Map Snapshot

























267 Records
Status
Common throughout much of Maryland, but rare on the mid and lower Eastern Shore.
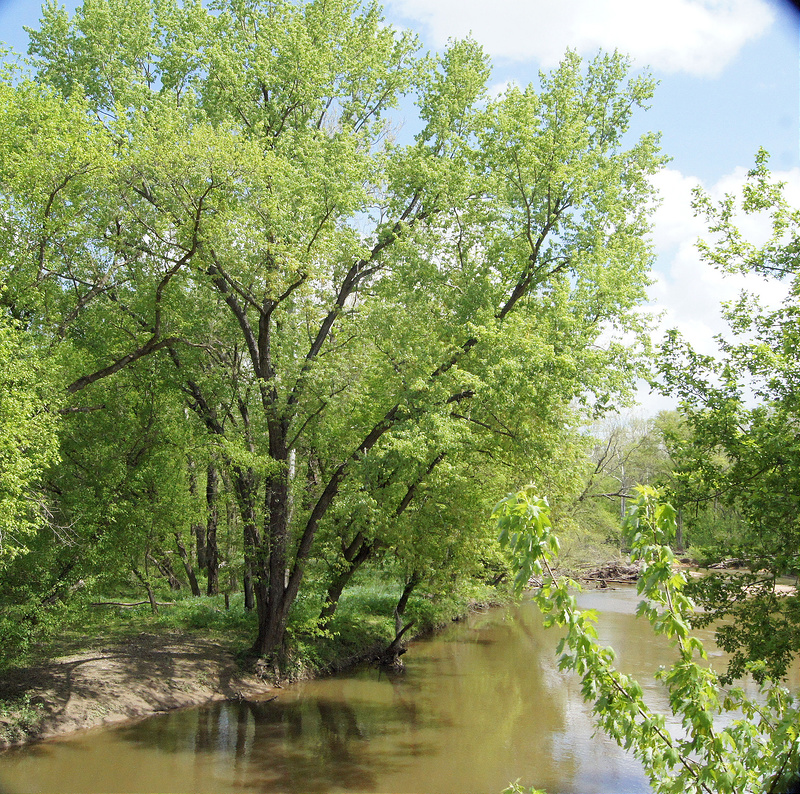
Silver Maple ranges from eastern Canada to South Dakota, and south to Arkansas and Florida. It is common in swamps and along streambanks but will also grow in drier places. It is often planted as a street or shade tree, but its branches are brittle and it is not long lived.
Description
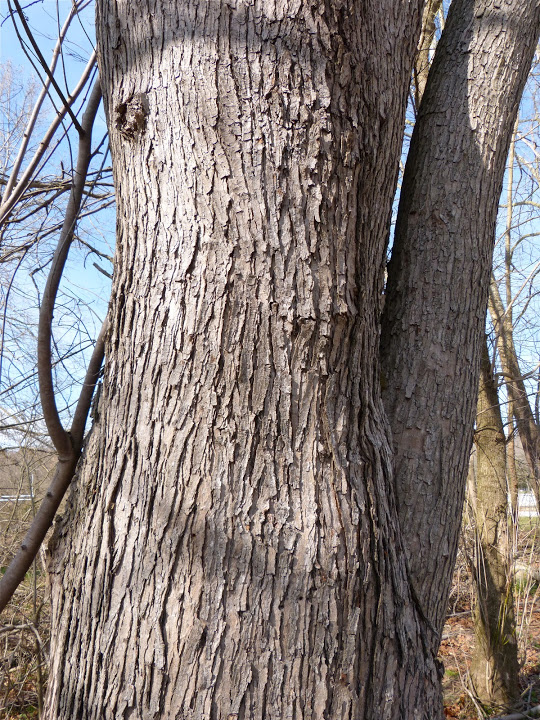
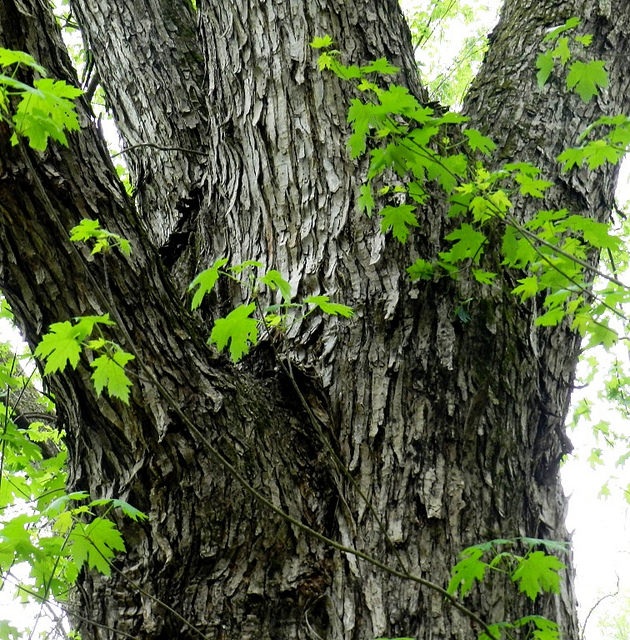
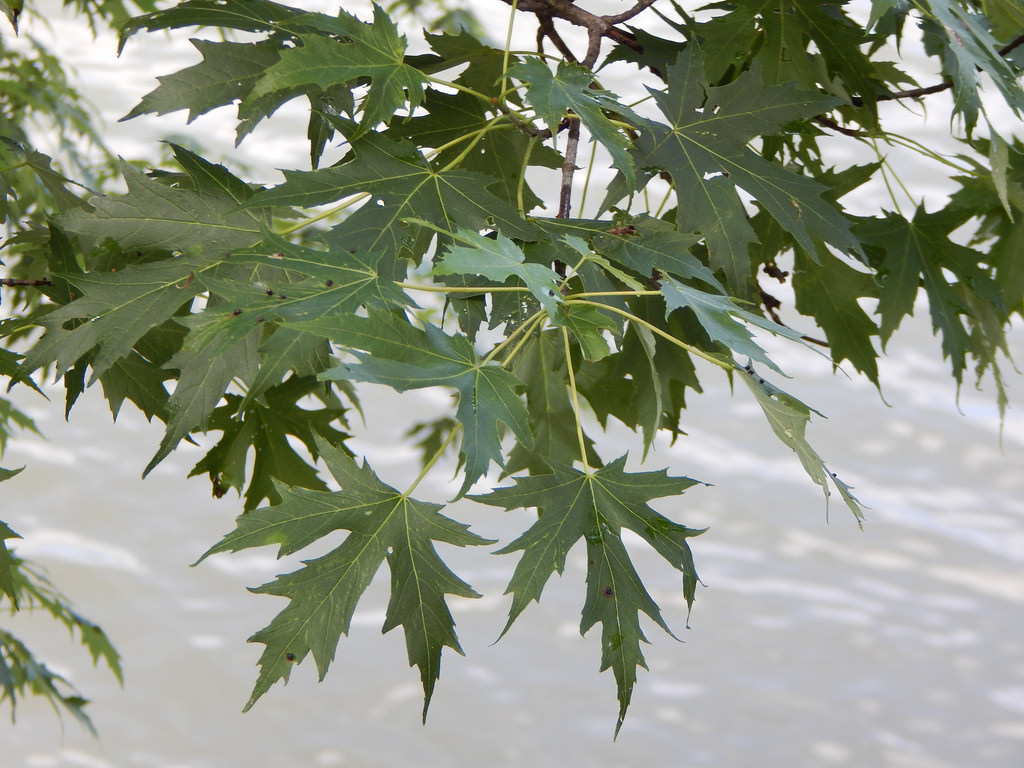
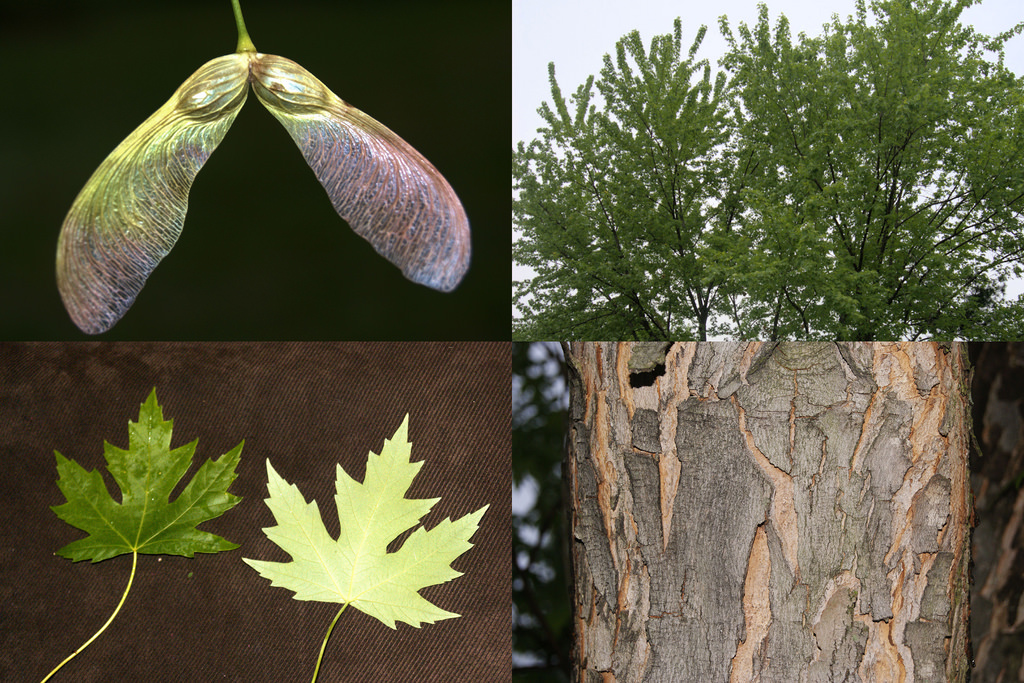
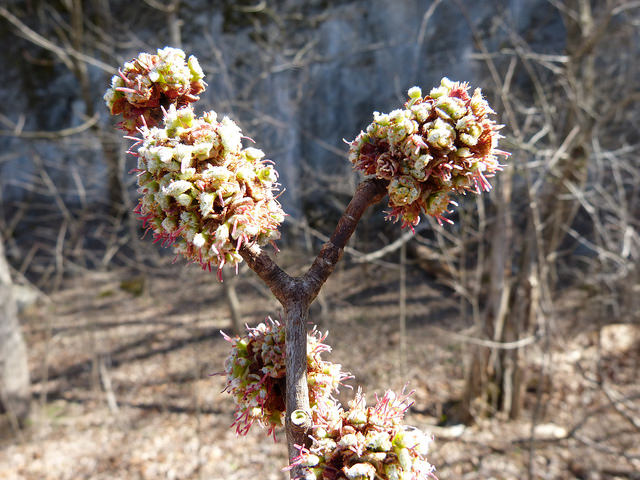
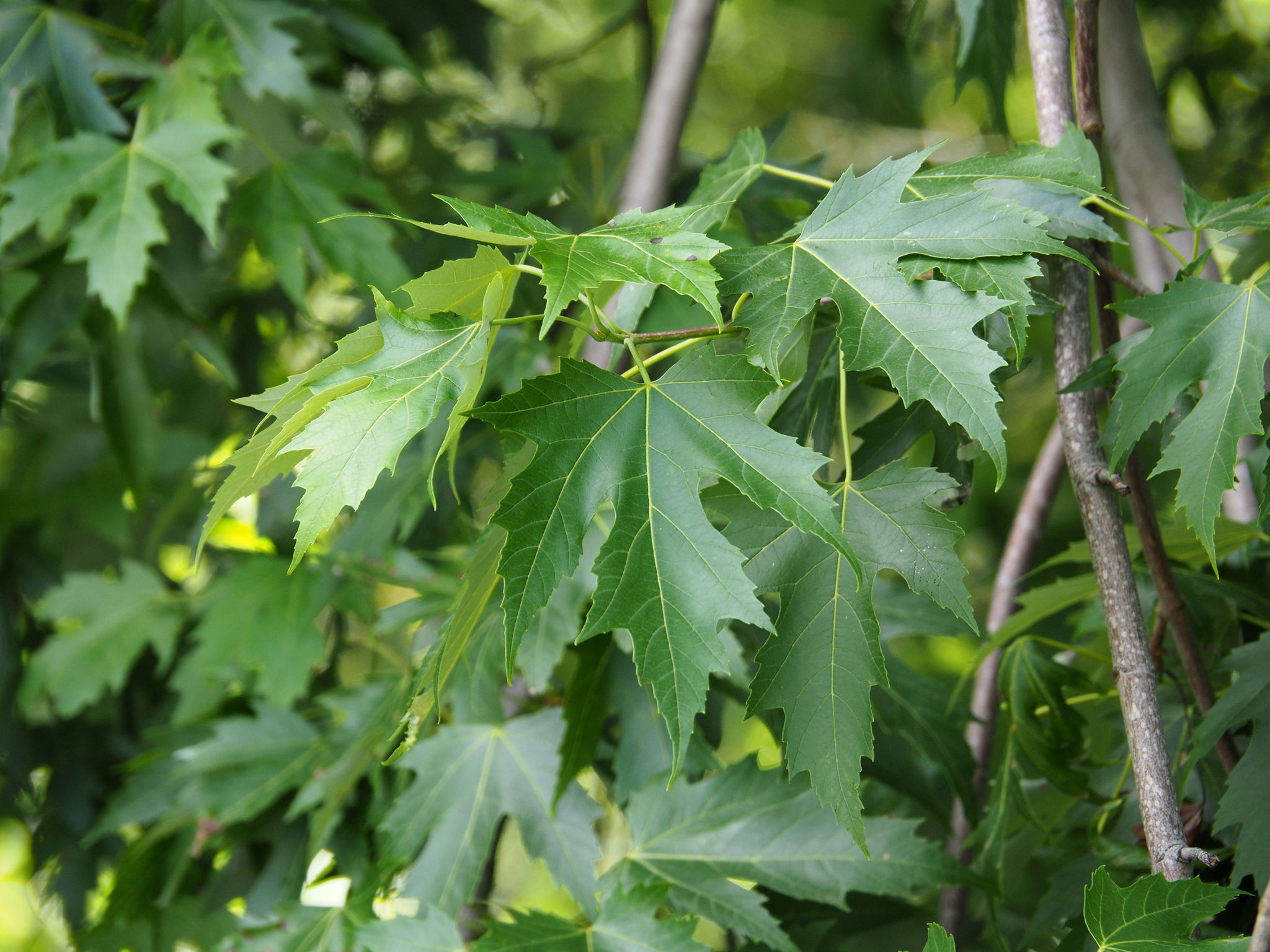
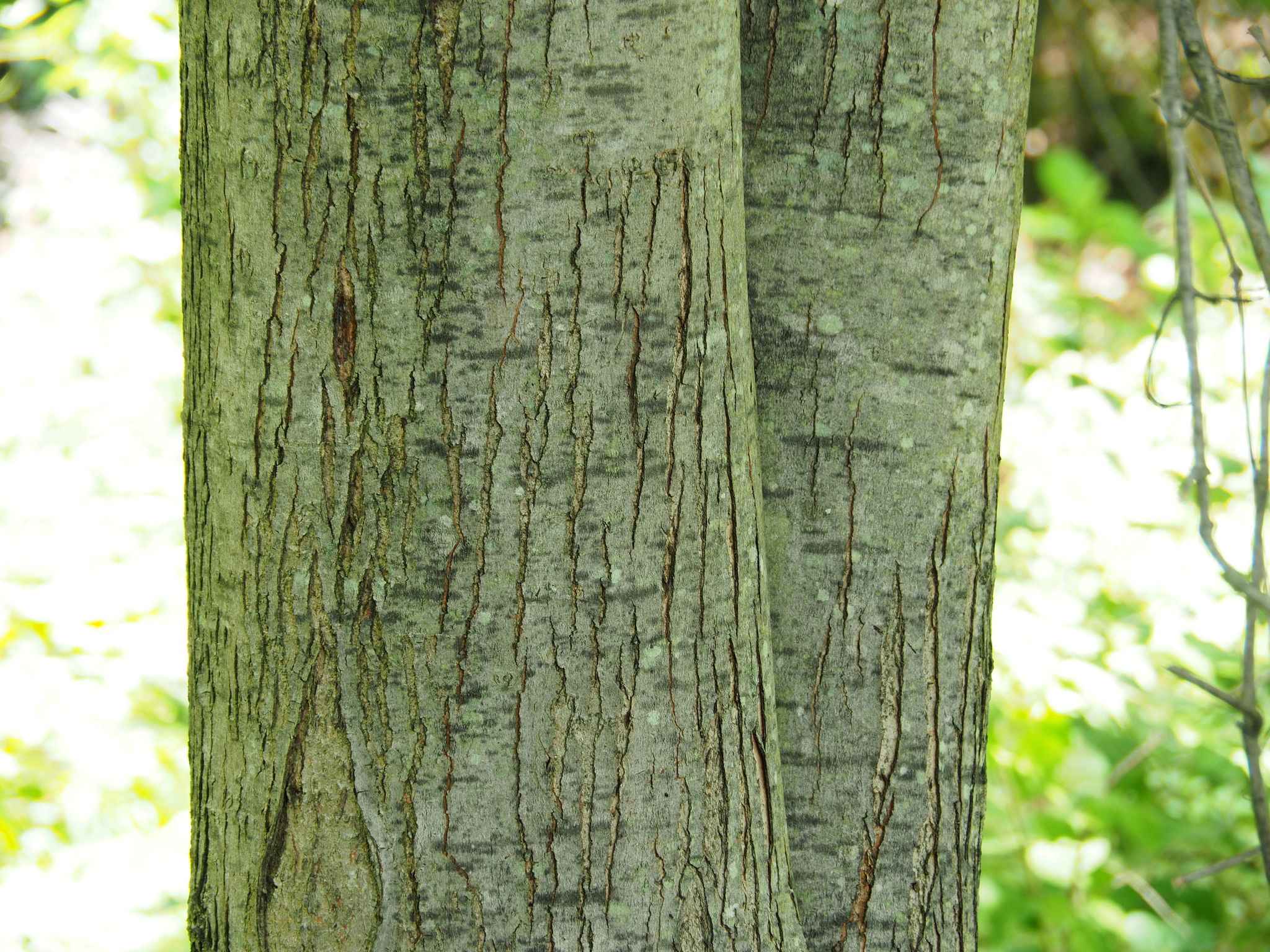
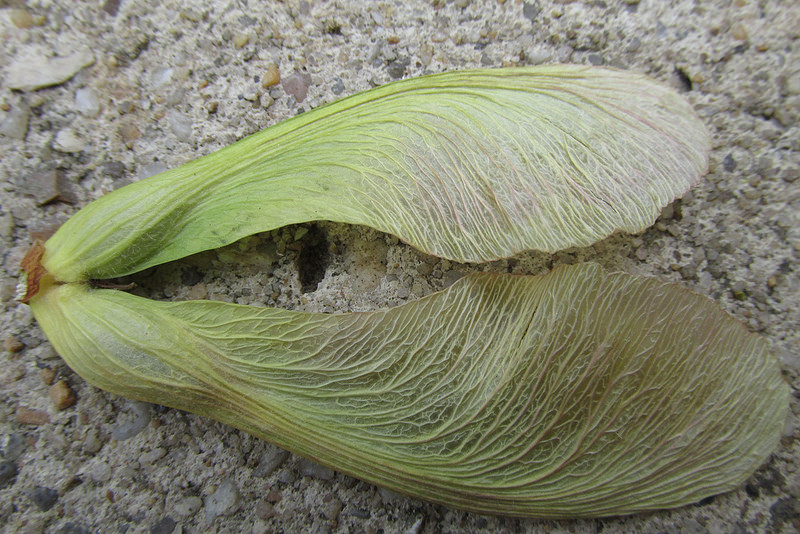
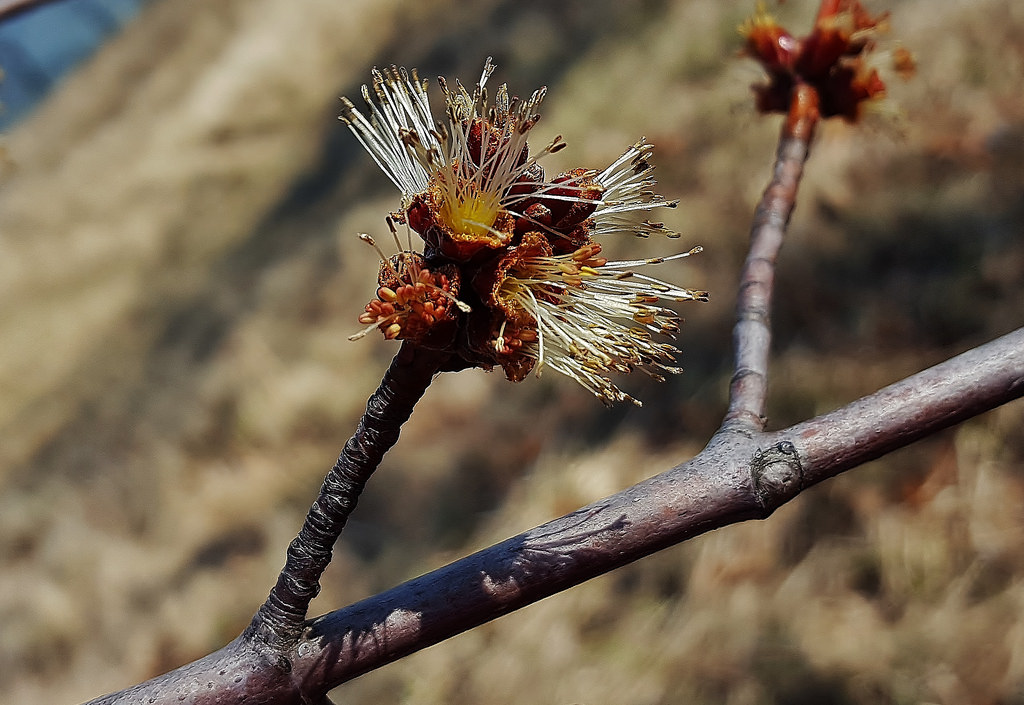
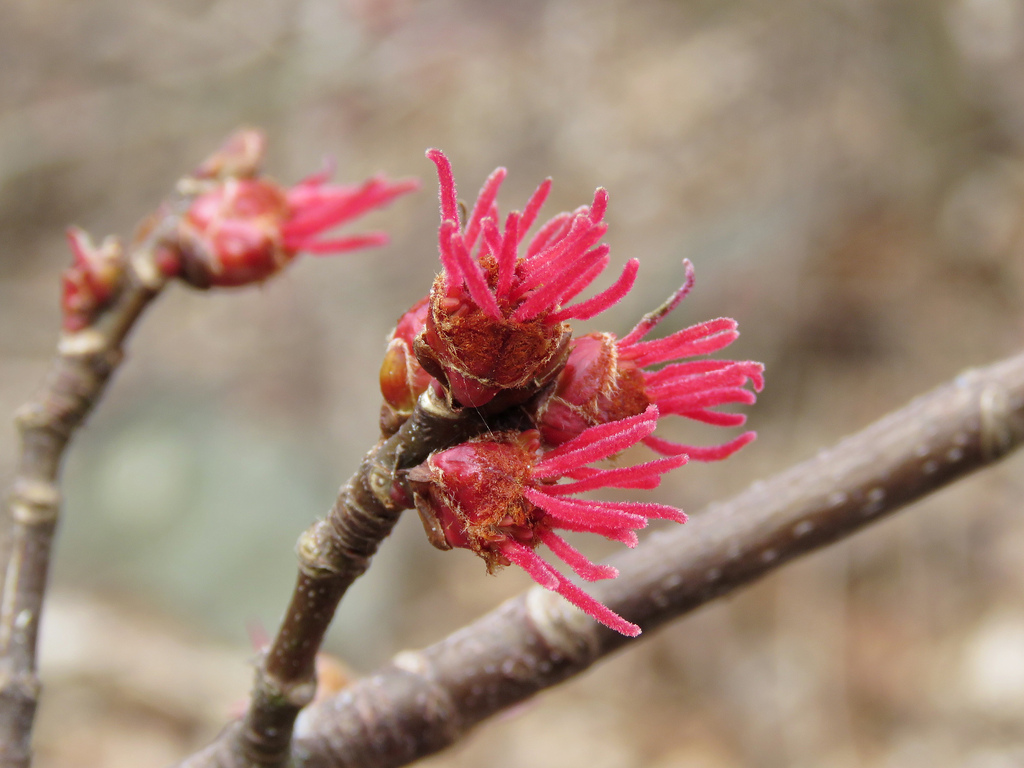
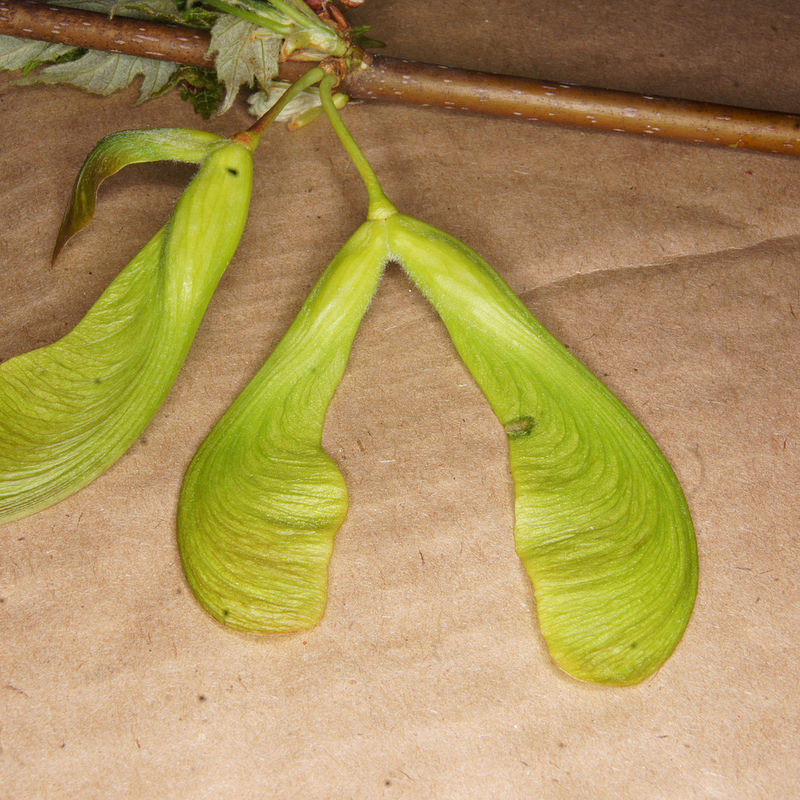
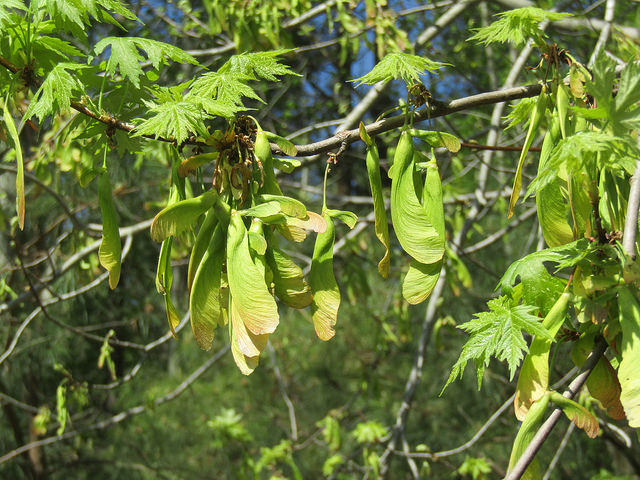
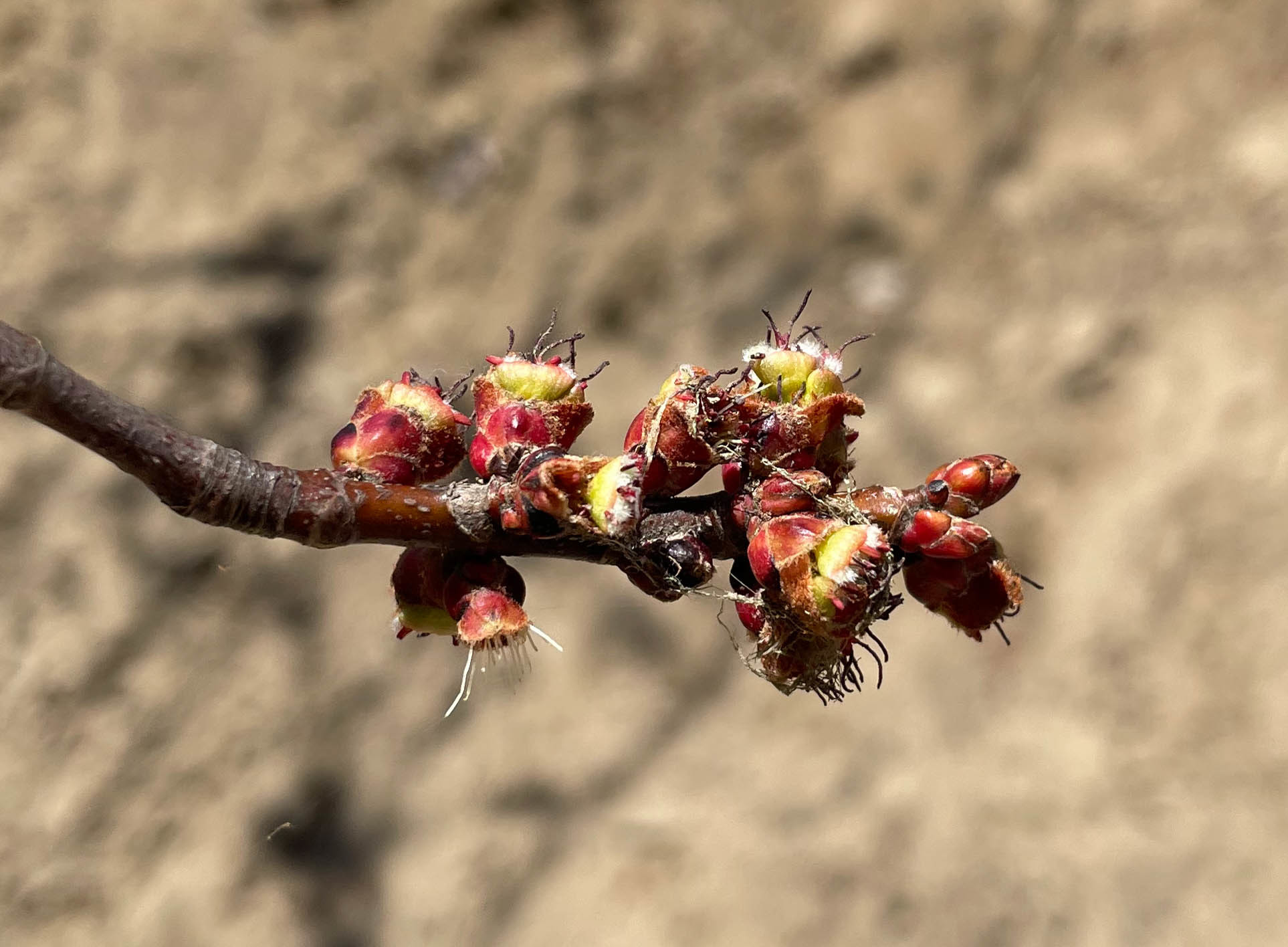
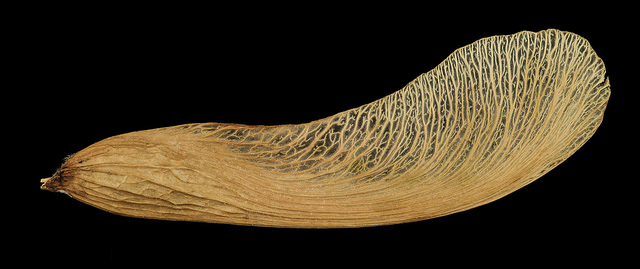
Silver Maple is a medium to large forest tree. Leaves are green above, silvery beneath, and have five deeply V-shaped lobes with teeth on their margins. Flowers are reddish green and appear in early spring, long before leaves. In fall, the leaves usually turn pale yellow. The fruits (samaras), with their widely flaring wings, are the largest of the native maples. The fruits mature in late spring and the seeds germinate at once. Bark is smooth and gray in young trees, then becomes shaggy, breaking into long, thin vertical strips that are loose at the ends.
Silver Maple, along with Red Maple, is considered a "soft maple," in contrast to the other native maples, which have harder wood and are called "hard maples."
Where To Find
Along the banks of the Susquehanna River at Susquehanna SP. Also common along the banks of the Potomac River. Easily viewed along the C&O Canal.
Relationships
Silver Maple is the alternate host for the Woolly Alder Aphid.
Host plant for various moth species including Maple Tip Borer Moth, Maple Bud Borer Moth, American Dagger Moth, and Banded Tussock Moth (Database of World's Lepidopteran Host Plants).
Seasonality Snapshot
Source: Wikipedia
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (September 2016) |
| Acer saccharinum | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Sapindales |
| Family: | Sapindaceae |
| Genus: | Acer |
| Section: | Acer sect. Rubra |
| Species: | A. saccharinum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Acer saccharinum L. 1753
| |

| |
| Natural range of Acer saccharinum | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
|
List
| |

Acer saccharinum, commonly known as silver maple,[3] creek maple, silverleaf maple,[3] soft maple, large maple,[3] water maple,[3] swamp maple,[3] or white maple,[3] is a species of maple native to the eastern and central United States and southeastern Canada.[3][4] It is one of the most common trees in the United States.
Although the silver maple's Latin name is similar, it should not be confused with Acer saccharum, the sugar maple. Some of the common names are also applied to other maples, especially Acer rubrum.
Description
[edit]

The silver maple tree is a relatively fast-growing deciduous tree, commonly reaching a height of 15–25 m (49–82 ft), exceptionally 35 m (115 ft). Its spread will generally be 11–15 m (36–49 ft) wide. A 10-year-old sapling will stand about 8 m (26 ft) tall. It is often found along waterways and in wetlands, leading to the colloquial name "water maple". It is a highly adaptable tree, although it has higher sunlight requirements than other maple trees. The leaves are simple and palmately veined, 8–16 cm (3+1⁄4–6+1⁄4 in) long and 6–12 cm (2+1⁄4–4+3⁄4 in) broad, with deep angular notches between the five lobes. The 5–12 cm (2–4+3⁄4 in) long, slender stalks of the leaves mean that even a light breeze can produce a striking effect as the downy silver undersides of the leaves are exposed. The autumn color is less pronounced than in many maples, generally ending up a pale yellow, although some specimens can produce a more brilliant yellow and even orange and red colorations. The tree has a tendency to color and drop its leaves slightly earlier in autumn than other maples.


The flowers are in dense clusters, produced before the leaves in early spring,[5] with the seeds maturing in early summer. The fruit is a schizocarp of two single-seeded, winged samaras. The wing of each samara is about 3–5 cm (1+1⁄4–2 in) long. The fruit of this species is the largest among the maples native to its range. Although the wings provide for some transport by air, the fruit are heavy and are also transported by water. Silver maple and its close cousin red maple are the only Acer species which produce their fruit crop in spring instead of fall. The seeds of both trees have no epigeal dormancy and will germinate immediately. Seed production begins at 11 years of age and large crops are produced most years. Like most maples, silver maple can be variably dioecious (separate male or female trees) or monoecious (male and female flowers on the same tree) but dioecious trees are far more common. They can also change sex from year to year.[6]
On mature trunks, the bark is gray and shaggy. On branches and young trunks, the bark is smooth and silvery gray.[citation needed]
Cultivation and uses
[edit]
Wildlife uses the silver maple in various ways. In many parts of the eastern U.S., the large rounded buds are one of the primary food sources for squirrels during the spring, after many acorns and nuts have sprouted and the squirrels' food is scarce. The seeds are also a food source for chipmunks and birds. The bark can be eaten by beaver and deer. The trunks tend to produce cavities, which can shelter squirrels, raccoons, opossums, owls and woodpeckers, and are frequented by carpenter ants.[7] Additionally, the leaves serve as a source of food for species of Lepidoptera, such as the rosy maple moth (Dryocampa rubicunda).[8]
The wood can be used as pulp for making paper.[9] Lumber from the tree is used in furniture, cabinets, flooring, musical instruments, crates, and tool handles, because it is light and easily worked. Because of the silver maple's fast growth, it is being researched as a potential source of biofuels.[7] Silver maple produces a sweet sap but it is generally not used by commercial sugarmakers because its sugar content is lower than in other maple species.[10]
Silver maple is often planted as an ornamental tree because of its rapid growth and ease of propagation and transplanting. It is highly tolerant of urban situations and is frequently planted next to streets. However, its quick growth produces brittle wood which is commonly damaged in storms. The silver maple's root system is shallow and fibrous and easily invades septic fields and old drain pipes; it can also crack sidewalks and foundations. It is a vigorous resprouter, and if not pruned, will often grow with multiple trunks. Although it naturally is found near water, it can grow on drier ground if planted there. In ideal natural conditions, A. saccharinum may live up to 130 years but in urban environments often 80 or less.[citation needed]
Following World War II, silver maples were commonly used as a landscaping and street tree in suburban housing developments and cities due to their rapid growth, especially as a replacement for the blighted American elm. However, they fell out of favor for this purpose because of brittle wood, unattractive form when not pruned or trained, and tendency to produce large numbers of volunteer seedlings. Today the tree has fallen so far out of favor that some towns and cities have banned its use as a street tree.[11][12]
Silver maple's natural range encompasses most of the eastern US, the Midwestern US and southern Canada, that being Southern Ontario and southwestern Quebec. It is generally absent from the humid US coastal plain south of Maryland, so it is confined to the Appalachians in those states. It does not occur along the Gulf Coast or in Florida outside a few scattered locations in the panhandle.
It is commonly cultivated outside its native range, showing tolerance of a wide range of climates, and growing successfully as far north as central Norway. It also is in Anchorage, Alaska.[13] It can thrive in a Mediterranean climate, as at Jerusalem and Los Angeles, if summer water is provided. It is also grown in temperate parts of the Southern Hemisphere: Argentina, Uruguay, Venezuela, the southern states of Brazil (and in a few low-temperature locations within the states of São Paulo and Minas Gerais).[citation needed]
The silver maple is closely related to the red maple (Acer rubrum) and can hybridise with it. The hybrid is known as the Freeman maple (Acer × freemanii). The Freeman maple is a popular ornamental tree in parks and large gardens, combining the fast growth of silver maple with the less brittle wood, less invasive roots, and the beautiful bright red fall foliage of the red maple. The cultivar Acer × freemanii Autumn Blaze = 'Jeffersred'[14] has gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit.
The silver maple is the favored host of the maple bladder gall mite Vasates quadripedes.[15]
Native American ethnobotany
[edit]Native Americans used the sap of wild trees to make sugar, as medicine, and in bread. They used the wood to make baskets and furniture.[7] An infusion of bark removed from the south side of the tree is used by the Mohegan as cough medicine.[16] The Cherokee take an infusion of the bark to treat cramps, menstrual pains, dysentery, and hives.[17] They boil the inner bark and use it with water as a wash for sore eyes. They take a hot infusion of the bark to treat measles. They use the tree to make baskets, for lumber, building material, and for carving.[17]
References
[edit]- ^ Barstow, M.; Crowley, D. (2017). "Acer saccharinum". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2017: e.T193862A2287256. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2017-3.RLTS.T193862A2287256.en. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- ^ "Acer saccharinum". World Checklist of Selected Plant Families. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew – via The Plant List. Note that this website has been superseded by World Flora Online
- ^ a b c d e f g Gabriel, William J. (1990). "Acer saccharinum". In Burns, Russell M.; Honkala, Barbara H. (eds.). Hardwoods. Silvics of North America. Vol. 2. Washington, D.C.: United States Forest Service (USFS), United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) – via Southern Research Station.
- ^ "Acer saccharinum". State-level distribution map from the North American Plant Atlas (NAPA). Biota of North America Program (BONAP). 2014.
- ^ Jepson Flora Project (ed.). "Key to Acer". Jepson eFlora. The Jepson Herbarium, University of California, Berkeley.
- ^ "Silber-Ahorn: Expertenwissen für den Garten". www.naturadb.de (in German). Retrieved 2024-05-02.
- ^ a b c Geyer, W. A.; J. Dickerson; J. M. Row (2010). "Plant Guide for Silver Maple (Acer saccharinum L.)" (PDF). Plant Guide. Manhattan, KS: U.S. Department of Agriculture - Natural Resources Conservation Service. Retrieved 2012-10-10.
- ^ "Dryocampa rubicunda (rosy maple moth)". Animal Diversity Web. Retrieved 2017-11-14.
- ^ "Silver Maple, Acer saccharinum L." Maple Field Guide. MapleInfo.org. Archived from the original on 2013-01-09. Retrieved 2012-10-10.
- ^ Geyer, W. A.; J. Dickerson; J. M. Row (2010). "Plant Guide for Silver Maple (Acer saccharinum L.)" (PDF). USDA- Natural Resources Conservation Service.
- ^ "Approved Street Tree List for Denver's Public Rights-of-way" (PDF). denvergov.org. Denver Office of the City Forester. Retrieved 2018-11-21.
- ^ "Prohibited Street Trees/Shrubs". cityoflodi.us. City of Lodi. Retrieved 2018-11-21.
- ^ Tony. "Trees Near Their Limits -- Alaska". Retrieved 2023-05-31.
- ^ "Acer × freemanii Autumn Blaze = 'Jeffersred'". Royal Horticultural Society. Retrieved 29 December 2017.
- ^ Redfern M.; Shirley P.R.; Bloxham M. (2011). British Plant Galls (Second ed.). Preston Montford: Field Studies Council. p. 23. ISBN 978-1-85153-284-1.
- ^ Tantaquidgeon, Gladys. "1928 Mohegan Medicinal Practices, Weather-Lore and Superstitions". SI-BAE Annual Report #43: 264-270 (p. 269)
- ^ a b Hamel, Paul B. and Mary U. Chiltoskey, 1975, Cherokee Plants and Their Uses -- A 400 Year History, Sylva, N.C.: Herald Publishing Co., page 44
External links
[edit]- United States Department of Agriculture Plants Profile: Acer saccharinum
- University of Connecticut Plant Database: Silver Maple
- Trees of Western North Carolina: Silver Maple
- Acer saccharinum images from Vanderbilt University
- Portrait of the Earth, Winter ID pictures
- Plant Maps, Interactive Distribution Map for Acer saccharinum Archived 2013-01-13 at the Wayback Machine
- photo of herbarium specimen at Missouri Botanical Garden, collected in Missouri in 1989