Map Snapshot


1 Record
Seasonality Snapshot
Source: Wikipedia
| Cantharellus flavus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Basidiomycota |
| Class: | Agaricomycetes |
| Order: | Cantharellales |
| Family: | Cantharellaceae |
| Genus: | Cantharellus |
| Species: | C. flavus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cantharellus flavus M.J. Foltz & T.J.Volk
| |
| Cantharellus flavus | |
|---|---|
| Ridges on hymenium | |
| Cap is convex or infundibuliform | |
| Hymenium is decurrent | |
| Stipe is bare | |
| Spore print is yellow | |
| Ecology is mycorrhizal | |
| Edibility is edible | |
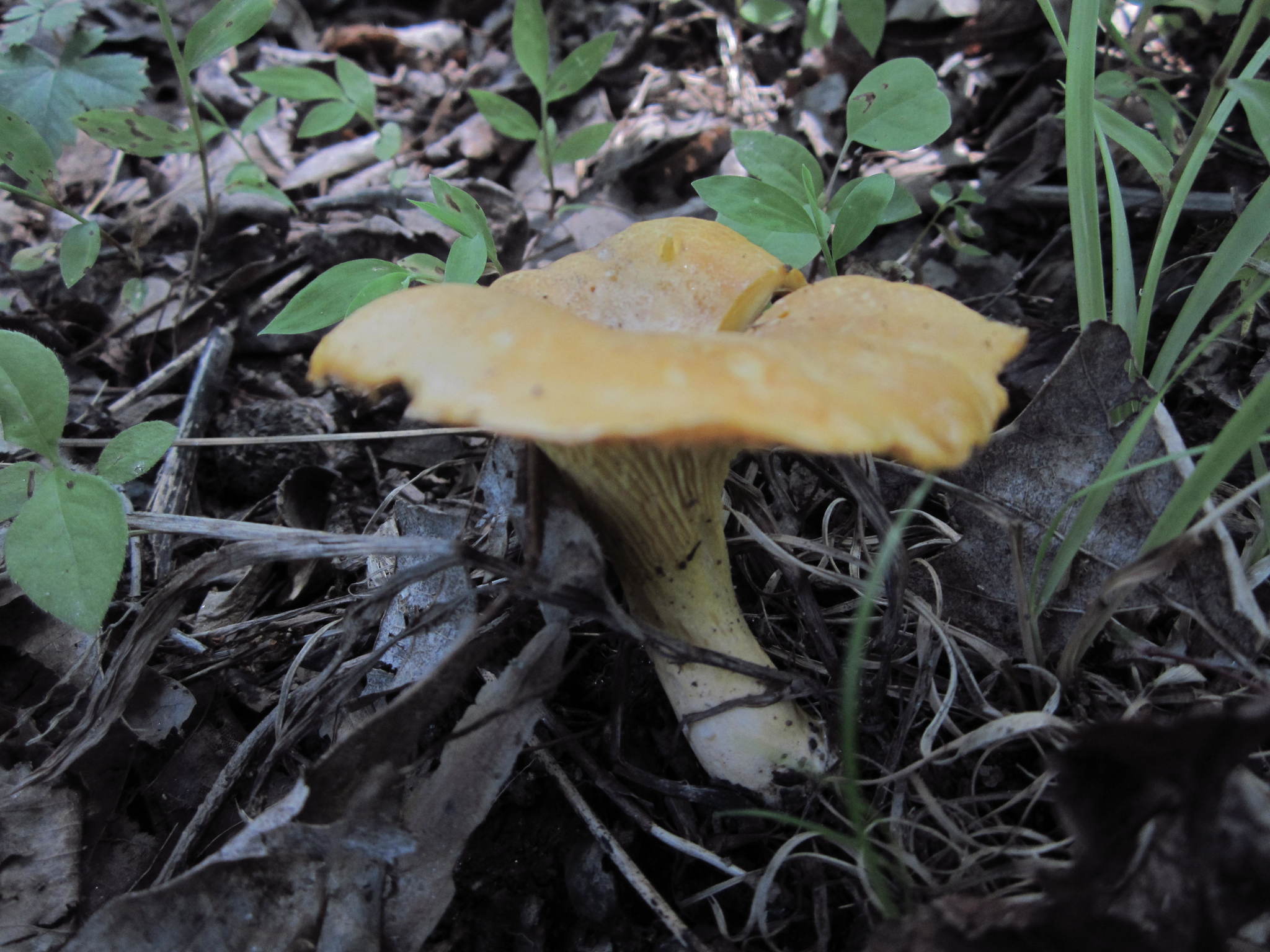
Cantharellus flavus, also called the American golden chanterelle, Eastern yellow chanterelle or Midwestern yellow chanterelle, is a species of fungus in the genus Cantharellus.[1][2] Found in North America, it is an edible mushroom.
Taxonomy
[edit]Cantharellus flavus was described in 2013 by Matthew Foltz and Tom Volk.[3]
Initially, C. flavus was classified along with similar species under the species name Cantharellus cibarius.[4] Since the description of this species in 2013, its validity as a distinct species has been questioned, due to the heterogeneity of its morphology and habitat, which overlaps with the distinguishing characteristics of other species, and only minor molecular differences. Therefore, it has been suggested that C. flavus is part of the species complex of Cantharellus tenuithrix.[5][6]
Its epithet flavus comes from the Latin word for "yellow", referring to this species' yellow spore print, stipe, false gills and cap.[2]
Description
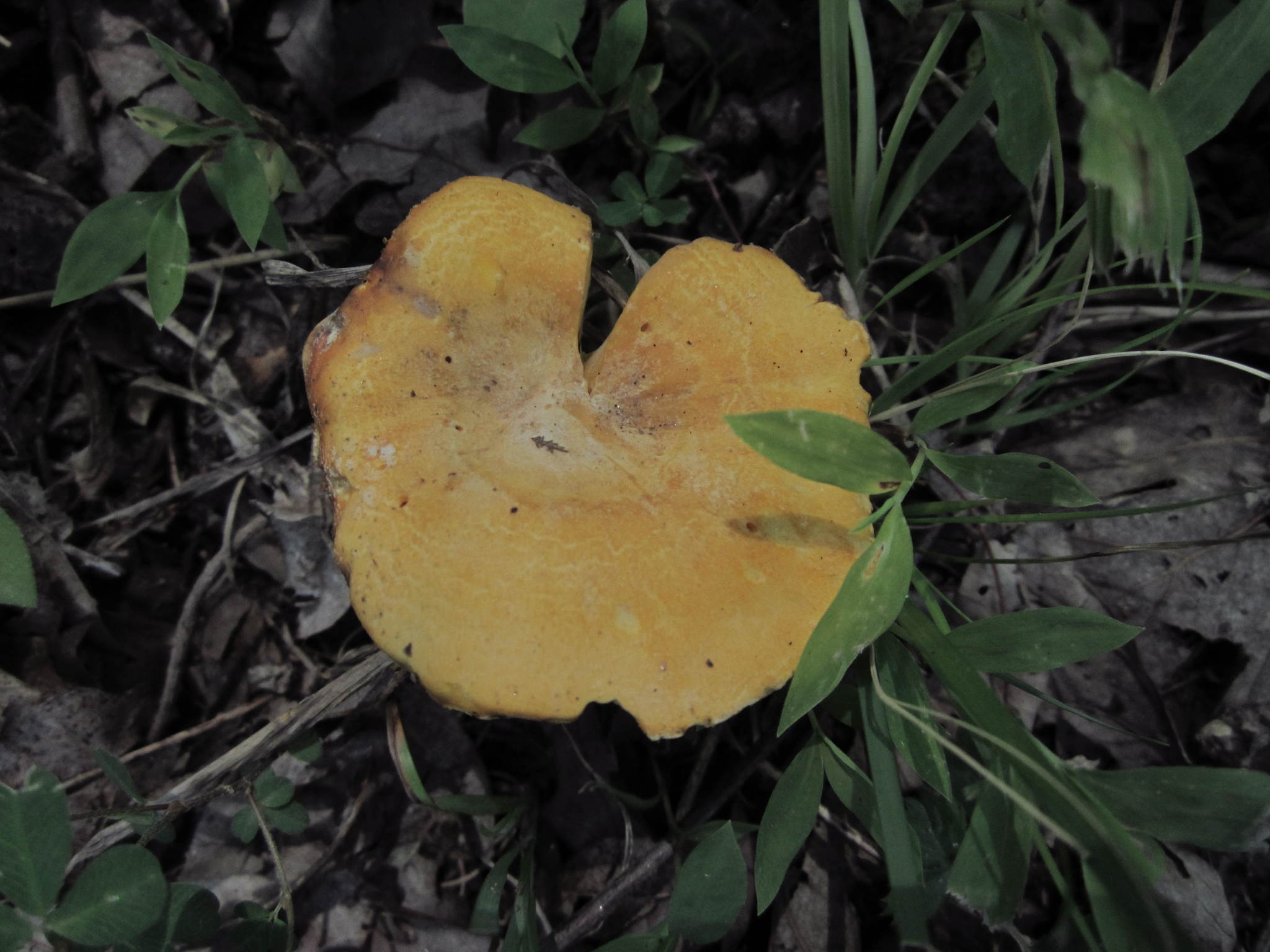
[edit]The cap is convex when young, flattening out, and arching with age, developing a depressed center. When mature, it can be broadly infundibuliform.[1] It measures 2–10 centimetres (3⁄4–4 in) wide and has a wavy, tucked in margin. The hyphae of the cap have long terminal cells that measure 85–95 by 4.5–5.5 μm, a characteristic shared with C. phasmatis and C. tenuithrix. The flesh is yellow, though it pales towards the end of the stipe, and with age.[7] The stipe measures 3–8 cm long and 5–20 millimetres (1⁄4–3⁄4 in) broad and may be tapered towards the base. Applying KOH to the flesh intensifies its color. Clamp connections are found throughout the fungal tissue.[2]
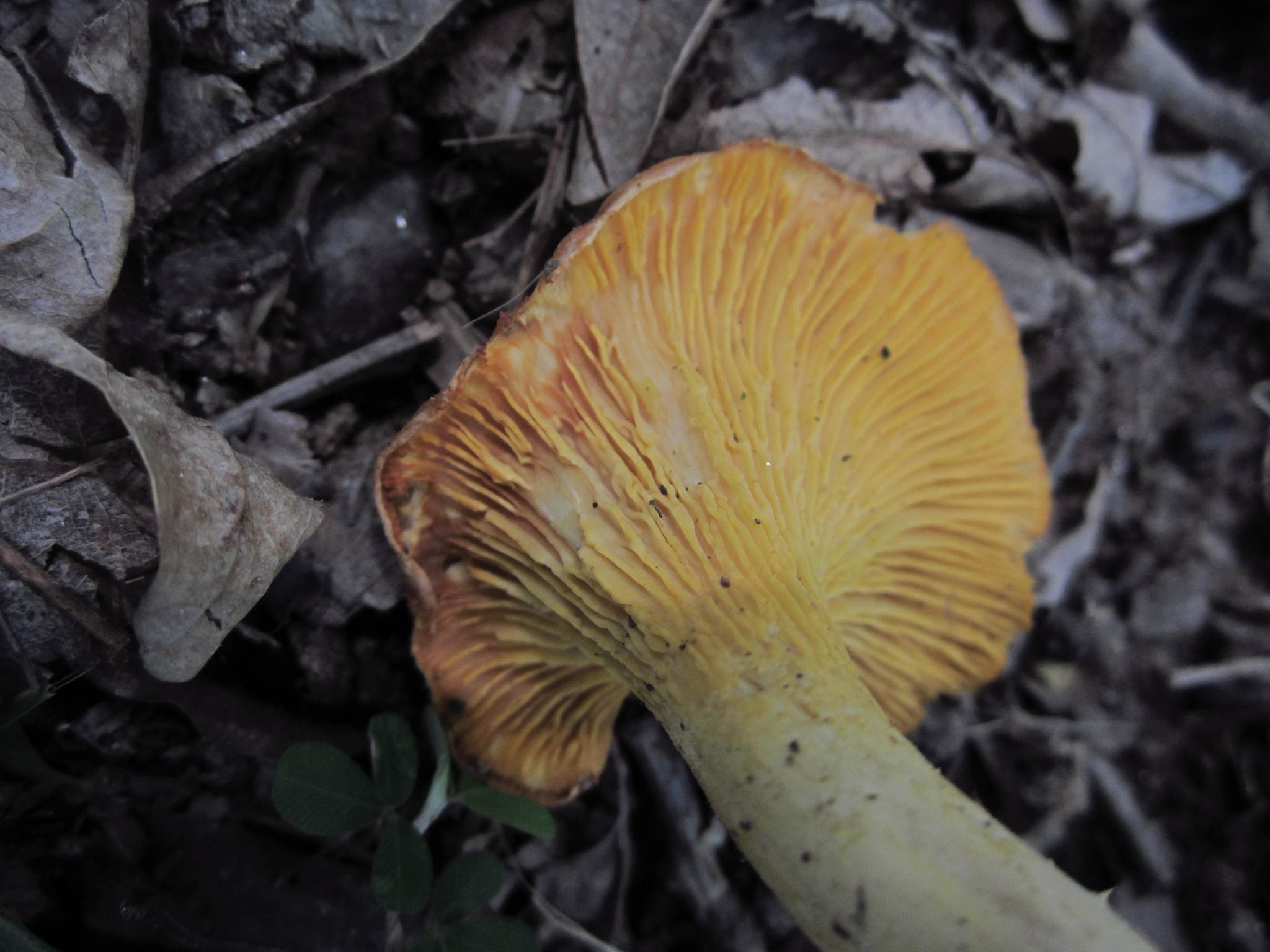
The false gills are decurrent and forking, with rounded edges, and the spore print is yellow. The spores are oblong, transparent and smooth, measuring 8–11 x 4.5–6 μm. They do not change colour when mounted with iodine-based reagant (inamyloid).[7] The basidia measure 75–80 by 7–9 μm and have 4–6 sterigma.[2]
The taste is mild and slightly peppery and the odour is faintly of apricots.[7]
Similar species
[edit]Cantharellus flavus can be distinguished from similar species by its yellow rather than white or orange false gills and stipe and yellow rather than pink spore print. It can be distinguished from C. lateritius by its well-developed false gills.[8]
Distribution and habitat
[edit]The distribution of C. flavus is obscure due to its previous grouping with other species as C. cibarius. Its presence has been confirmed in Wisconsin, Tennessee, North Carolina and Texas, though it is presumed that it is common throughout eastern North America.[4]
It prefers growing under oak, but can also grow under hardwoods, or a mixed stand of hardwoods and conifers. It is likely ectomycorrhizal with oak (Quercus spp.). It is found in well-drained soils, often on hillsides. It typically grows from July to September and can grow clustered, solitary, or scattered.
It was categorised as "least concern" by the IUCN red list in 2021.[4]
Edibility
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Foltz, Matthew J. (August 2011). Systematics and molecular phylogeny of Cantharellus spp. in western Wisconsin (Master of Science in Biology thesis).
- ^ a b c d Foltz, Matthew J.; Perez, Kathryn E.; Volk, Thomas J. (2013). "Molecular phylogeny and morphology reveal three new species of Cantharellus within 20 m of one another in western Wisconsin, USA". Mycologia. 105 (2): 447–461. ISSN 0027-5514.
- ^ Foltz M, Perez KE, Volk T (2013). "Molecular phylogeny and morphology reveals three new species of Cantharellus within 20 meters of one another in western Wisconsin, USA". Mycologia. 105 (2): 447–461. doi:10.3852/12-181. PMID 23080022. S2CID 2218602.
- ^ a b c IUCN (2021-03-19). Cantharellus flavus: Siegel, N.: The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2021: e.T198623052A198623972 (Report). International Union for Conservation of Nature. doi:10.2305/iucn.uk.2021-2.rlts.t198623052a198623972.en.
- ^ Buyck, Bart; Hofstetter, Valérie; Olariaga, Ibai (September 2016). "Setting the Record Straight on North American Cantharellus". Cryptogamie, Mycologie. 37 (3): 405–417. doi:10.7872/crym/v37.iss3.2016.405. ISSN 0181-1584.
- ^ Swenie, Rachel A.; Matheny, P. Brandon (2023-01-02). "New reports, new species, and high diversity of Cantharellus in the southern Appalachians". Mycologia. 115 (1): 44–68. doi:10.1080/00275514.2022.2141558. ISSN 0027-5514.
- ^ a b c Baroni, Timothy J. (2017). Mushrooms of the Northeastern United States and Eastern Canada. Portland, OR: Timber Press. p. 453. ISBN 9781604696349.
- ^ "Three new chanterelle mushrooms discovered in the Midwest | U-M LSA University of Michigan Herbarium". lsa.umich.edu. Retrieved 2024-02-03.
- ^ Initiative, The Global Fungal Red List. "Cantharellus flavus". redlist.info. Retrieved 2024-03-11.
External links
[edit]