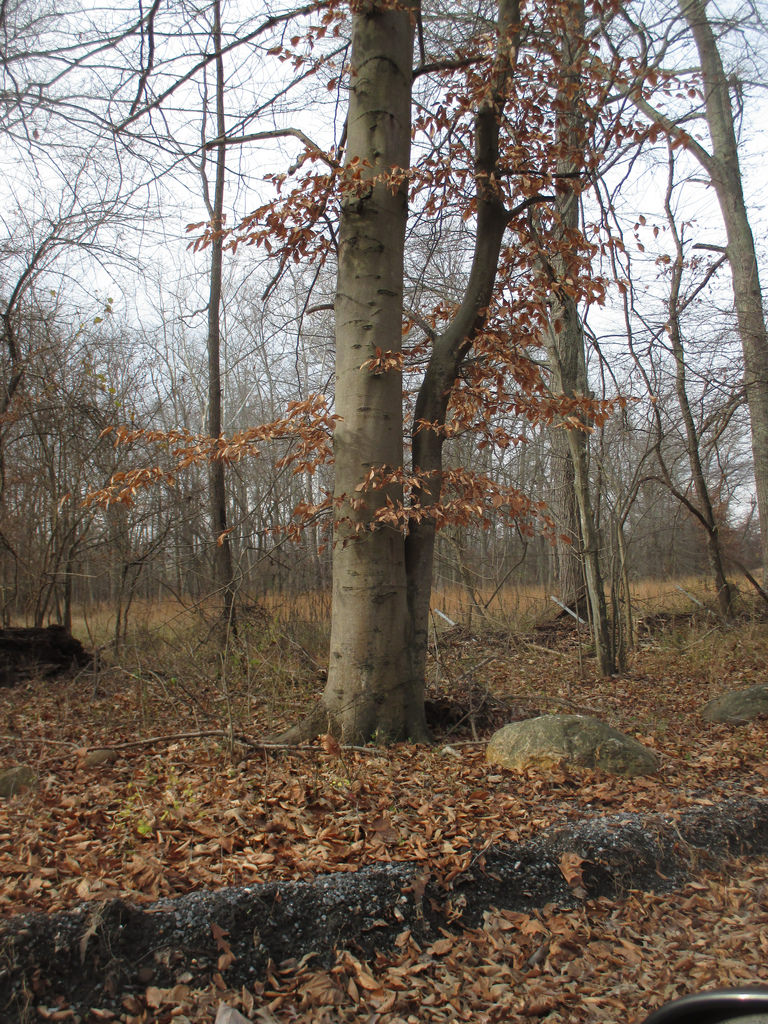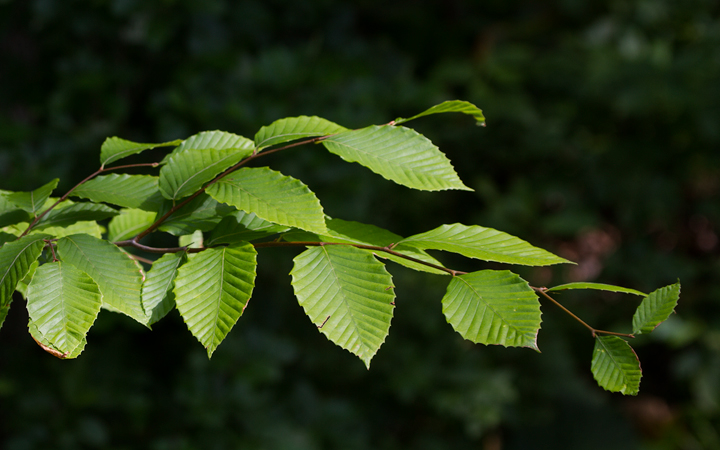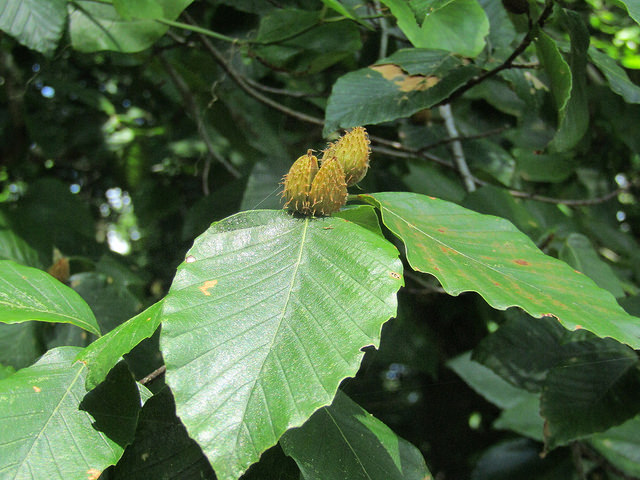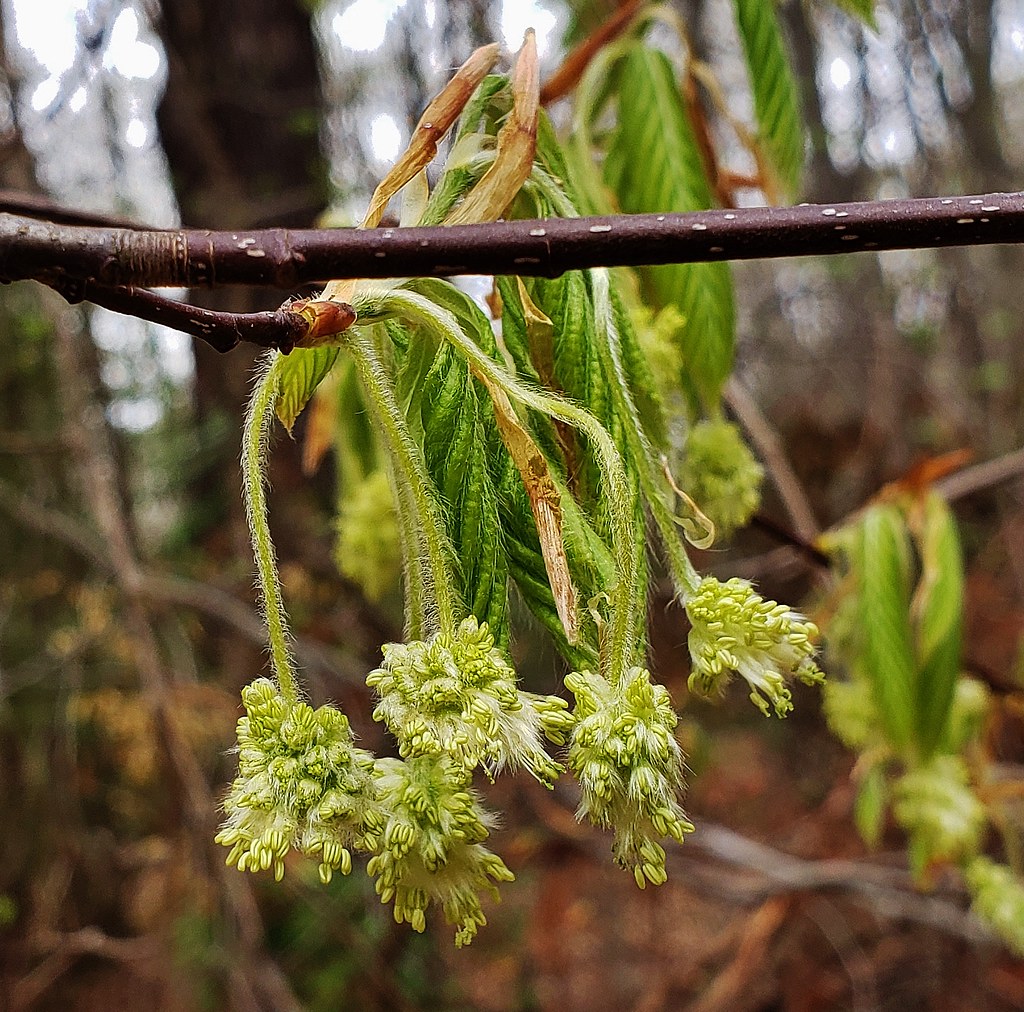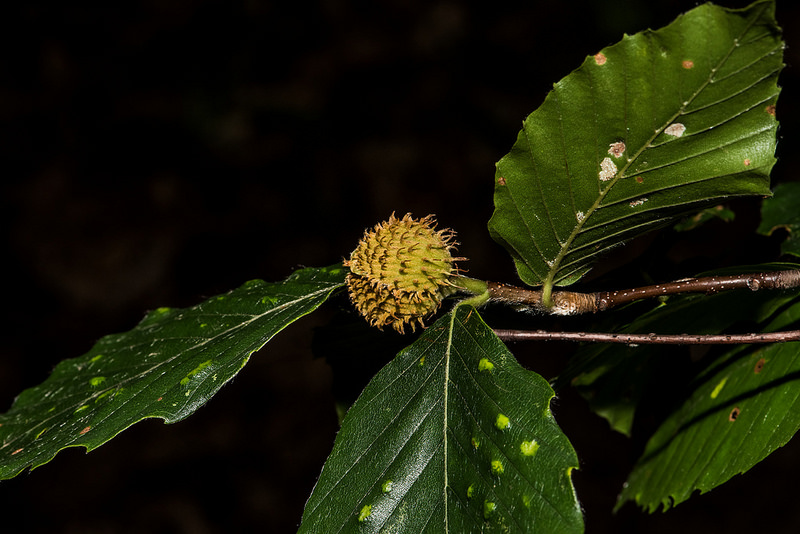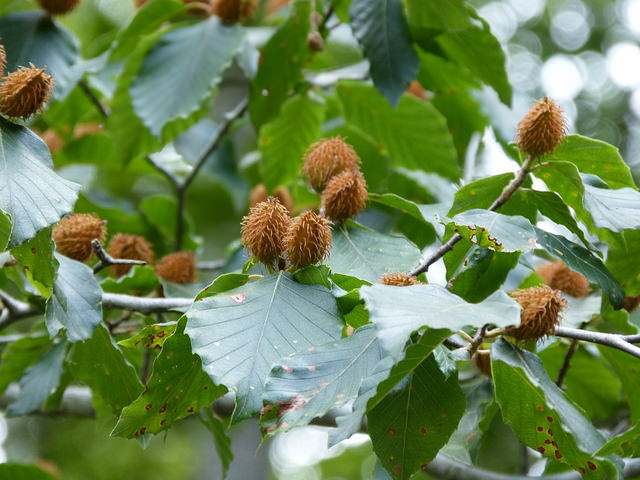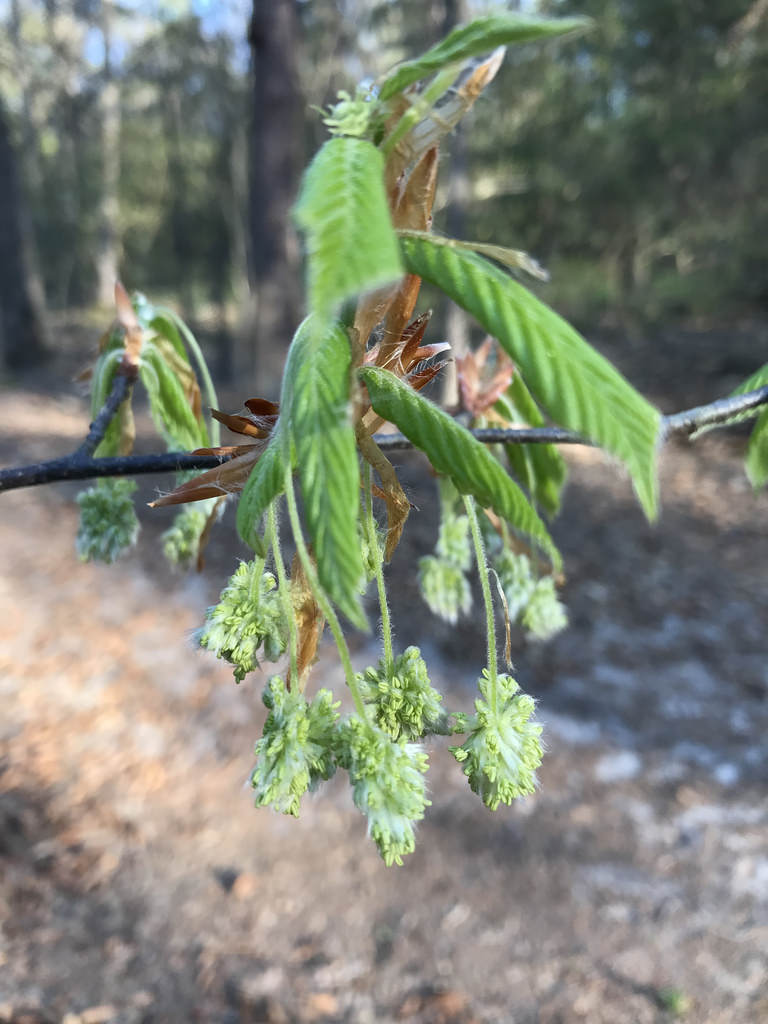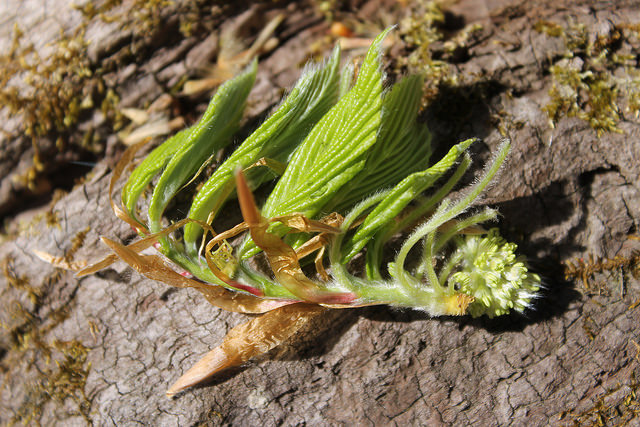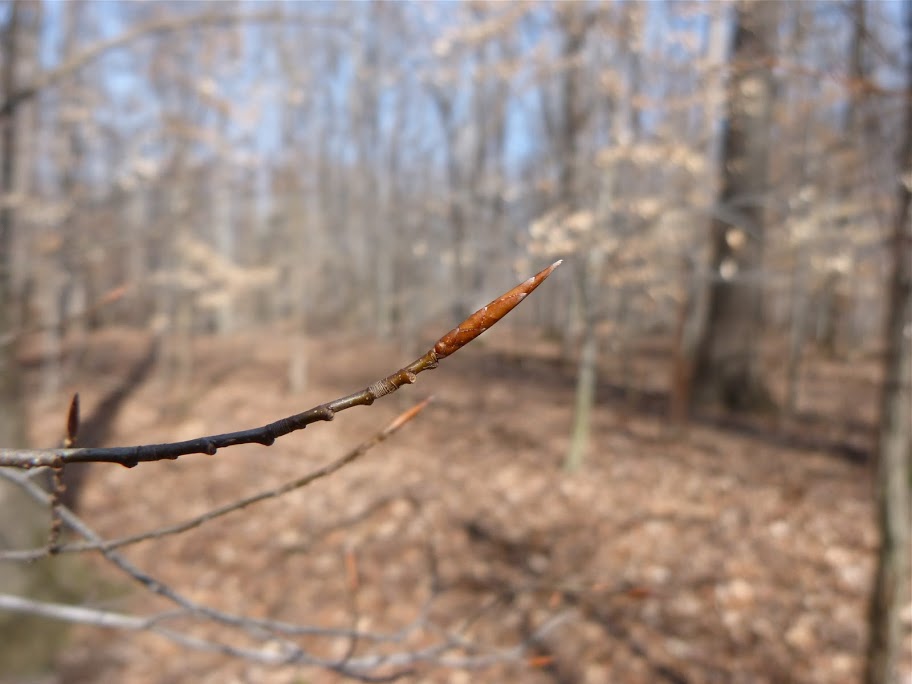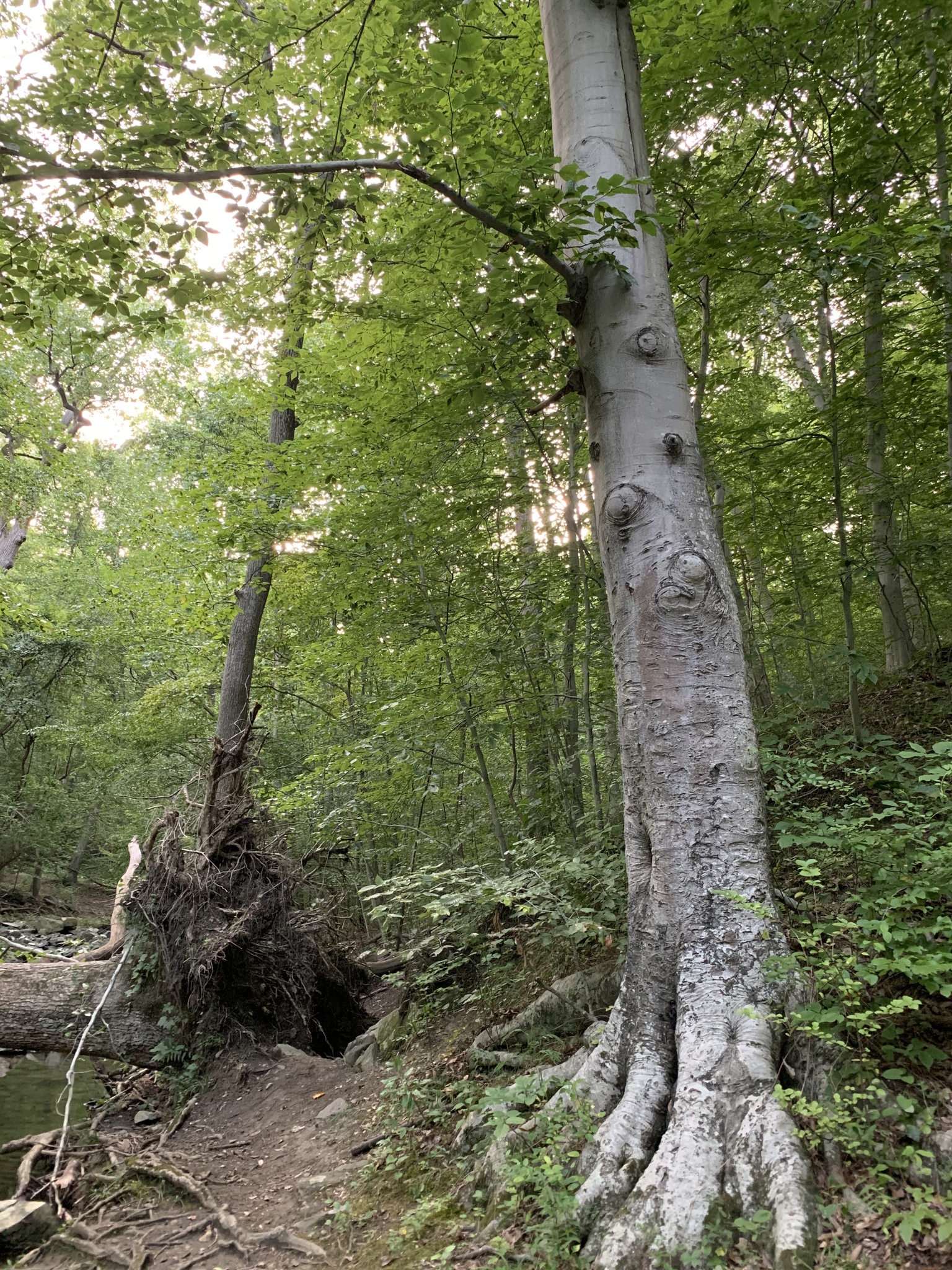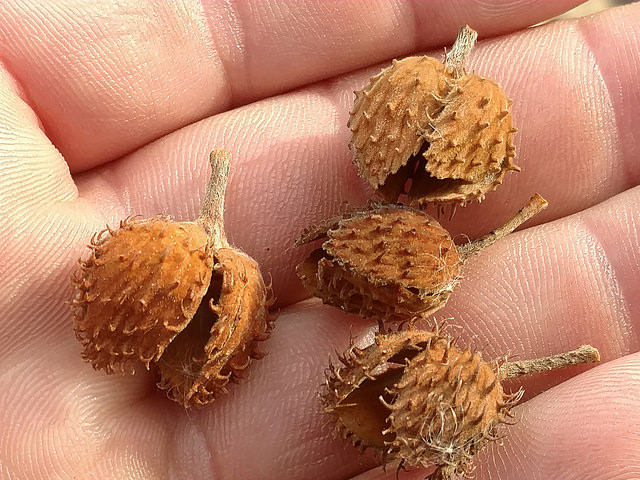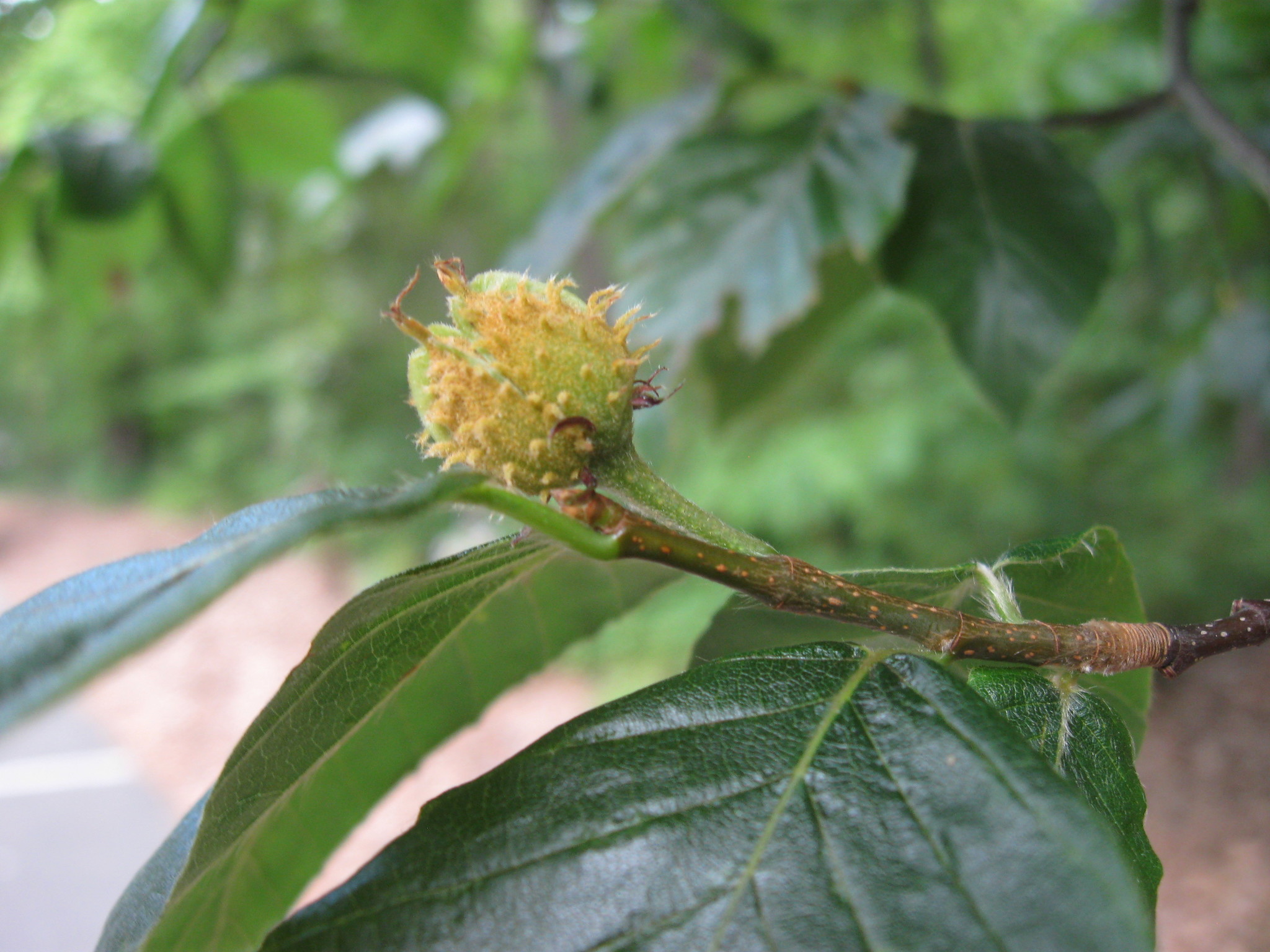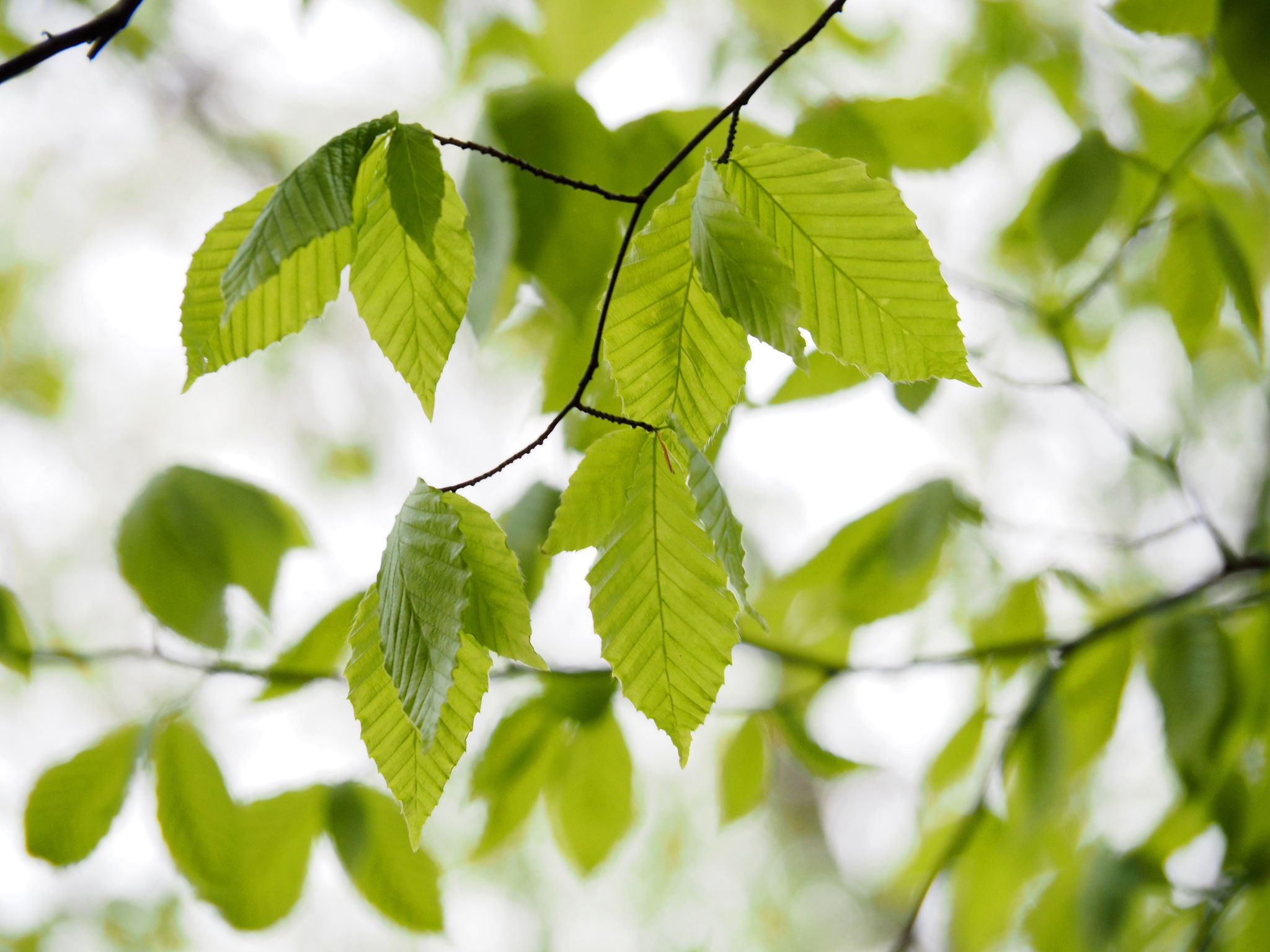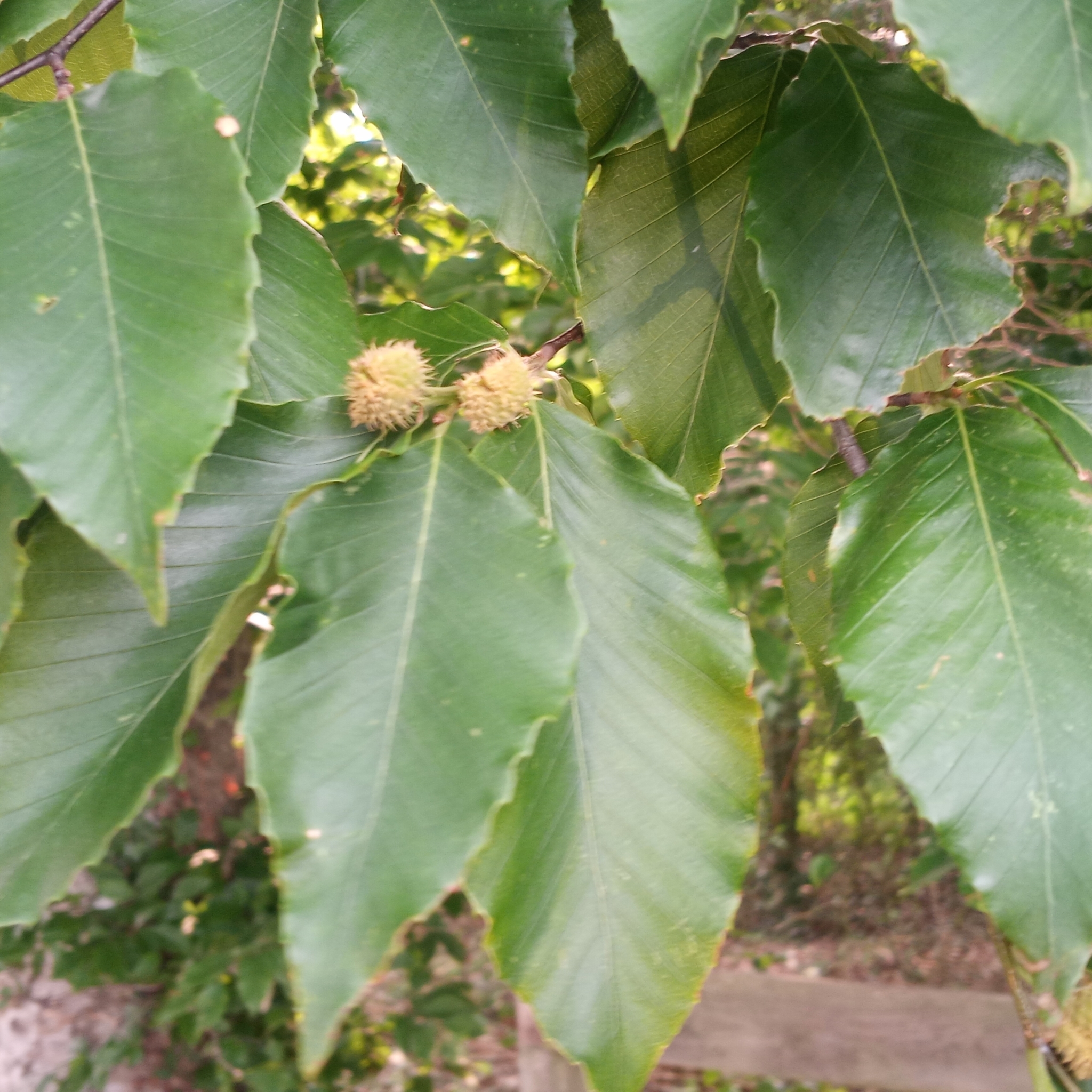



















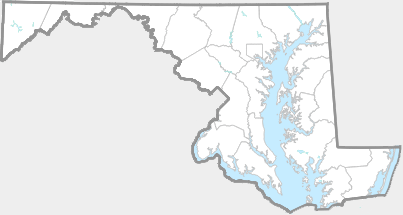
Grows in rich, moist woods, sometimes in nearly pure stands (Brown and Brown, 1972). Occurs in every county in Maryland.
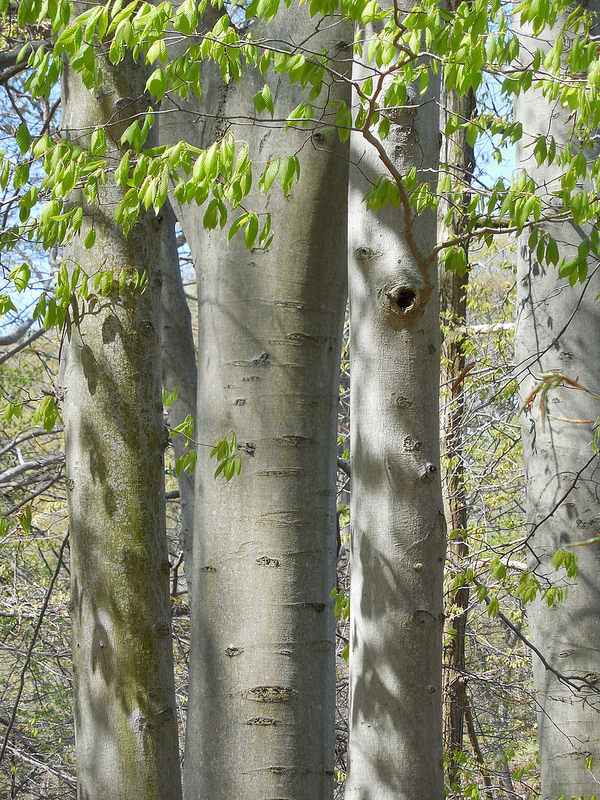
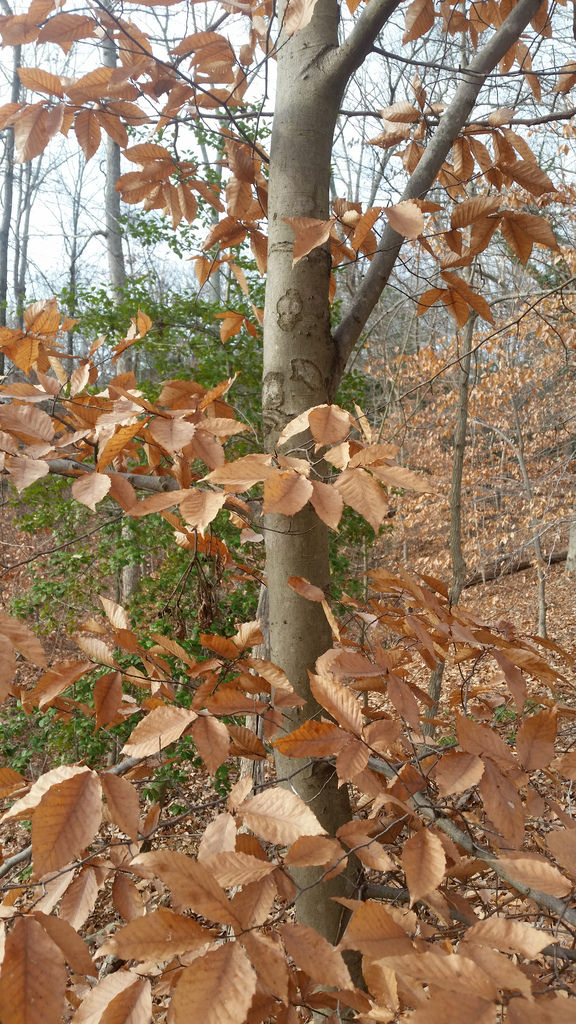
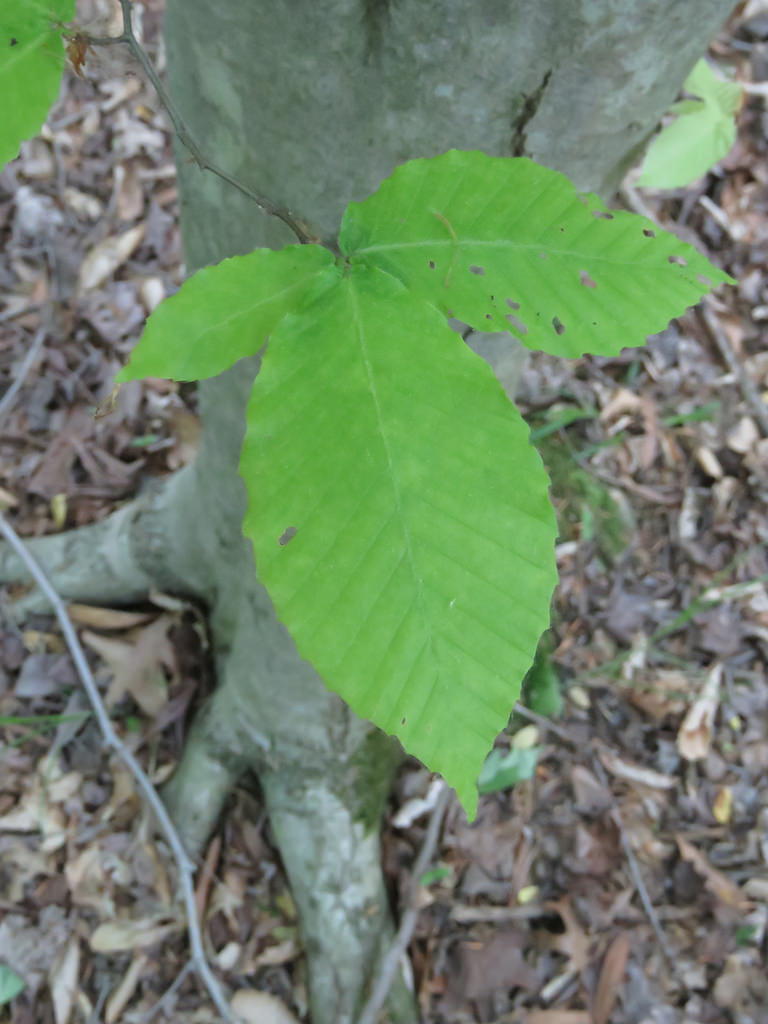
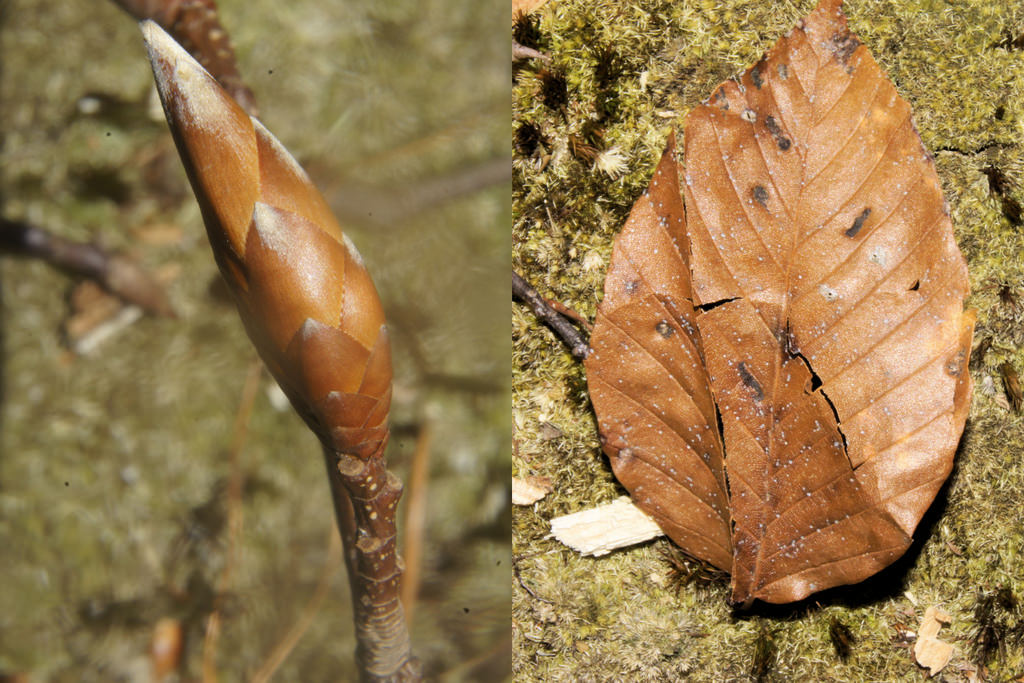
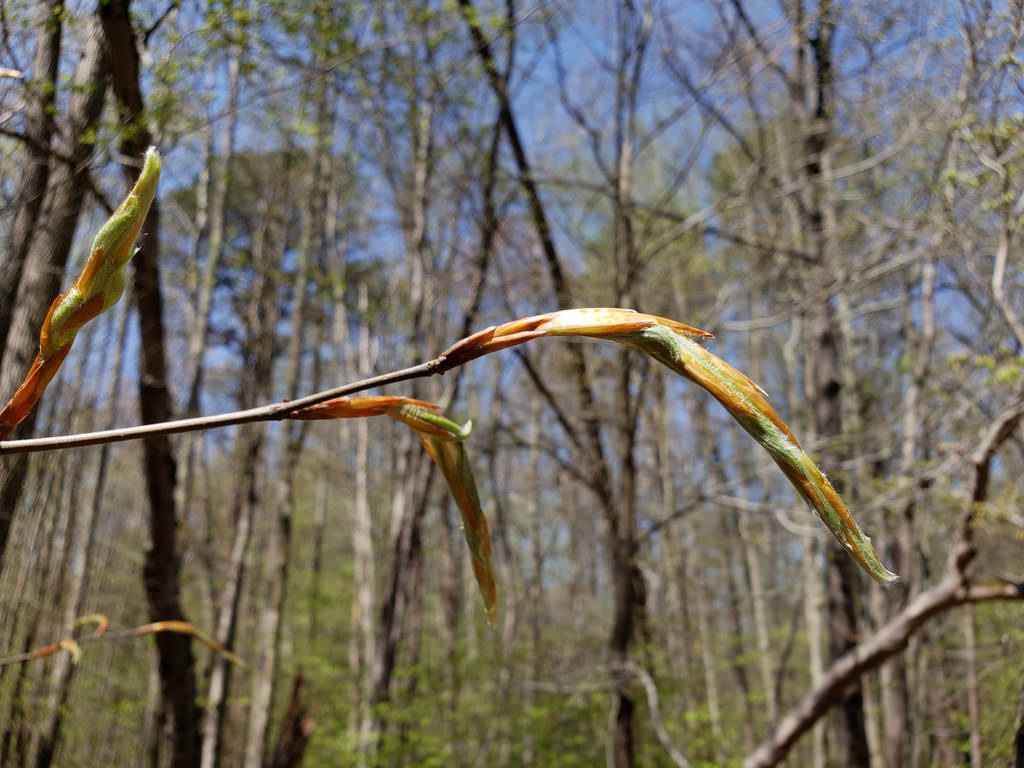
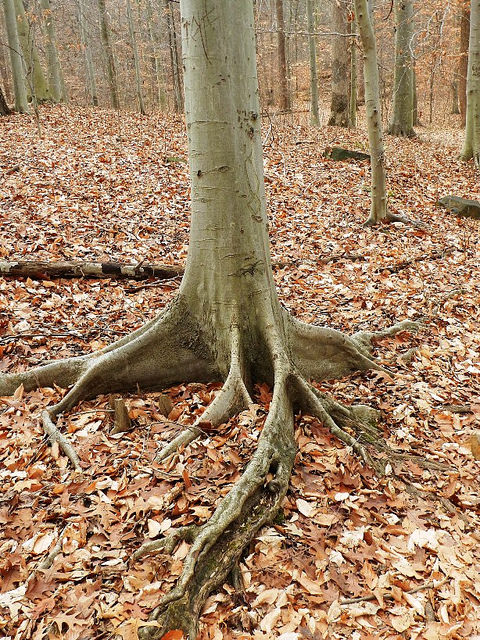
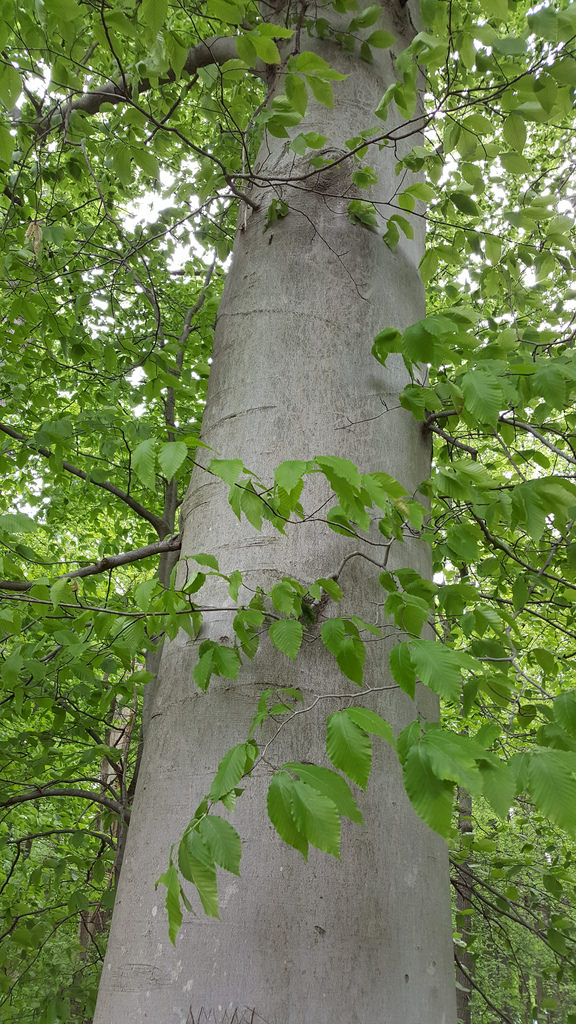
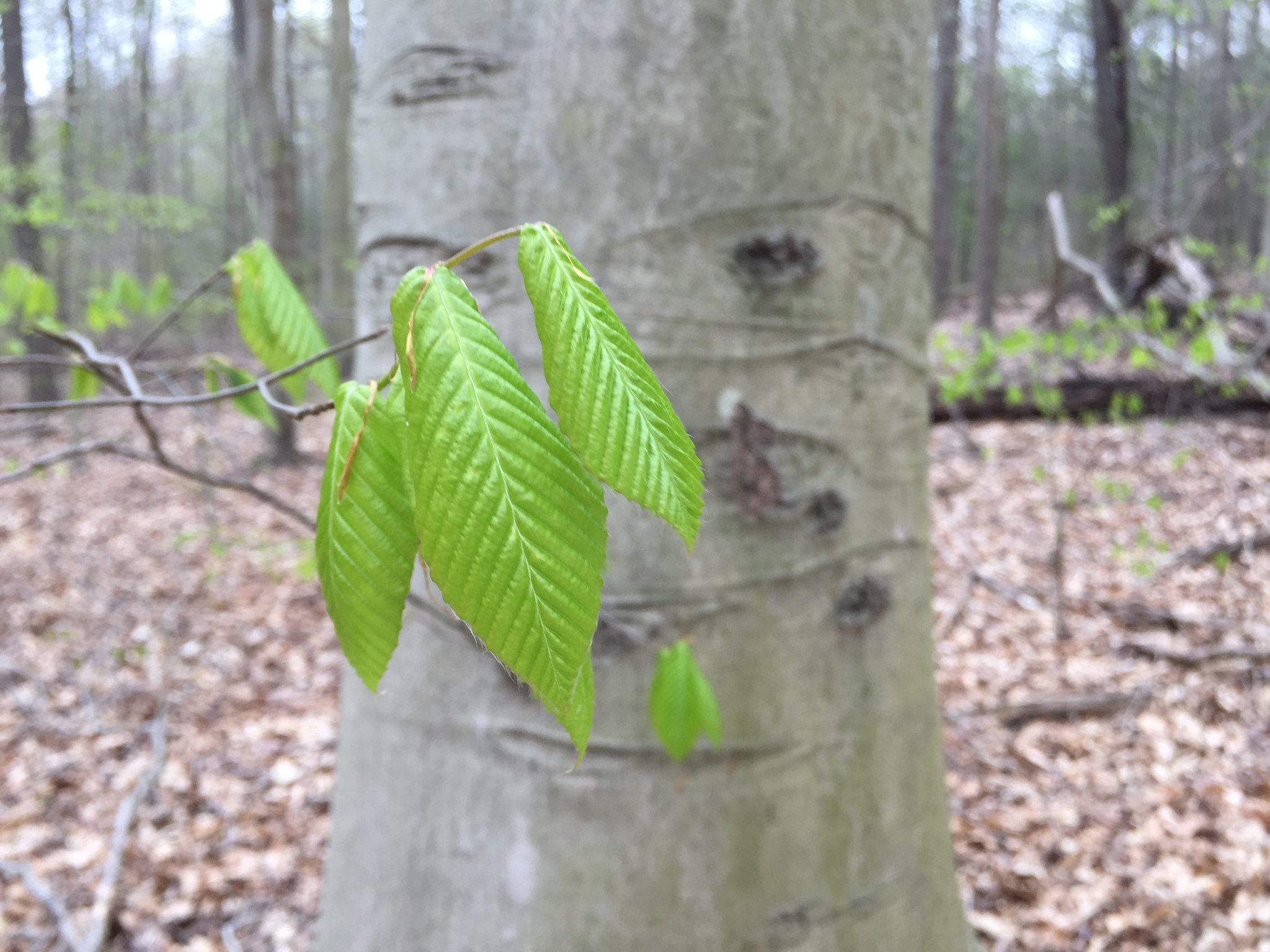
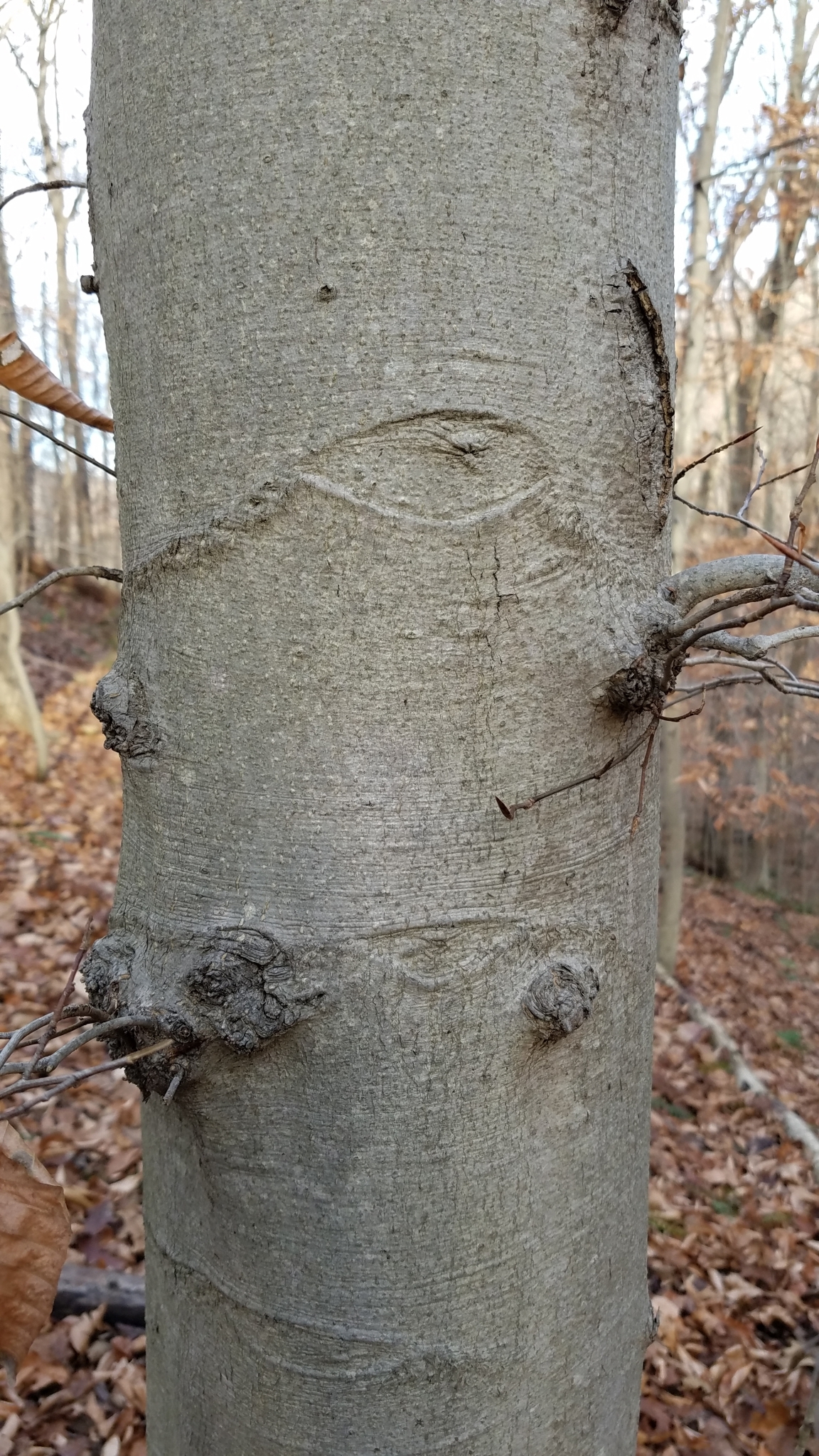
American Beech trees have smooth gray bark without furrows or ridges. Buds are long and sharp pointed. Brown, dead leaves commonly remain on the branches in winter. This phenomenon, called "marcescence," is also displayed by many oaks (Quercus species). The persistent dead leaves commonly make beech and oak trees stand out in winter woods.
The angiospermous, above-ground plant Beechdrops is entirely dependent for its nutrition (i.e., parasitic) on roots of American Beech.
Host plant for various moth species including Olethreutes fagigemmeana, Serviceberry Leafroller Moth, Filbertworm Moth, Banded Tussock Moth, and Angulose Prominent Moth (Database of World's Lepidopteran Host Plants, Gilligan, Wright, & Gibson, 2008, Miller et al., 2018).
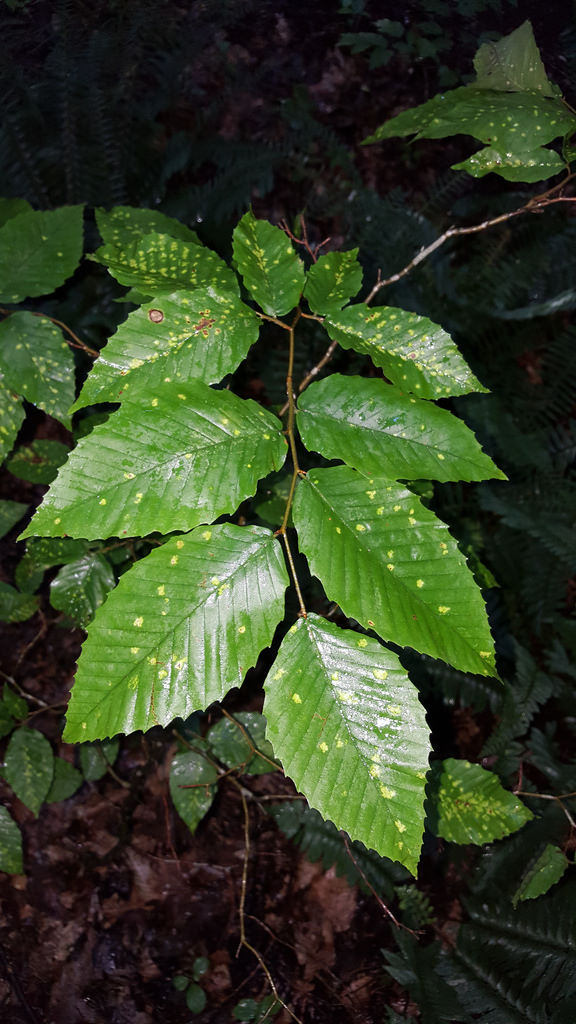
Frequently host to the mite Aceria ferruginea.
Host to Beech Blight Aphid and the fungus Scorias spongiosa, which grows on the honeydew secreted by the aphid.
Associated with Knothole Moss.
There are 977 records in the project database.
| GA | AL | WA | FR | CL | MO | HO | BA | BC | HA | CE | PG | AA | CV | CH | SM | KE | QA | CN | TA | DO | WI | SO | WO |