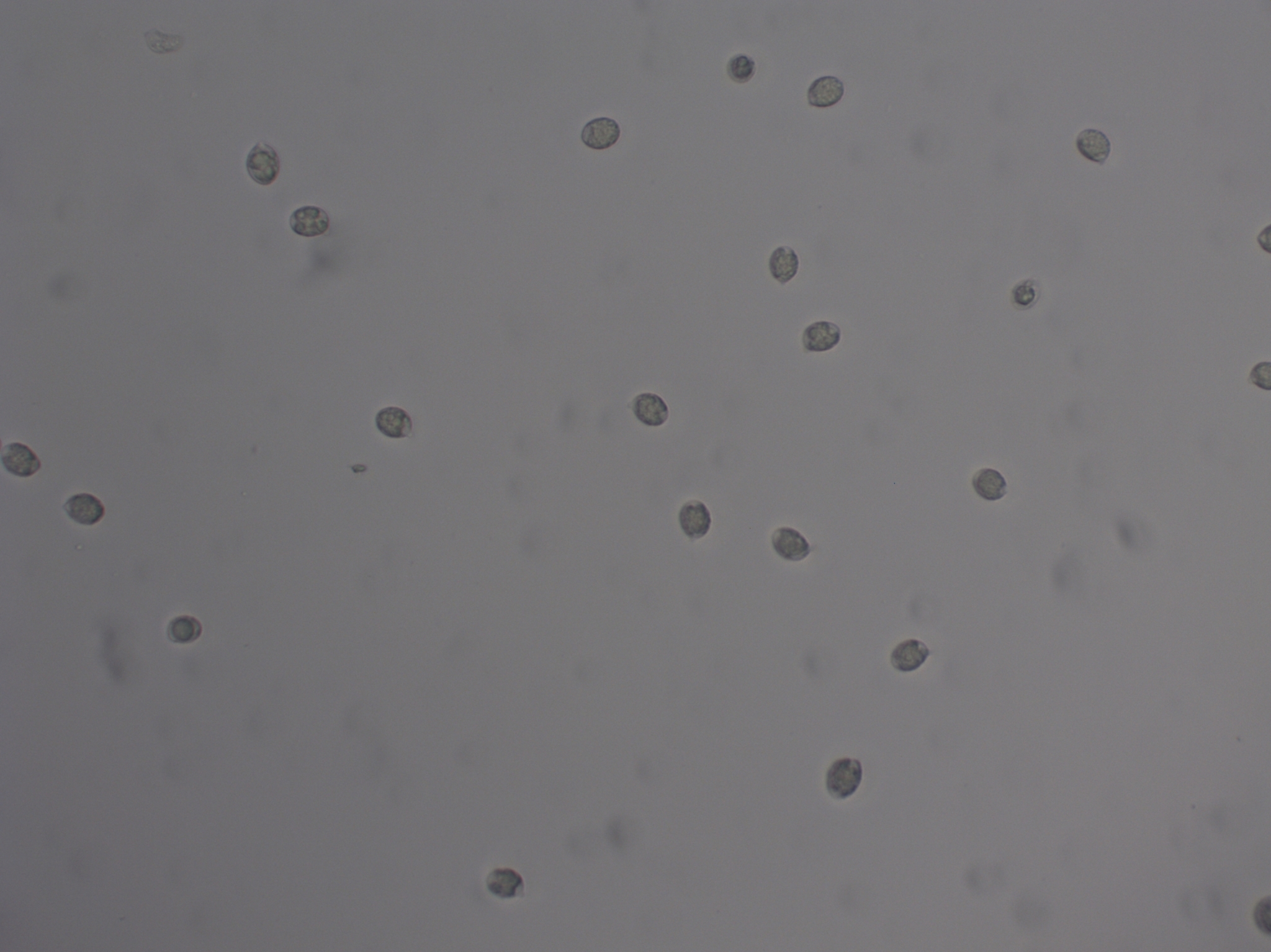
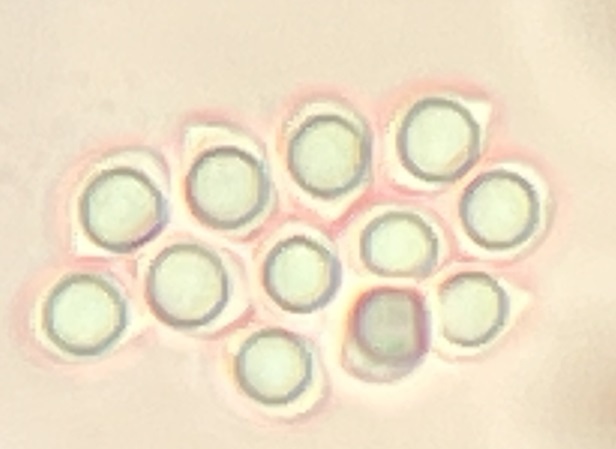
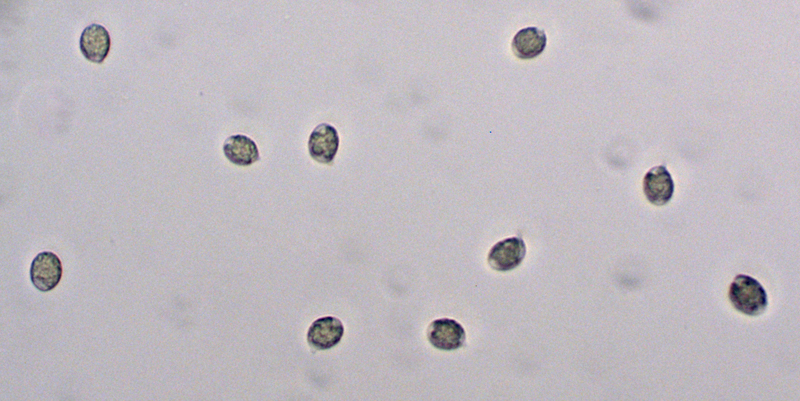
Map Snapshot






32 Records
Status
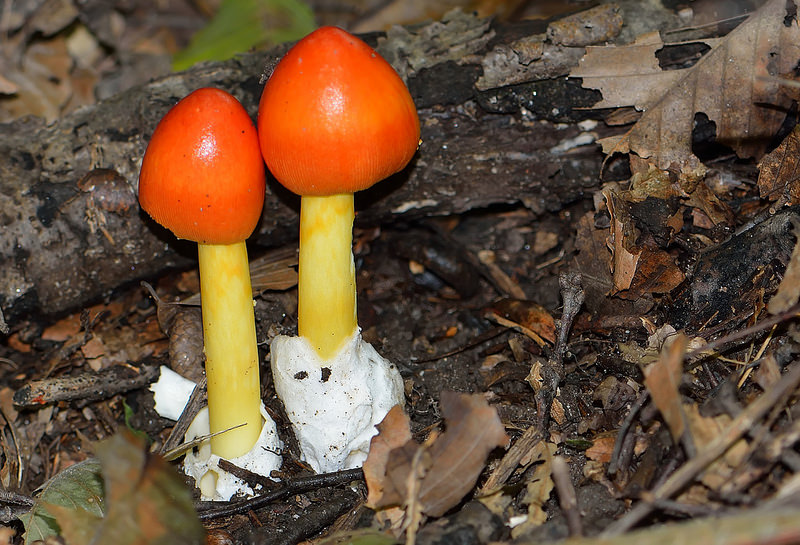
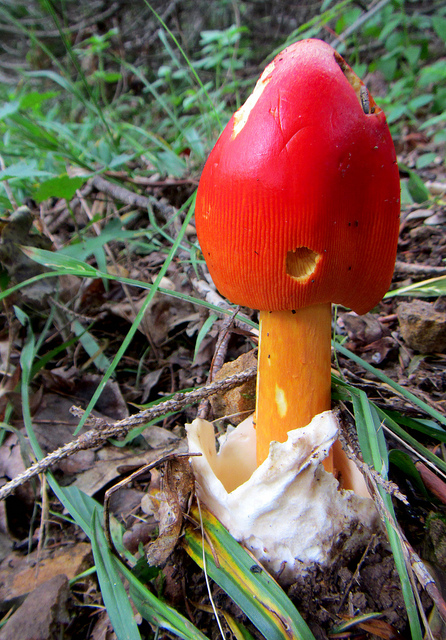
Found solitary or in loose groups on ground in mixed forests.
Description
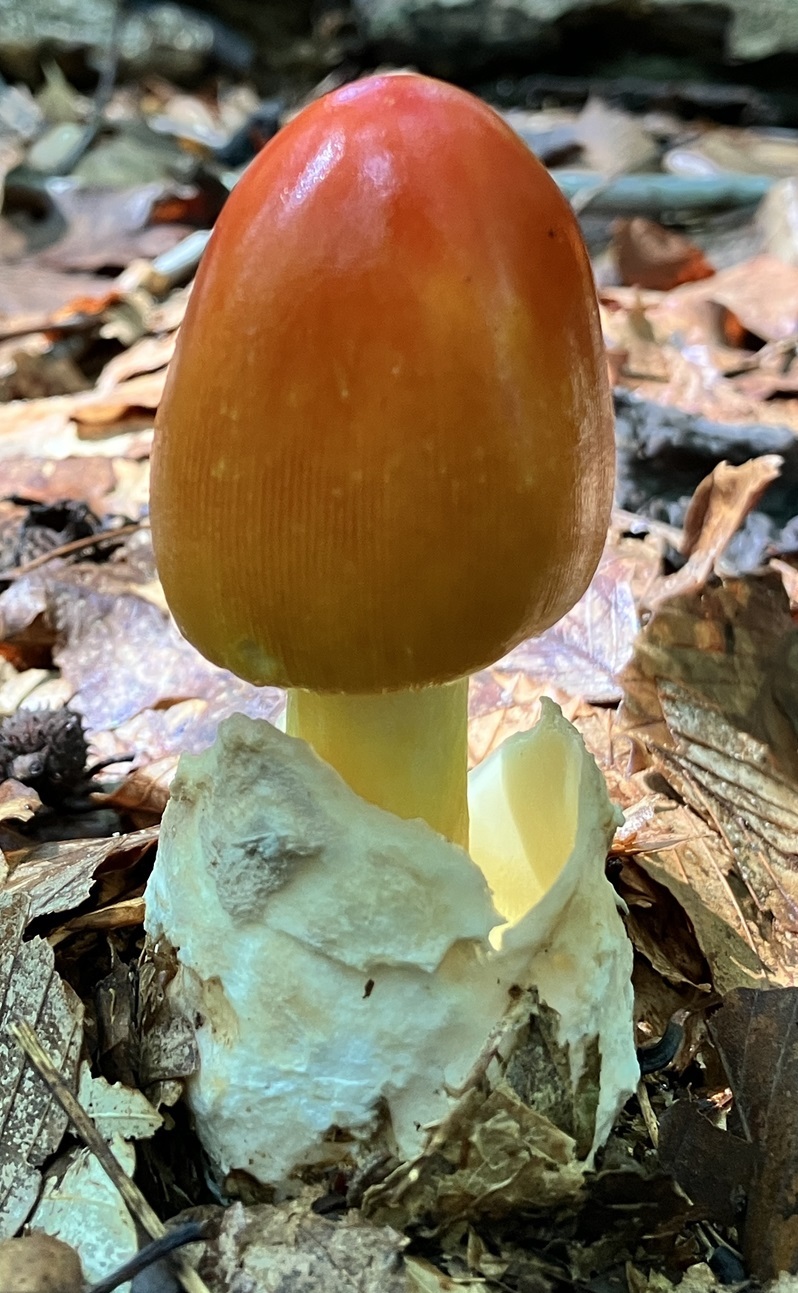
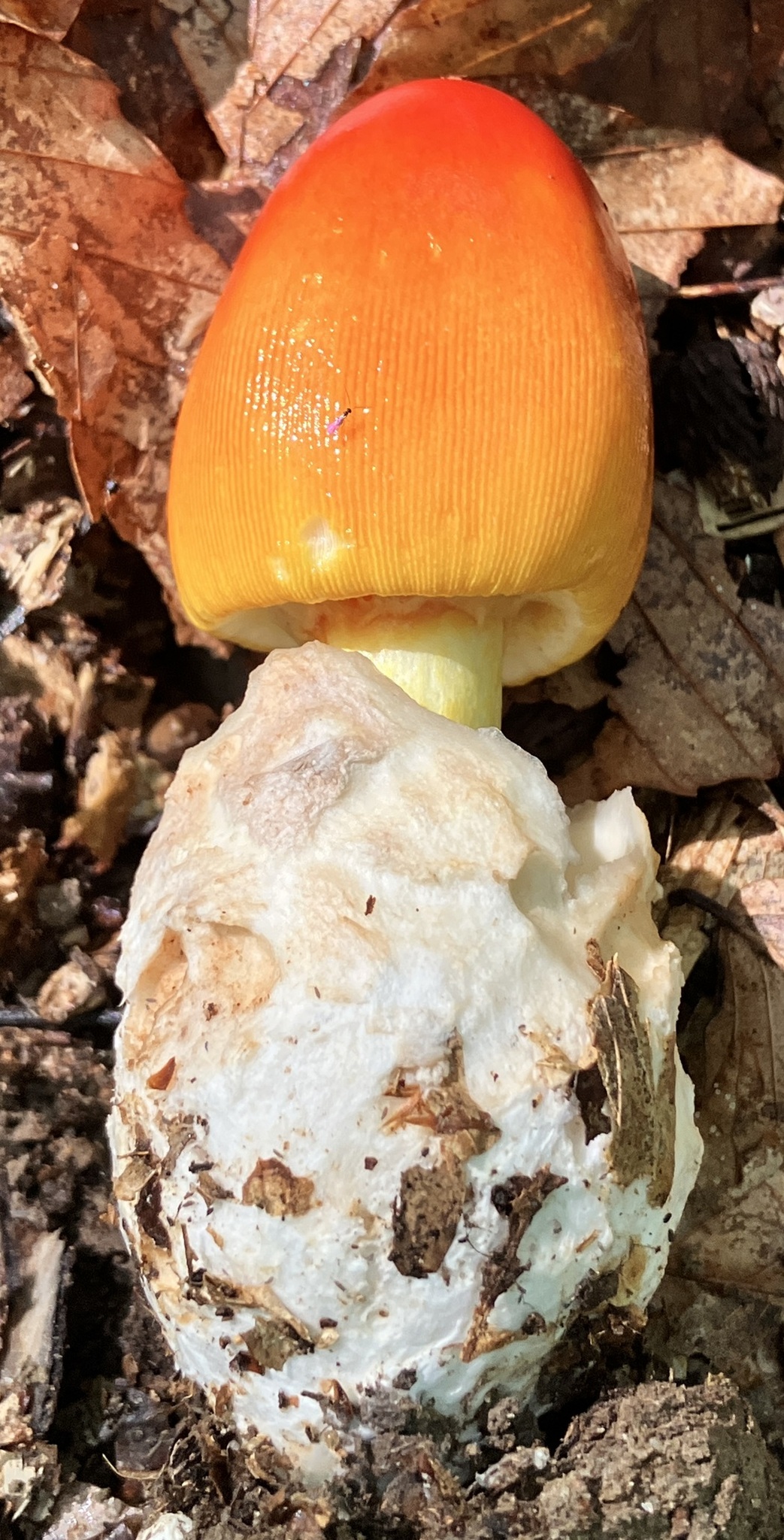
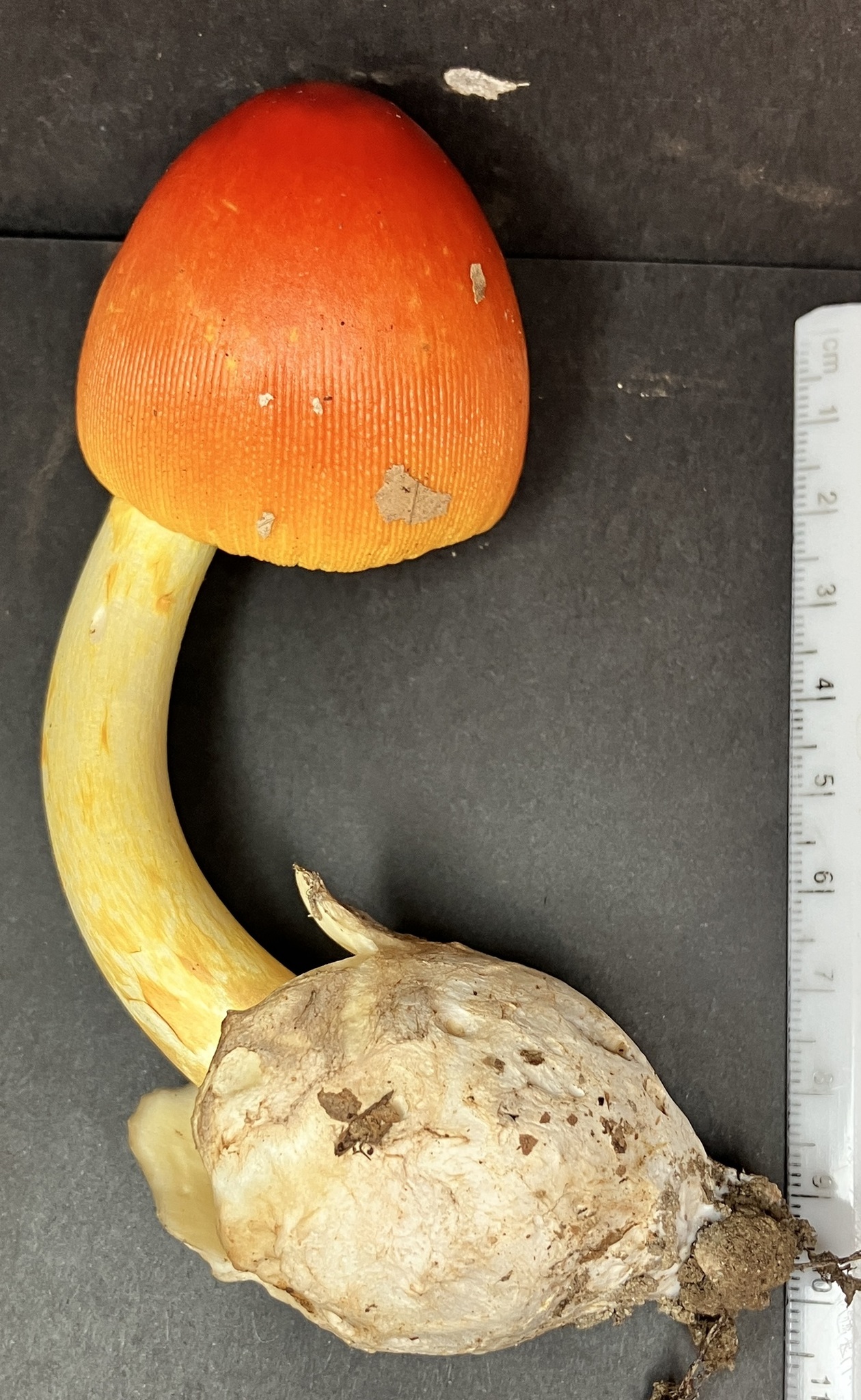
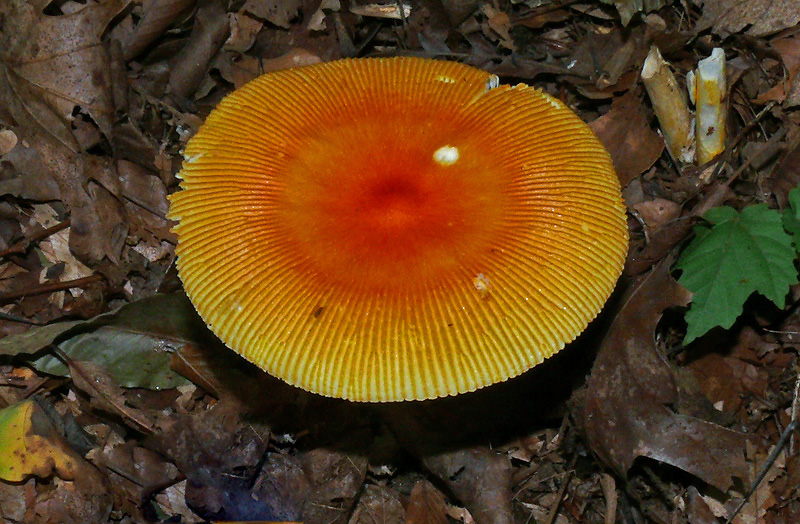
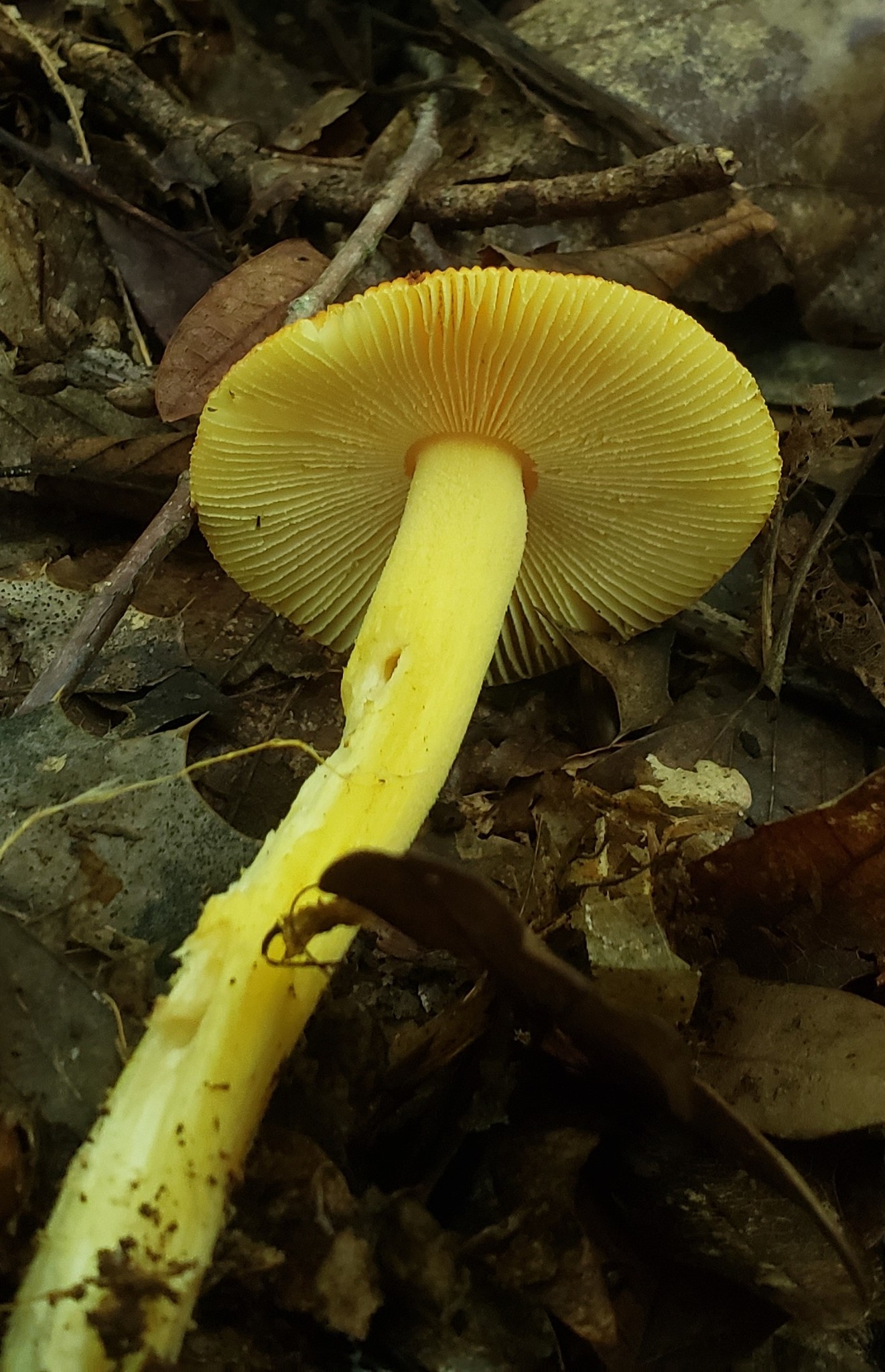
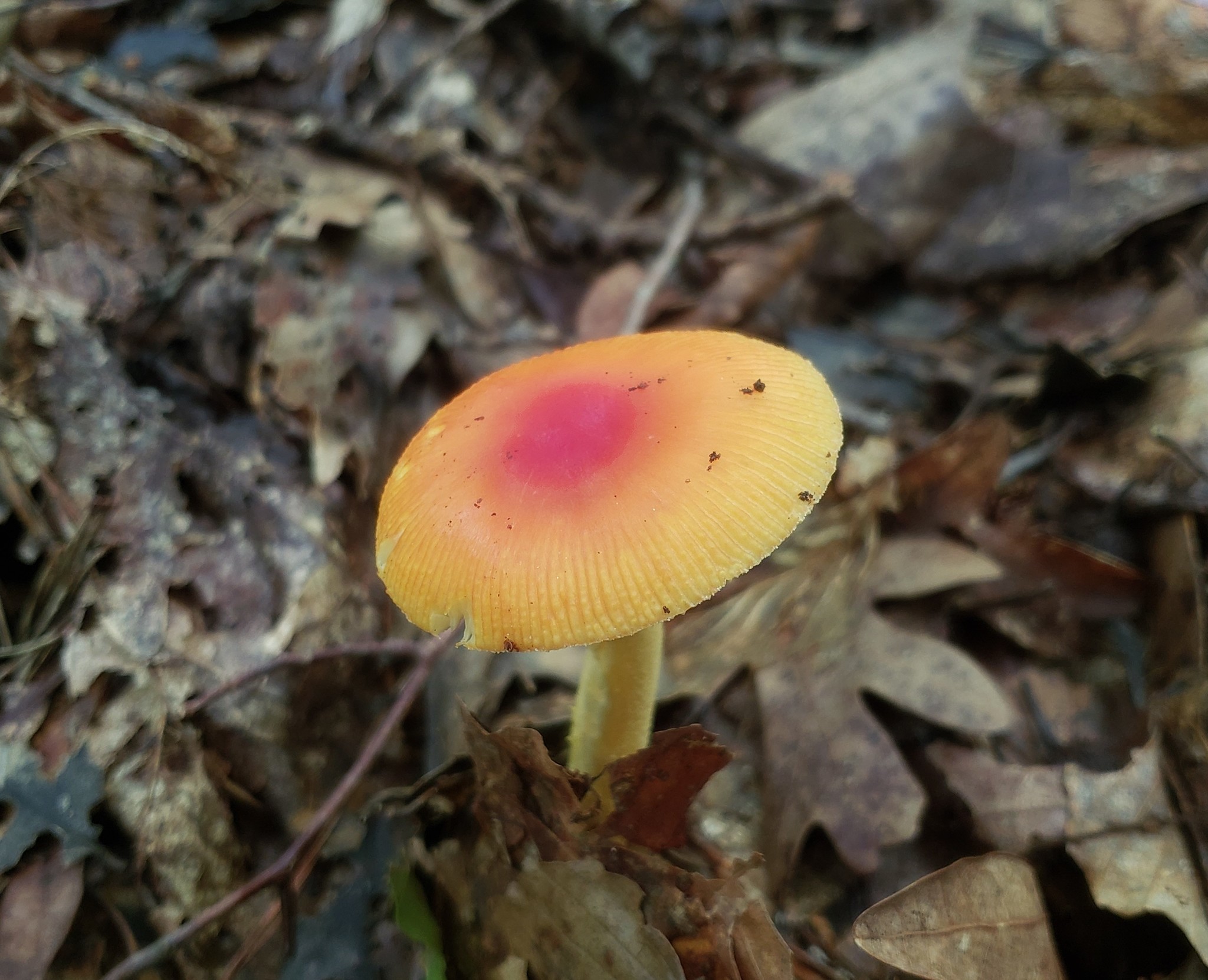
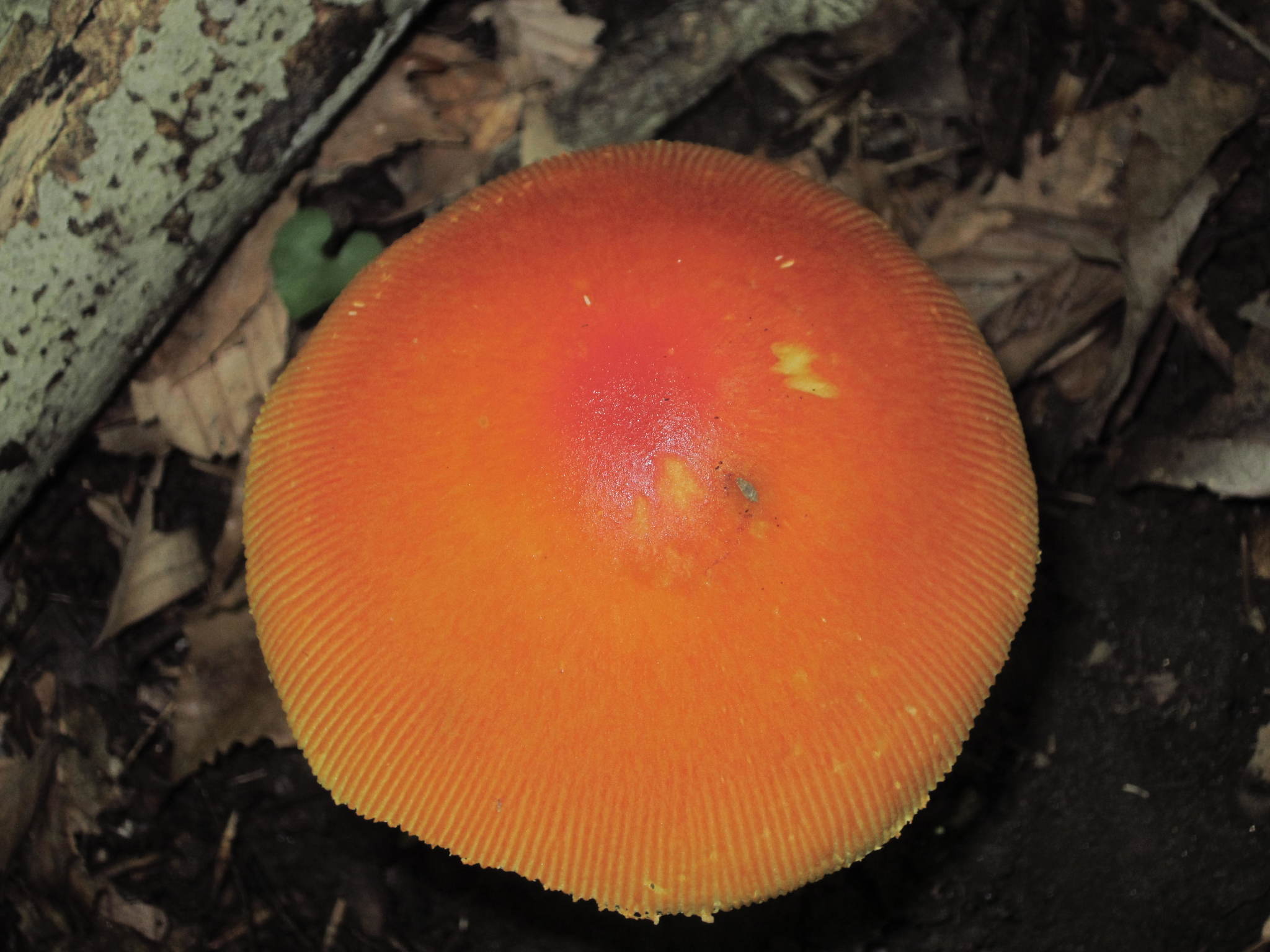
Cap: Reddish-orange disc, yellow-orange margin; dry or sticky; smooth, shiny; convex to flat usually with small umbo; grooved margin; may be small patches of white veil tissue; flesh white. Gills: Pale yellow; crowded; pale yellow partial veil. Stalk: Pale yellow (may be streaked with orange); smooth or roughened; tapers up; pale yellow/orange superior ring; white, thick-lobed, sheathing volva; stuffed or hollow; brittle (J. Solem, pers. comm.).
Seasonality Snapshot
Source: Wikipedia
| Amanita jacksonii | |
|---|---|

| |
| A. Jacksonii in Maine, USA, July 2021. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Basidiomycota |
| Class: | Agaricomycetes |
| Order: | Agaricales |
| Family: | Amanitaceae |
| Genus: | Amanita |
| Species: | A. jacksoni
|
| Binomial name | |
| Amanita jacksoni | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
|
Amanita umbonata Pomerl. | |
| Amanita jacksonii | |
|---|---|
| Gills on hymenium | |
| or convex | |
| Hymenium is free | |
| Stipe has a ring and volva | |
| Spore print is white | |
| Ecology is mycorrhizal | |
| Edibility is choice but not recommended | |


Amanita jacksonii, also known as Jackson's slender amanita,[2] American Slender Caesar, and Eastern Caesar's Amanita,[3] is a North American species of fungus in the family Amanitaceae. It is a reddish-orange colored mushroom species which can be identified by its yellow gills, large, white, sacklike volva.[4]
Taxonomy
[edit]It was given its current name in 1984 by Canadian mycologist René Pomerleau.[5]
Description
[edit]The cap of the mushroom is 8–12 centimetres (3–4+1⁄2 inches) wide; oval at first, becoming convex, typically with a central bump; sticky; brilliant red or orange, fading to yellow on the margin; typically without warts or patches; the margin lined for about 40–50% of the cap's radius. The red pigment fades from margin toward the center with age.[6] Gills are moderately crowded to crowded, orange-yellow to yellow-orange to yellow. They are free from the stem or slightly attached to it; yellow to orange-yellow; crowded; not bruising. The short gills are subtruncate to truncate. Its stipe measures 90–140 by 9–16 millimetres (3+1⁄2 in–5+1⁄2 in × 1⁄4 in–3⁄4 in), is yellow and decorated with orange fibrils and patches that are the remnants of a felted extension of the limbus internus of the otherwise white volva. The spores measure (7.0-) 7.8–9.8 (-12.1) × (5.2-) 5.8–7.5 (-8.7) μm and are broadly ellipsoid to ellipsoid (rarely subglobose or elongate) and inamyloid. Clamps are common at bases of basidia.[7] The flesh looks whitish to pale yellow, and does not stain on exposure.
Similar species
[edit]A. jacksonii looks similar to A. caesarea (Caesar's mushroom), which is found in Europe and North Africa, as well as poisonous species of Amanita.
Distribution and habitat
[edit]Its range extends from the Province of Quebec, Canada, to at least the State of Hidalgo, Mexico.[8]
Uses
[edit]The mushroom is considered a choice edible, although it can be misidentified with toxic species such as A. muscaria and A. phalloides.[9]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Amanita jacksonii - Amanitaceae.org - Taxonomy and Morphology of Amanita and Limacella". www.amanitaceae.org. Retrieved 21 September 2017.
- ^ "Standardized Common Names for Wild Species in Canada". National General Status Working Group. 2020.
- ^ https://plants.ces.ncsu.edu/plants/amanita-jacksonii/ accessed Aug. 2021
- ^ Kuo, M. (2008, March). Amanita jacksonii. Retrieved from the MushroomExpert.Com Web site: http://www.mushroomexpert.com/amanita_jacksonii.html
- ^ Pomerleau R. (1984). "A propos du nom scientifique de l'oronge américaine". Naturaliste Canadien (in French). 111 (3): 329–30.
- ^ http://www.eticomm.net/~ret/amanita/species/jacksoni.html Archived 2011-07-16 at the Wayback Machine By R. E. Tulloss.
- ^ http://www.amanitaceae.org/index.php?Amanita%20jacksonii Amanita jacksonii-www.amanitaceae.org
- ^ Mushroom Observer-Amanita jacksonii Pomerleau https://mushroomobserver.org/name/show_name?_js=on&_new=true&id=1067
- ^ Davis, R. Michael; Sommer, Robert; Menge, John A. (2012). Field Guide to Mushrooms of Western North America. Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 70–71. ISBN 978-0-520-95360-4. OCLC 797915861.