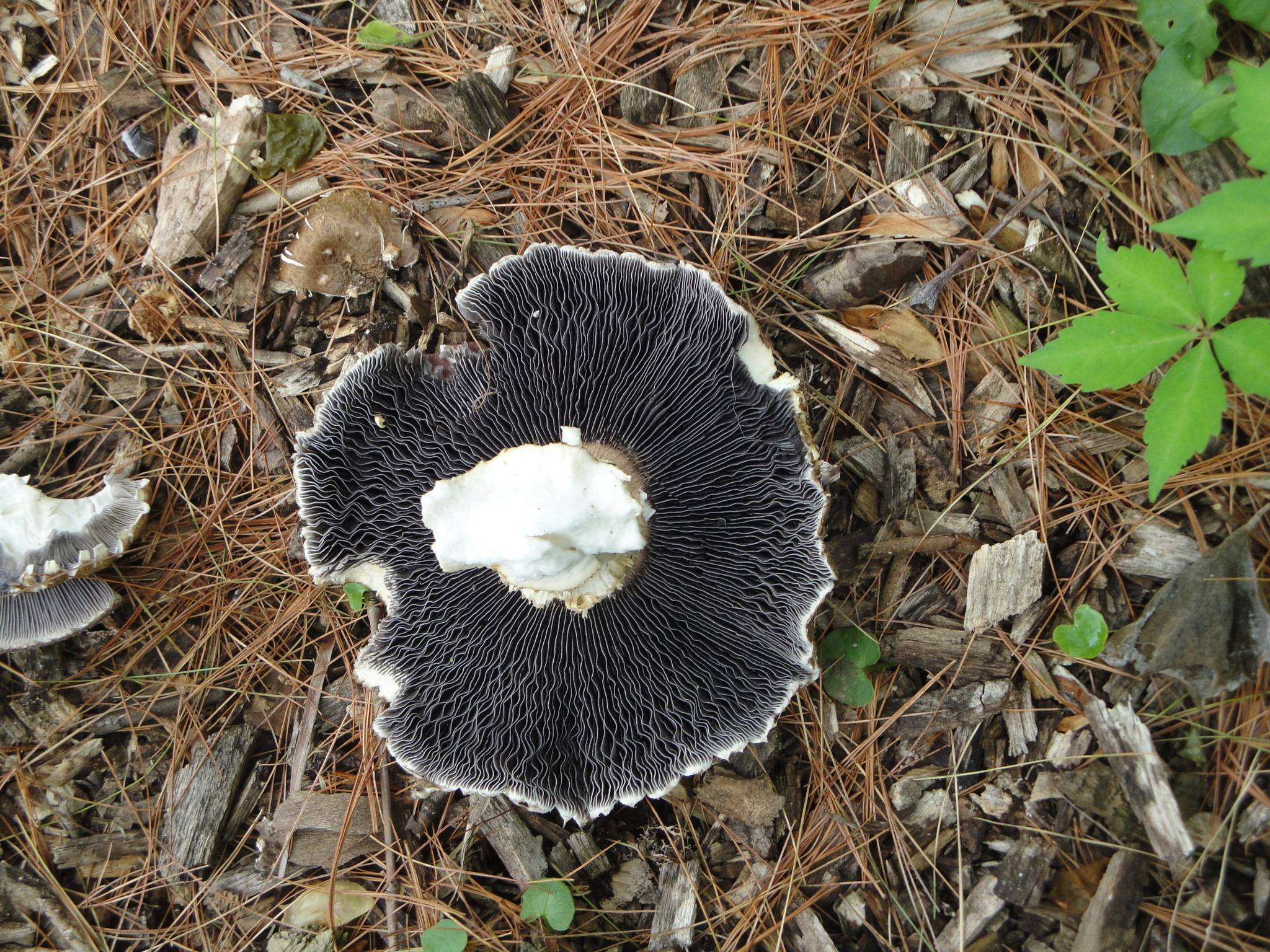
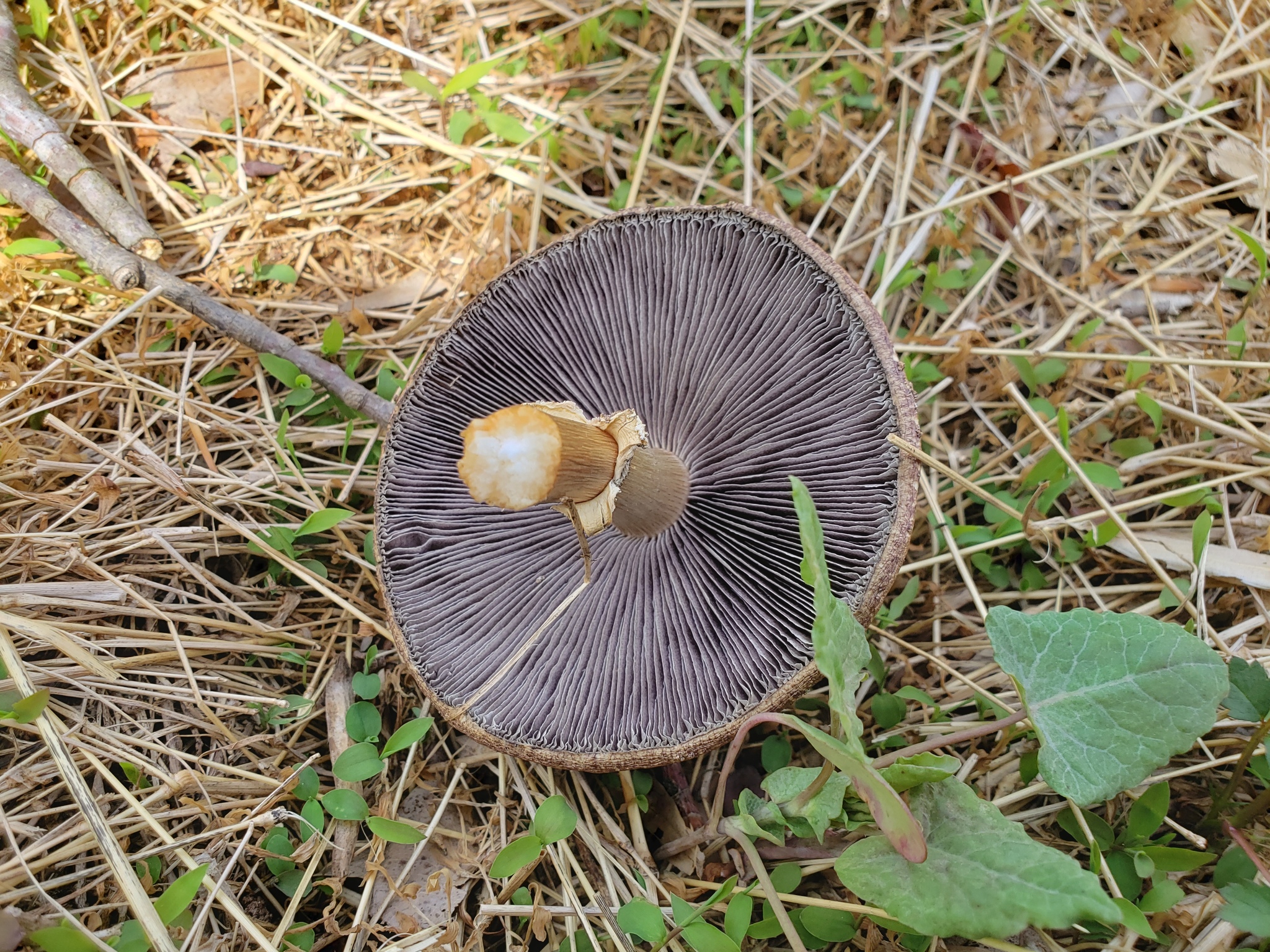
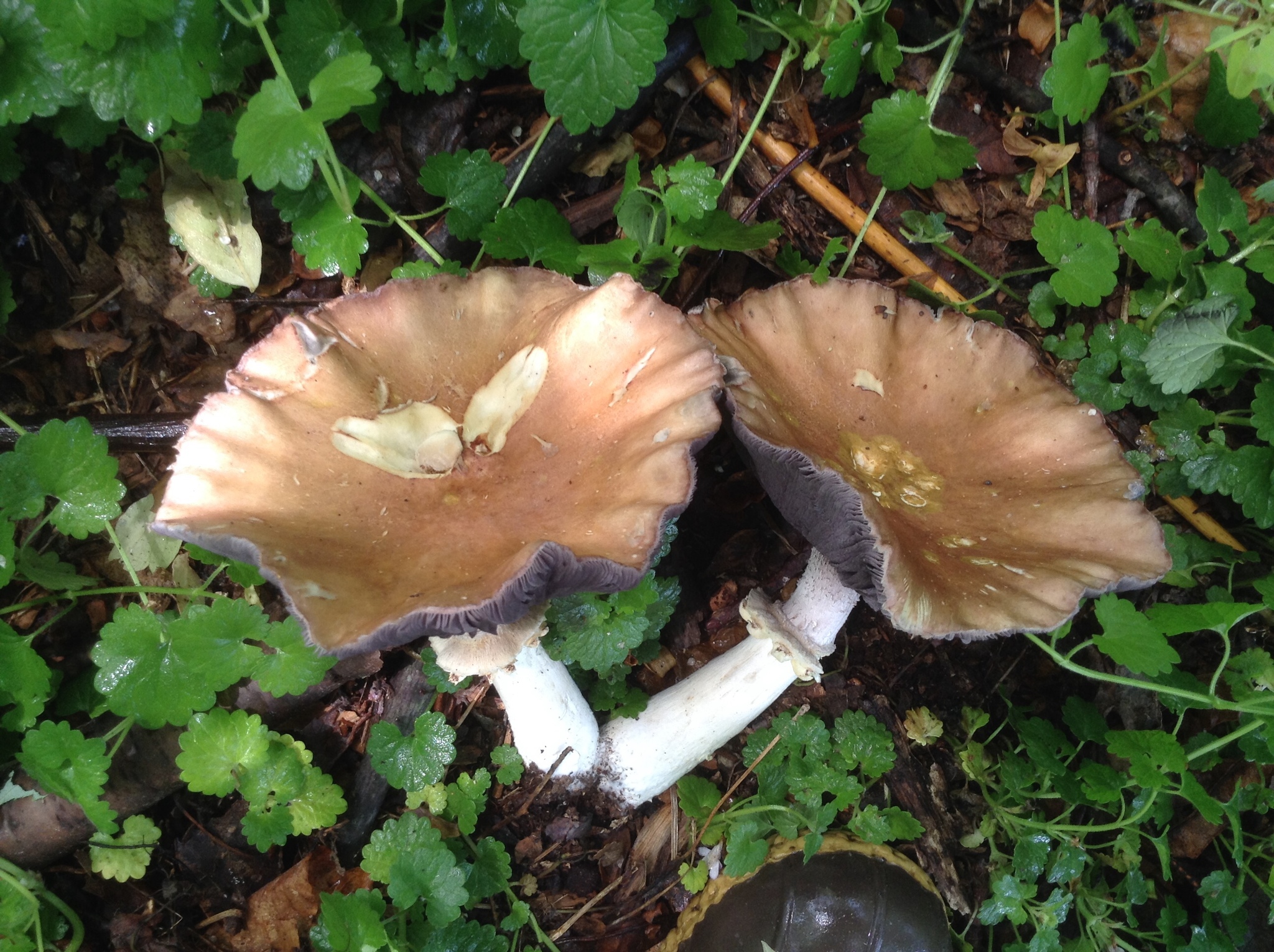
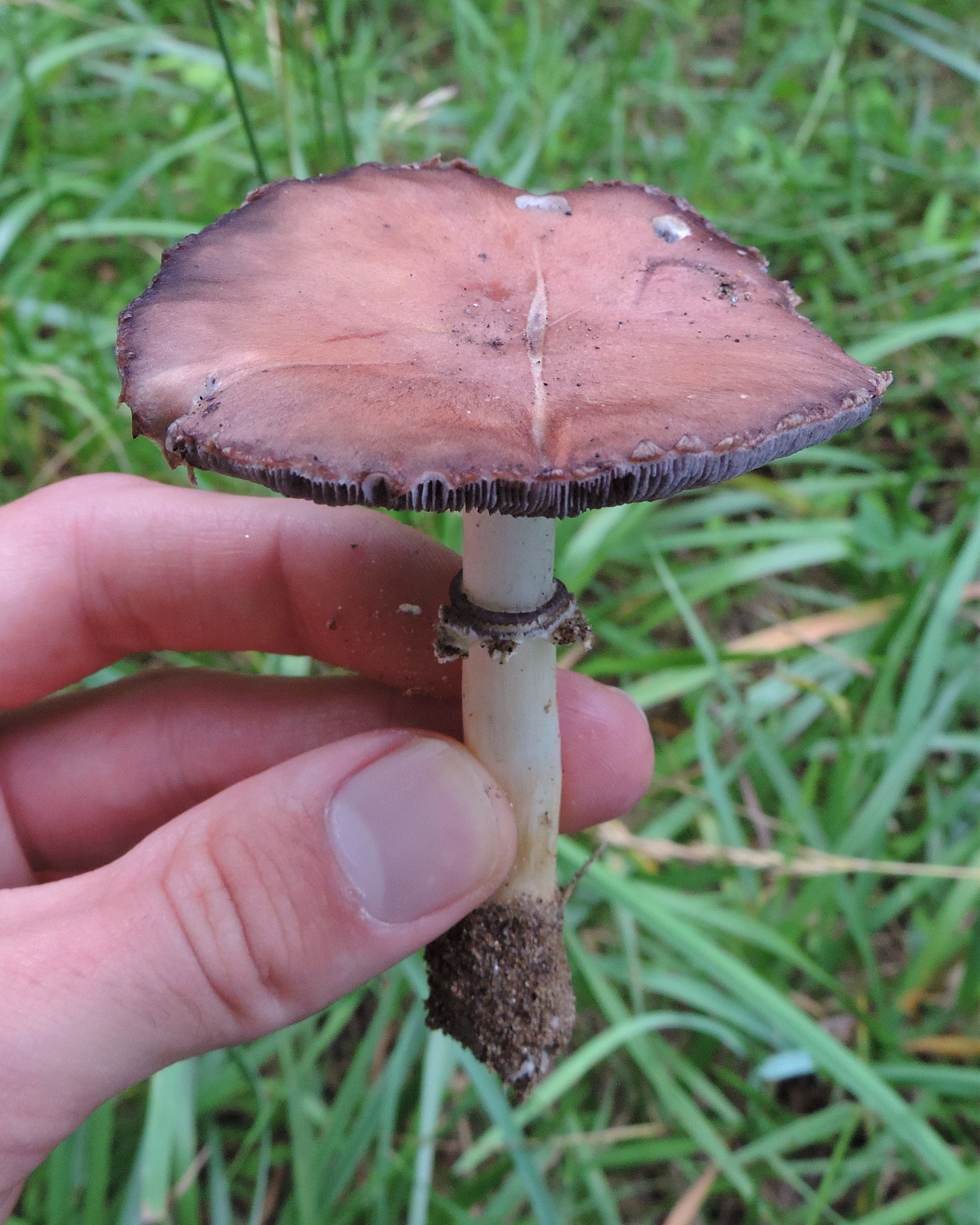
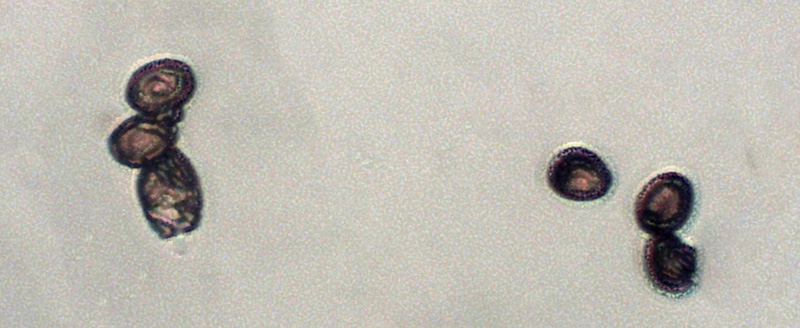
Cap: Reddish-purple to tan (in age); bell-shaped to flat; smooth; dry; flesh thick, white. Gills: White, soon becoming purplish-gray, then purplish-black; crowded. Stalk: White staining yellow/brown in age; fibrous; persistent thick cottony ring with segmented underside and segmented/grooved upper surface (J. Solem, pers. comm.).
Seasonality Snapshot
Source: Wikipedia
| Stropharia rugosoannulata | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Basidiomycota |
| Class: | Agaricomycetes |
| Order: | Agaricales |
| Family: | Strophariaceae |
| Genus: | Stropharia |
| Species: | S. rugosoannulata
|
| Binomial name | |
| Stropharia rugosoannulata | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
|
Geophila rugosoannulata (Farl. ex Murrill) Kühner & Romagn. (1953) | |
| Stropharia rugosoannulata | |
|---|---|
| Gills on hymenium | |
| Cap is convex or flat | |
| Hymenium is adnate | |
| Stipe has a ring | |
| Spore print is purple-brown | |
| Ecology is saprotrophic | |
| Edibility is choice | |
Stropharia rugosoannulata, commonly known as the wine cap stropharia, "garden giant", burgundy mushroom, king stropharia, or wine-red stropharia,[2] is a species of agaric mushroom in the family Strophariaceae native to Europe and North America. Unlike many other members of the genus Stropharia, it is regarded as a choice edible[3] and is commercially cultivated.
Description
[edit]The king stropharia can grow to 20 centimetres (8 inches) high with a reddish-brown convex to flattening cap up to 30 cm (12 in) across,[4] the size leading to another colloquial name godzilla mushroom.[5] The gills are initially pale, then grey, and finally dark purple-brown in colour. The firm flesh is white, as is the tall stem which bears a wrinkled ring. This is the origin of the specific epithet which means "wrinkled-ringed".[6]
Distribution and habitat
[edit]The species is found on wood chips across North America in summer and autumn. It is also found in Europe, and has been introduced to Australia and New Zealand.
Ecology
[edit]In Paul Stamets' book Mycelium Running, a study done by Christiane Pischl showed that the king stropharia makes an excellent garden companion to corn. The fungus also has a European history of being grown with corn.
A 2006 study, published in the journal Applied and Environmental Microbiology, found the king stropharia to have the ability to attack the nematode Panagrellus redivivus; the fungus produces unique spiny cells called acanthocytes which are able to immobilise and digest the nematodes.[7]
Uses
[edit]Described as very tasty by some authors, the fungus is easily cultivated on a medium similar to that on which it grows naturally. Antonio Carluccio recommends sautéeing them in butter or grilling them.[5]
References
[edit]- ^ "Stropharia rugosoannulata Farl. ex Murrill 1922". MycoBank. International Mycological Association. Retrieved 2011-09-11.
- ^ Arora, David (1986). Mushrooms demystified: a comprehensive guide to the fleshy fungi (Second ed.). Berkeley: Ten Speed Press. ISBN 978-0-89815-169-5.
- ^ Phillips, Roger (2010). Mushrooms and Other Fungi of North America. Buffalo, NY: Firefly Books. p. 229. ISBN 978-1-55407-651-2.
- ^ Sisson, Liv; Vigus, Paula (2023). Fungi of Aotearoa: a curious forager's field guide. Auckland, New Zealand: Penguin Books. p. 138. ISBN 978-1-76104-787-9. OCLC 1372569849.
- ^ a b Carluccio A (2003). The Complete Mushroom Book. Quadrille. ISBN 1-84400-040-0.
- ^ Pacioni G (1981). Simon & Schusters Guide to Mushrooms. Simon & Schuster. ISBN 0-671-42849-7.
- ^ Hong Luo; Xuan Li; Guohong Li; Yanbo Pan & Keqin Zhang (2006). "Acanthocytes of Stropharia rugosoannulata Function as a Nematode-Attacking Device". Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72 (4): 2982–7. Bibcode:2006ApEnM..72.2982L. doi:10.1128/AEM.72.4.2982-2987.2006. PMC 1449000. PMID 16598005.
Further reading
[edit]- Zadrazil, Frantisek and Joachim Schliemann: "Ein Beitrag zur Ökologie und Anbautechnik von Stropharia rugosoannulata (Farlow ex Murr.)" in: Der Champignon Nr.163, March 1975