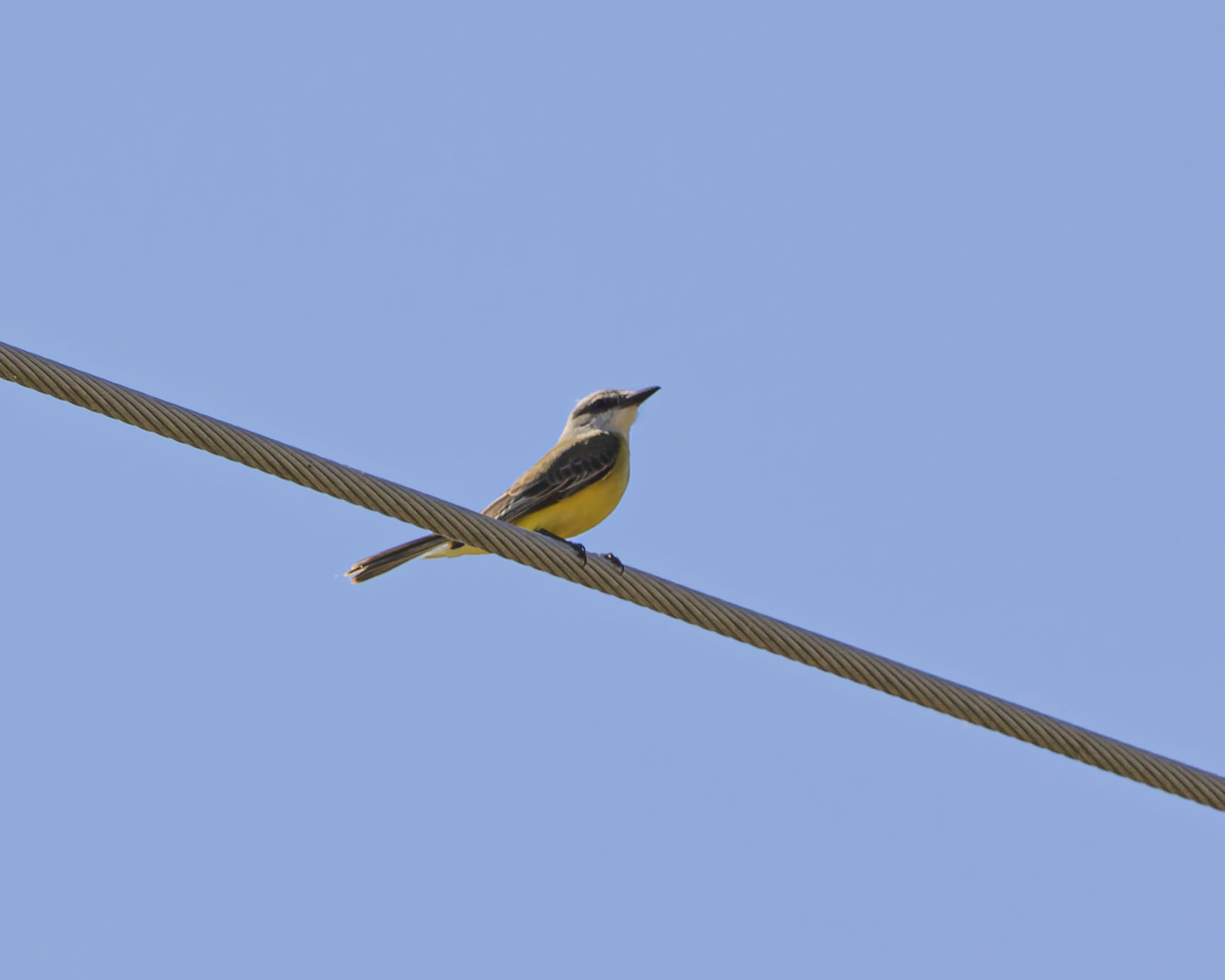
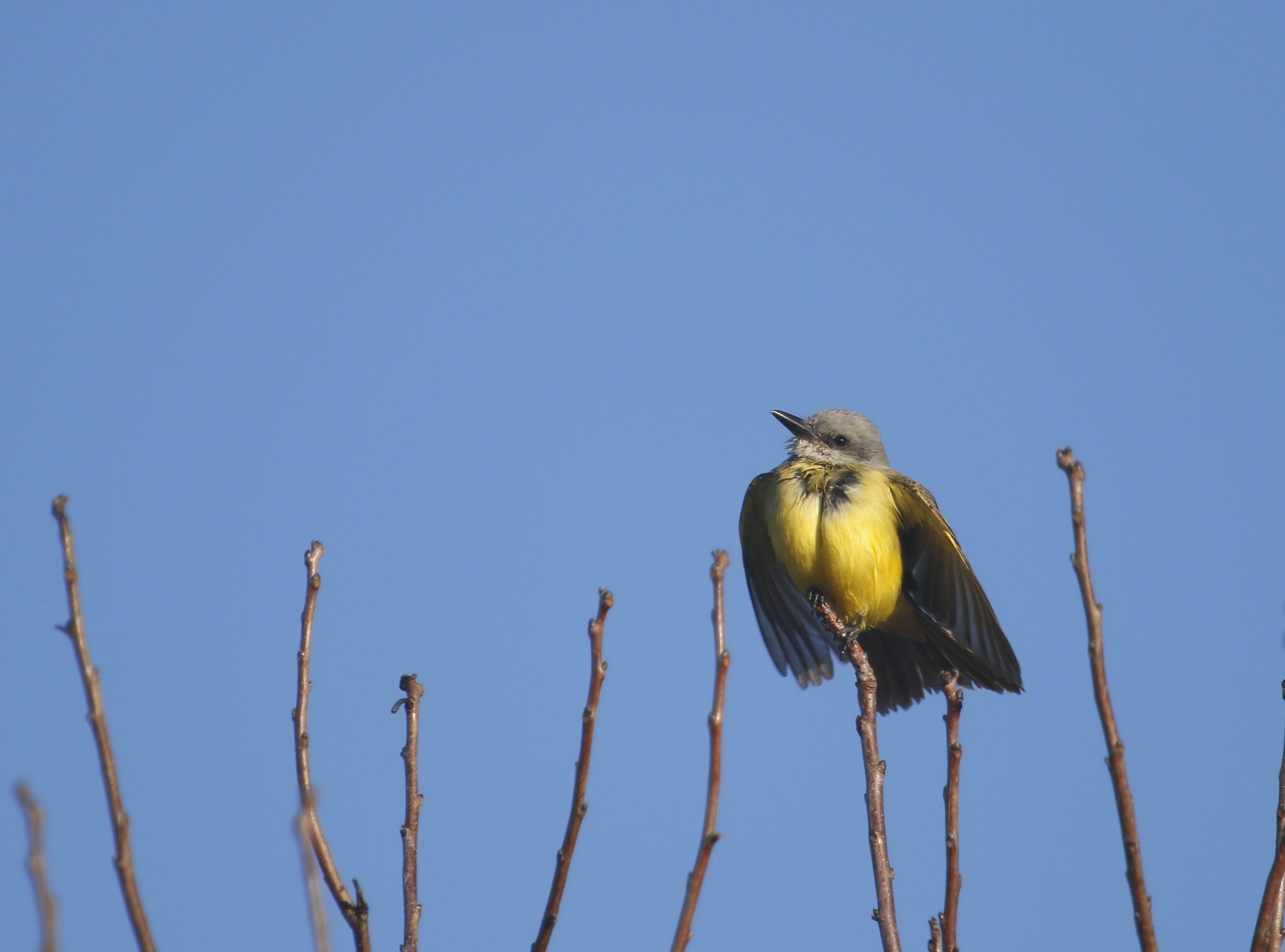
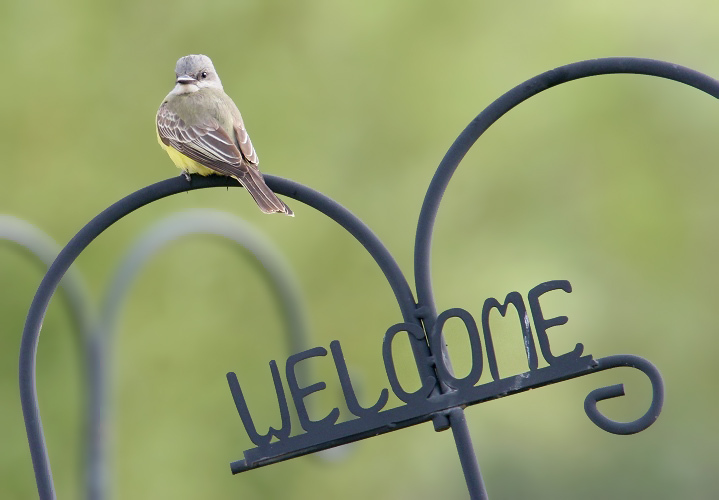
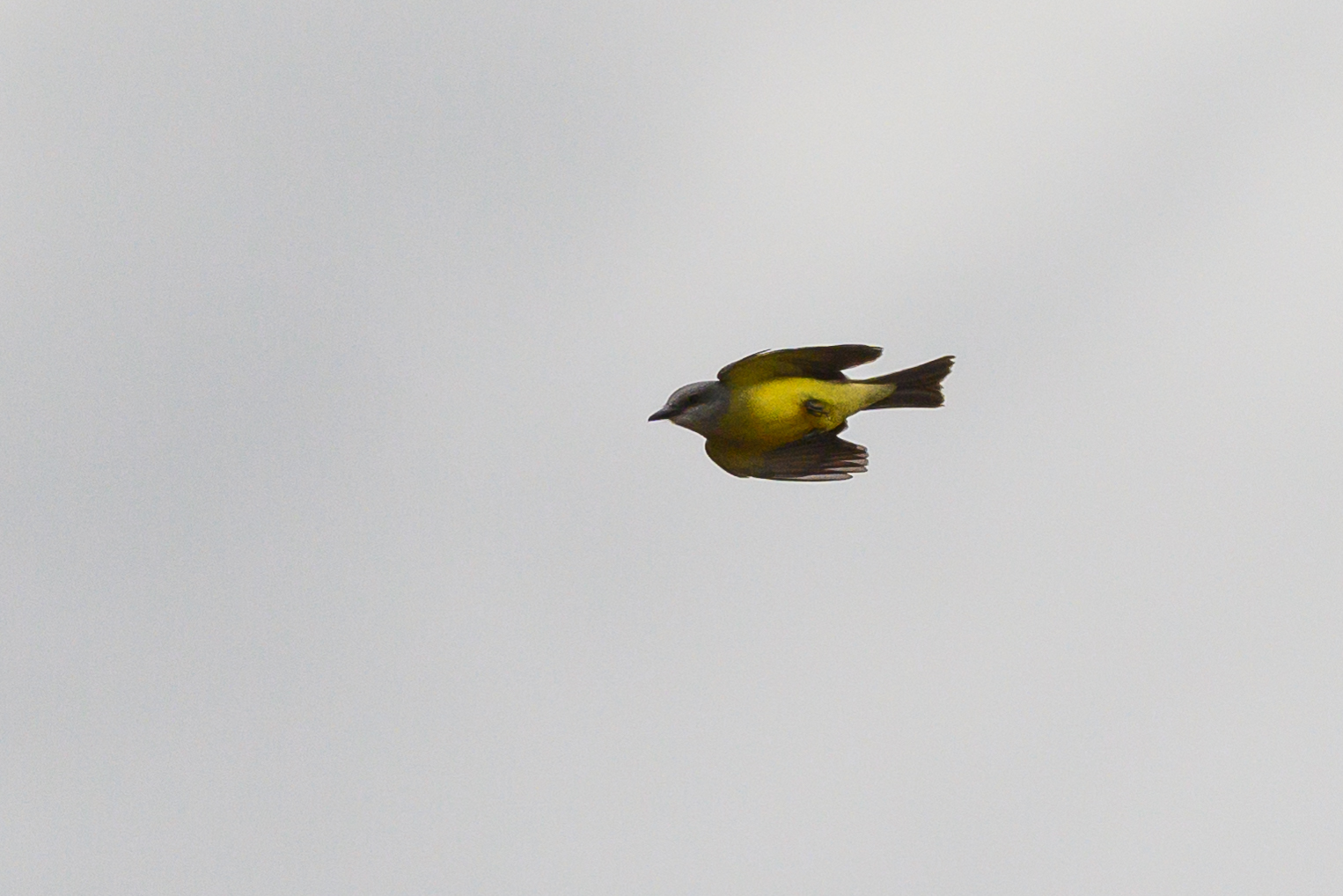
Map Snapshot



38 Records
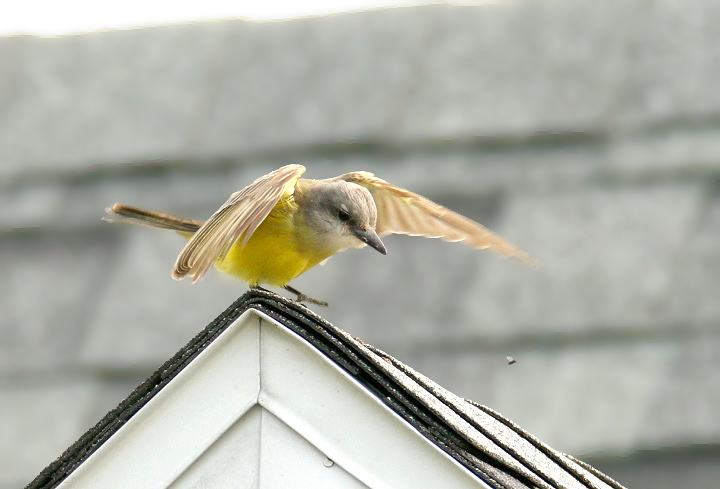
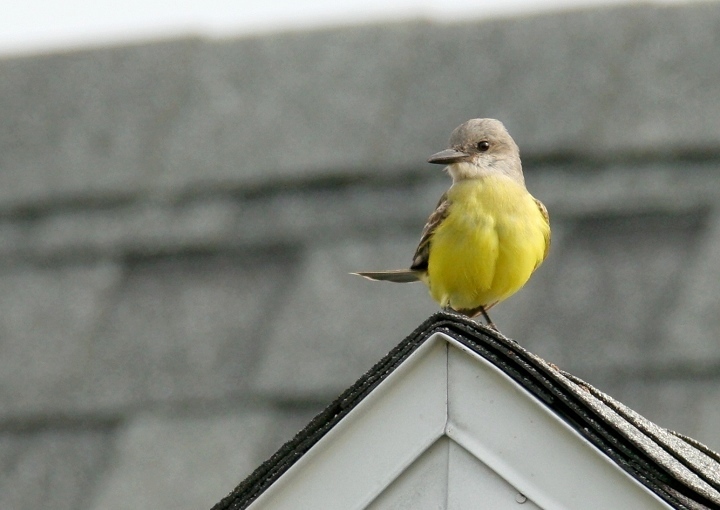
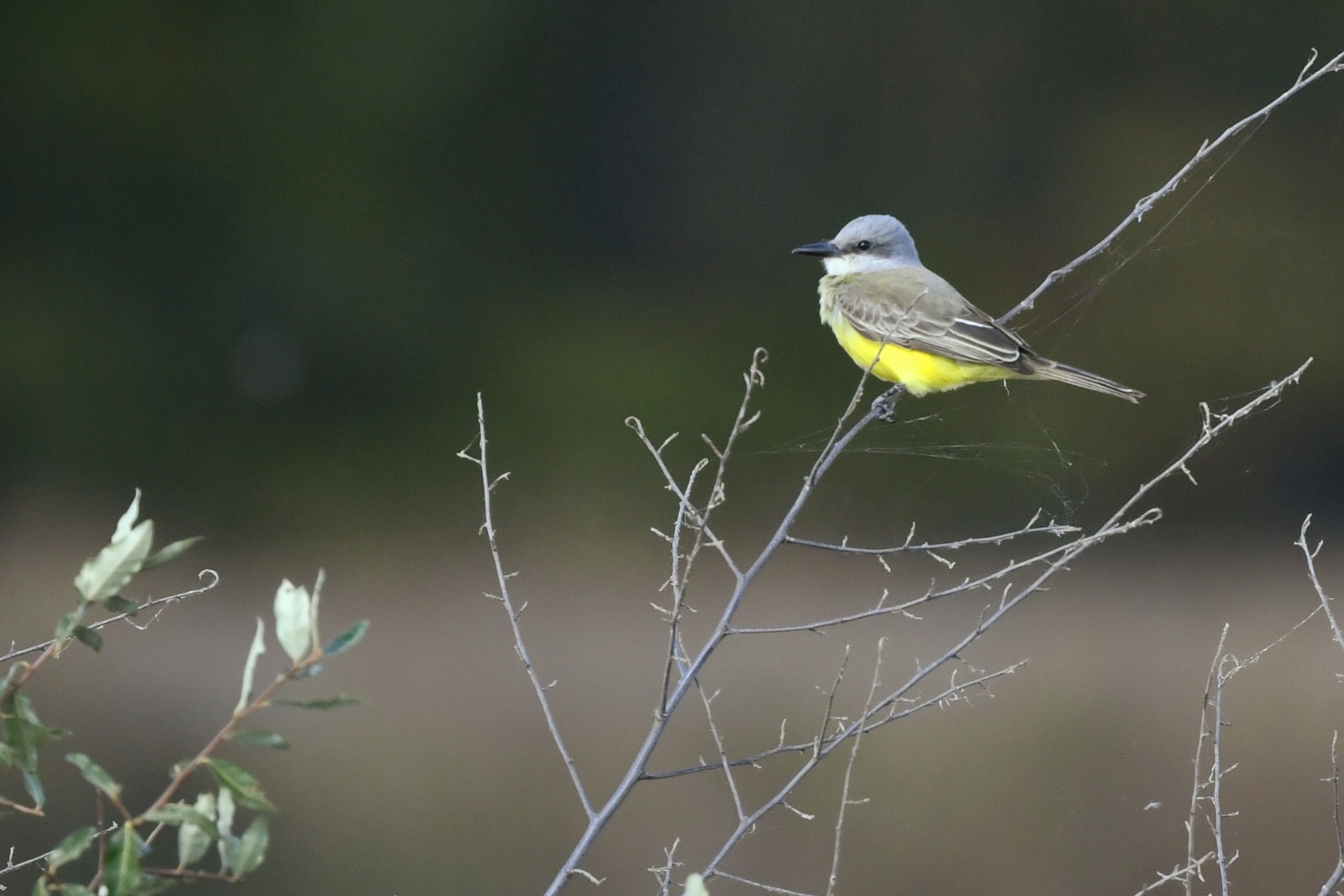
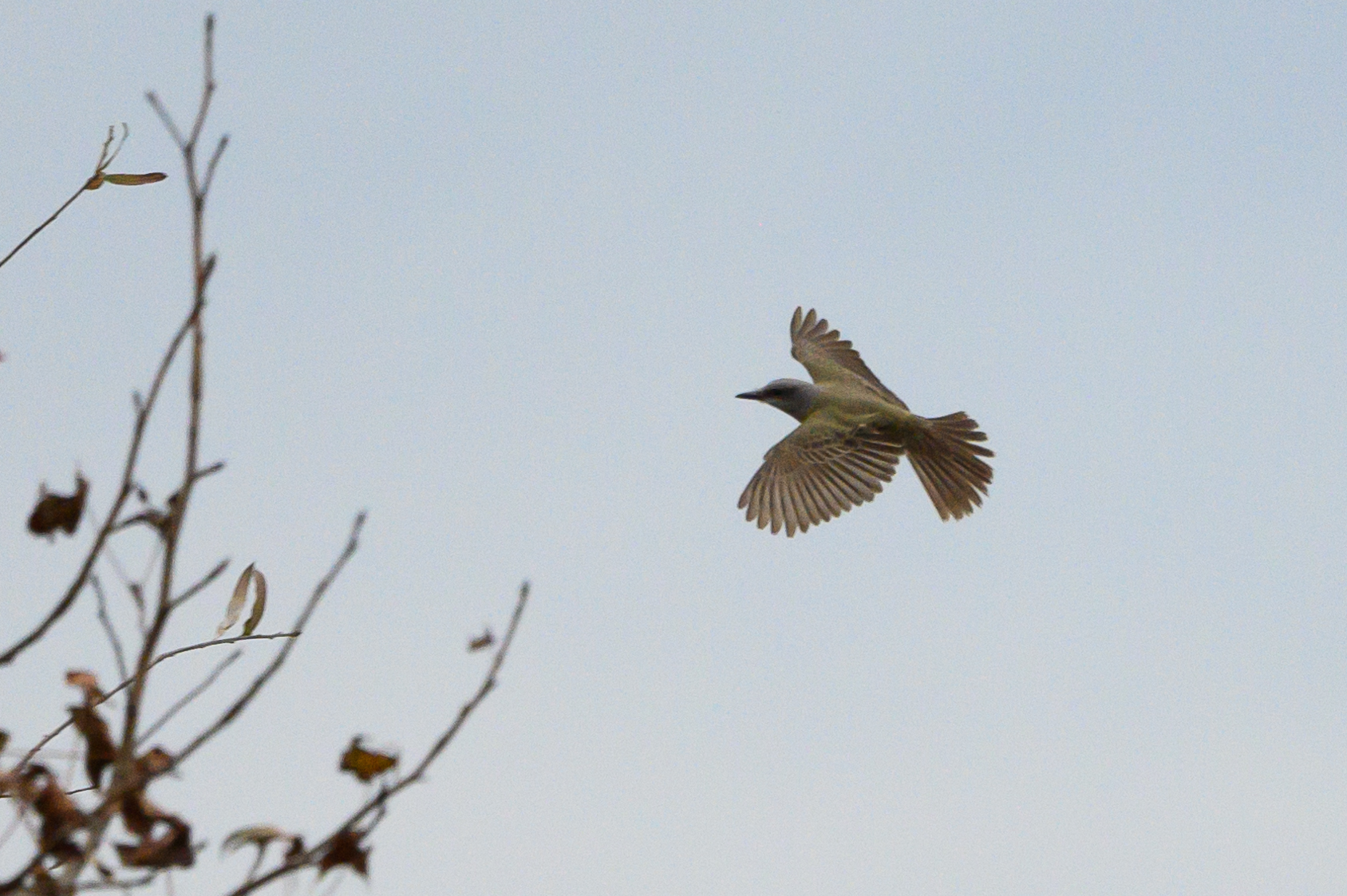
Tropical Kingbird in Dorchester Co., Maryland (10/31/2021). (c) Stephen John Davies, all rights reserved. - Stephen John Davies via iNaturalist.
Status
Maryland has two records of this very rare vagrant to the East Coast - Somerset Co. (MD/DCRC #2006-284) and July 2019 (T. Johnson, M. Hafner) (eBird).
Description
Compare Couch's Kingbird and other Tyrannus flycatchers. Voice is the most reliable way to distinguish Tropical vs. Couch's.
Seasonality Snapshot
Source: Wikipedia
| Tropical kingbird | |
|---|---|

| |
| T. m. melancholicus The Pantanal, Brazil | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Tyrannidae |
| Genus: | Tyrannus |
| Species: | T. melancholicus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Tyrannus melancholicus Vieillot, 1819
| |
| |
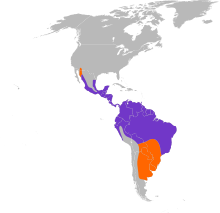
| Purple = year-round range; orange = breeding range | |
The tropical kingbird (Tyrannus melancholicus) is a large tyrant flycatcher. This bird breeds from southern Arizona and the lower Rio Grande Valley of Texas in the United States through Central America, South America as far as south as central Argentina and eastern Peru, and on Trinidad and Tobago. Birds from the northernmost and southern breeding areas migrate to warmer parts of the range after breeding.
Taxonomy
[edit]The tropical kingbird was formally described in 1819 by the French ornithologist Louis Pierre Vieillot under the binomial name Tyrannus melancholicus.[2] Vieillot based his description on the Suirirí-Guazú that had been described by the Spanish naturalist Félix de Azara in 1805 in his book Apuntamientos para la historia natural de los páxaros del Paragüay y Rio de la Plata.[3][4] The specific epithet is Latin meaning "melancholic" (that is "bad-tempered").[5]
Three subspecies are recognised:[6]
- T. m. satrapa (Cabanis & Heine, 1860) – southwest USA to north Colombia, north Venezuela and Trinidad
- T. m. despotes (Lichtenstein, MHK, 1823) – northeast Brazil
- T. m. melancholicus Vieillot, 1819 – north South America to central Argentina
Description
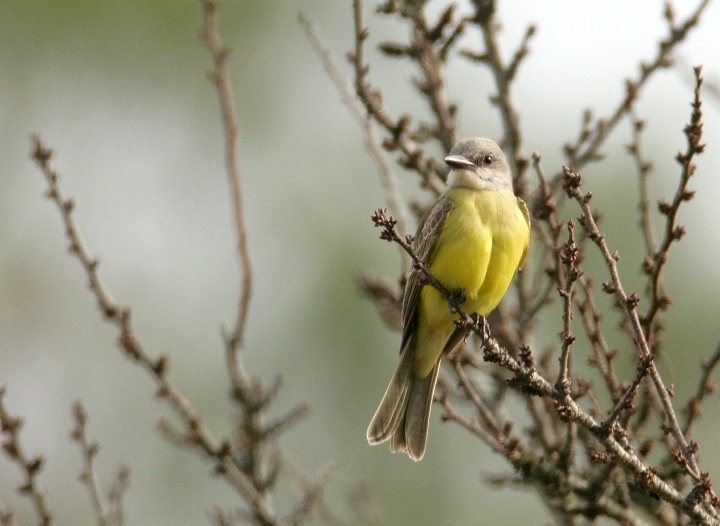
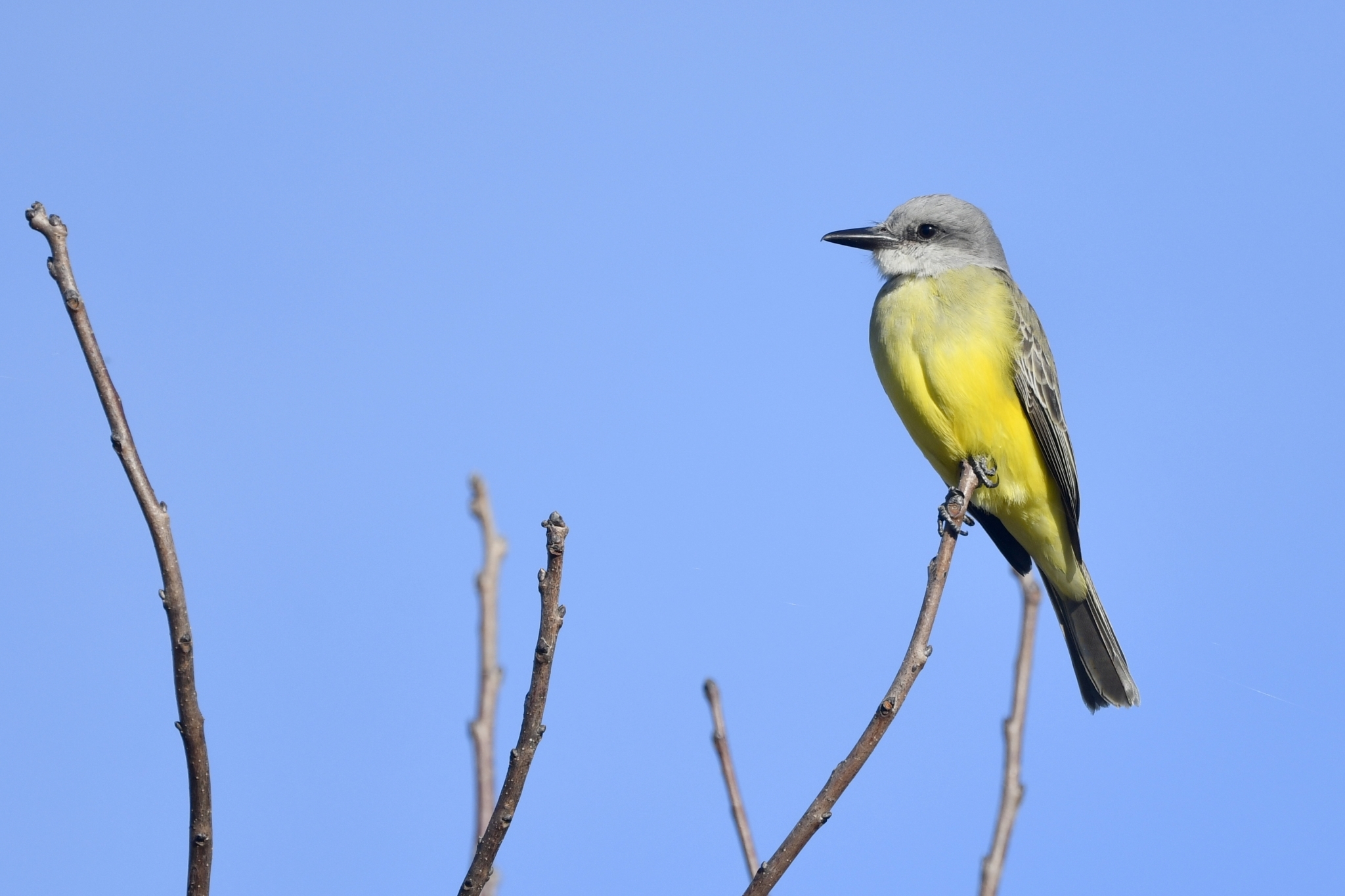
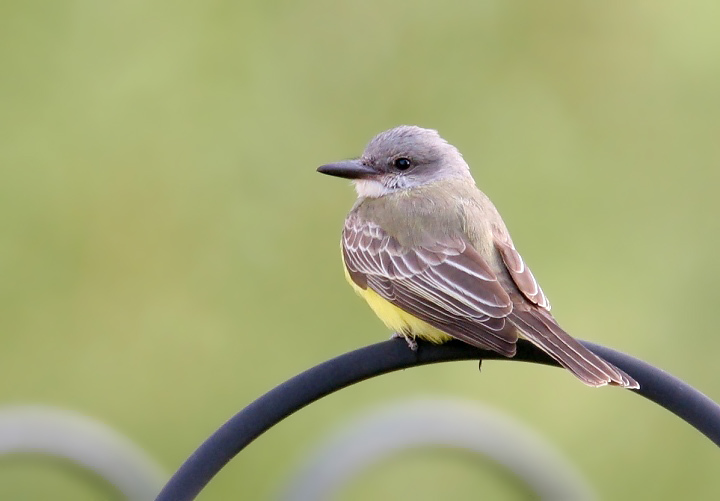
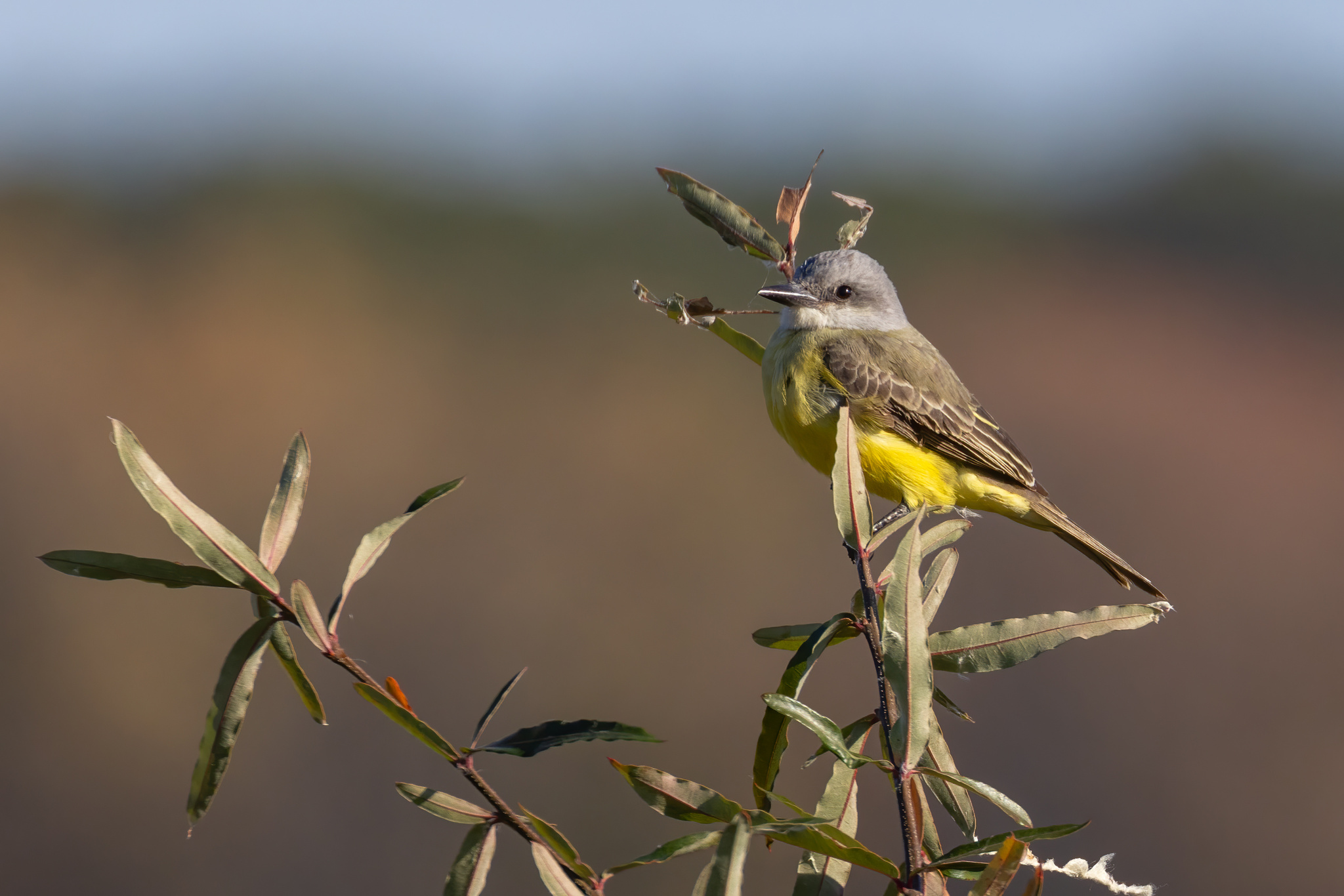
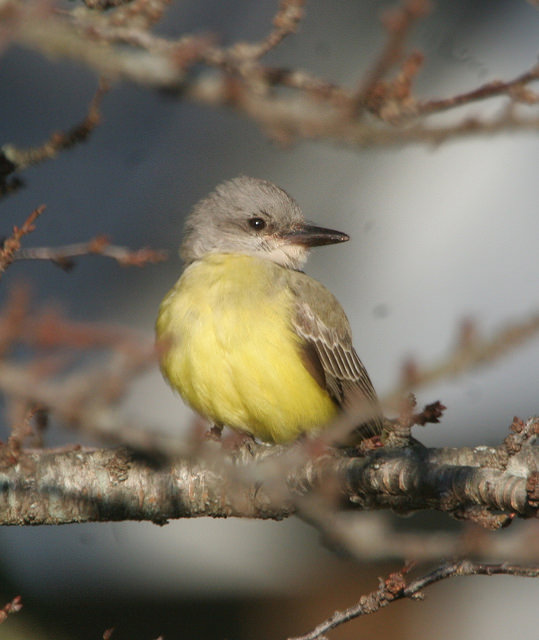
[edit]An adult tropical kingbird is 22 cm (8.7 in) long, weighs 39 g (1.4 oz) and has a wingspan range of 38–41 cm.[7] The head is pale gray, with a darker eye mask, an orange crown stripe, and a heavy gray bill. The back is grayish-green, and the wing and forked tail are brown. The throat is pale gray, becoming olive on the breast, with the rest of the underparts being yellow. The sexes are similar, but young birds have pale buff edges on the wing coverts.
Behaviour and ecology
[edit]Breeding
[edit]Tropical kingbirds appear to be monogamous. In most parts of the species' range, they are permanent residents and remain together in pairs year-round.(Sibley 2014)[page needed] The call is a high-pitched twittering trill, tree-e-e-e-e-e-e, with a more complex version sung by the male at dawn.
Their breeding habitat is semi-open areas with trees and shrubs, including gardens and roadsides. Tropical kingbirds like to observe their surroundings from a prominent open perch, usually high in a tree, undertaking long flights to acrobatically catch insects in mid-air (hawking), sometimes hovering to pick food off vegetation (gleaning).[8][9] The insects preyed upon include beetles, bees, wasps, termites, butterflies, moths, dragonflies and grasshoppers.[10][11] They also eat some berries and fruit from such diverse species as tamanqueiro (Alchornea glandulosa), common guava (Psidium guajava), the Annonaceae, Cymbopetalum mayanum and gumbo-limbo (Bursera simaruba);[9][10][12] foraging for these even in disturbed habitat. As they keep mainly to the upper levels of trees, they find little profit in following mixed-species feeding flocks in the understory.[13]
Aplomado falcons have been known to prey on adult tropical kingbirds, while eggs and young have been attacked by swallow-tailed kites and chestnut-mandibled toucans.[11][10] These birds aggressively defend their territory against intruders, even much larger birds such as magnificent frigatebirds, toucans, caracaras or hawks. In a study in Parque Nacional de La Macarena of Colombia, parasitism by microfilariae and trypanosomas (presumably T. everetti) was infrequently recorded in tropical kingbirds.[14]
The male and female inspect potential sites together before selecting a site, typically a fork or crotch high in a tree (up to 20 m (66 ft) high) but sometimes just a few metres above water.(Sibley 2014)[page needed] The female builds a bulky, sloppy-looking, shallow nest of vines, rootlets, twigs, weeds, and grasses; it is unlined or lined with hair. Nests average about 13.2 cm (5.2 in) across and 7.6 cm (3.0 in) tall, with interior cup about 7.6 cm (3.0 in) across and 4.1 cm (1.6 in) deep.[15][page needed]
The female incubates the typical clutch of two to four eggs for approximately 16 days, and the nestlings fledge in another 18 or 19 days. The eggs are whitish or pale pink with variable amounts of dark blotching.[15][page needed]
Status
[edit]The tropical kingbird is one of the most widespread and conspicuous inhabitants of open forest, forest edge, scrub and agricultural land from the southwestern United States south to Argentina (Jahn, Stouffer, & Chesser, 2013). As a result, the bird is considered as being of Least Concern and their population is increasing, according to the IUCN.[1] According to Partners in Flight, global estimates of tropical kingbird breeding population is around 200 million. They rate the species as 4 out of 20 on the continental concern scale, indicating that this species is of low conservation concern.[16]
Gallery
[edit]References
[edit]Citations
[edit]- ^ a b BirdLife International (2016). "Tyrannus melancholicus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22700485A93779037. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22700485A93779037.en. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ^ Vieillot, Louis Pierre (1817). Nouveau dictionnaire d'histoire naturelle, appliquée aux arts, à l'agriculture, à l'économie rurale et domestique, à la médecine, etc (in French). Vol. Tome 35. Paris: Deterville. pp. 84–85. doi:10.5962/bhl.title.20211.
- ^ Azara, Félix de (1805). "Num. CXCVIII Del Suirirí-Guazú". Apuntamientos para la historia natural de los páxaros del Paragüay y Rio de la Plata (in Spanish). Vol. 2. Madrid: Imprenta de la Hija de Ibarra. p. 152.
- ^ Traylor, Melvin A. Jr, ed. (1979). Check-List of Birds of the World. Vol. 8. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Museum of Comparative Zoology. p. 223.
- ^ Jobling, James A. (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. p. 246. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.
- ^ Gill, Frank; Donsker, David; Rasmussen, Pamela, eds. (July 2020). "Tyrant flycatchers". IOC World Bird List Version 11.1. International Ornithologists' Union. Retrieved 24 May 2021.
- ^ Oiseaux.net. "Tyran mélancolique - Tyrannus melancholicus - Tropical Kingbird". Oiseaux.net. Retrieved 2020-09-26.
- ^ de A. Gabriel, Vagner & Pizo, Marco A. (2005): Foraging behavior of tyrant flycatchers (Aves, Tyrannidae) in Brazil. Revista Brasileira de Zoologia 22 (4): 1072–1077 [English with Portuguese abstract]. doi:10.1590/S0101-81752005000400036 PDF fulltext
- ^ a b Pascotto, Márcia Cristina (2006): Avifauna dispersora de sementes de Alchornea glandulosa (Euphorbiaceae) em uma área de mata ciliar no estado de São Paulo [Seed dispersal of Alchornea glandulosa (Euphorbiaceae) by birds in a gallery forest in São Paulo, southeastern Brazil.]. Revista Brasileira de Ornitologia 14 (3): 291–296 [Portuguese with English abstract]. PDF fulltext Archived 2010-11-02 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b c "Tyrannus melancholicus (Tropical Kingbird)" (PDF). Sta.uwi.edu. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ a b "ADW: Tyrannus melancholicus: INFORMATION". Animaldiversity.org. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ Foster, Mercedes S. (2007): The potential of fruiting trees to enhance converted habitats for migrating birds in southern Mexico. Bird Conservation International 17 (1): 45–61. doi:10.1017/S0959270906000554
- ^ Machado, C. G. (1999): A composição dos bandos mistos de aves na Mata Atlântica da Serra de Paranapiacaba, no sudeste brasileiro [Mixed flocks of birds in Atlantic Rain Forest in Serra de Paranapiacaba, southeastern Brazil]. Revista Brasileira de Biologia 59 (1): 75–85 [Portuguese with English abstract]. doi:10.1590/S0034-71081999000100010 PDF fulltext
- ^ Basto, Natalia; Rodríguez, Oscar A.; Marinkelle, Cornelis J.; Gutierrez, Rafael & Matta, Nubia Estela (2006): Haematozoa in birds from la Macarena National Natural Park (Colombia). Caldasia 28 (2): 371–377 [English with Spanish abstract]. PDF fulltext
- ^ a b Sibley 2014.
- ^ Partners in Flight 2017.
General sources
[edit]- Jahn, A. E., P. C. Stouffer, and R. T. Chesser (2013). T. S. Schulenberg (ed.). "Tropical Kingbird (Tyrannus melancholicus), version 1.0". Neotropical Birds Online. Ithaca, NY: Cornell Lab of Ornithology. doi:10.2173/nb.trokin.01.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Sibley, D. A. (2014). The Sibley Guide to Birds (2nd ed.). New York: Alfred A. Knopf.
- Partners in Flight (2017). Avian Conservation Assessment Database.
Further reading
[edit]- Skutch, Alexander F. (1960). "Tropical kingbird" (PDF). Life Histories of Central American Birds II. Pacific Coast Avifauna, Number 34. Berkeley, California: Cooper Ornithological Society. pp. 349–352.
External links
[edit]- "Tropical kingbird media". Internet Bird Collection.
- Tropical kingbird photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)
- Tropical kingbird species account at Neotropical Birds (Cornell Lab of Ornithology)
- Interactive range map of Tyrannus melancholicus at IUCN Red List
- IUCN. (2019). Tropical Kingbird. Retrieved from: [1]
- Nesting Tyrannus melancholicus




















